
Qlik Compose Setup and User Guide
Qlik Compose
TM
November 2023 and Service Release 1
Last updated: July 02, 2024
Copyright © 1993-2024 QlikTech International AB. All rights reserved.
HELP.QLIK.COM
© 2024 QlikTech International AB. All rights reserved. All company and/or product names may be
trade names, trademarks and/or registered trademarks of the respective owners with which they
are associated.

Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
3
1 What's new? 8
1.1 Features and enhancements introduced in Compose November 2023 Service
Release 1 8
Support for bulk generation of data warehouse and workflow tasks 8
Support for basic validations when generating data mart tasks 8
Support for editing data warehouse tasks 8
Other enhancements 9
1.2 Features and enhancements introduced in Compose November 2023 Initial Release 9
Support for choosing the task mode for new data warehouse tasks 9
Support for using a separate schema for data mart tables in Amazon Redshift 10
Azure Synapse Analytics enhancements 10
Snowflake enhancements 11
Other enhancements to Data Warehouse projects 11
Enhancements to Data Lake projects 12
2 Introduction 13
2.1 Data warehouse projects 13
Data warehouse projects architecture 13
Key features 14
2.2 Data lake projects 14
Easy data structuring and transformation 14
Continuous updates 14
Historical data store 14
Data lake project architecture 15
3 Qlik Compose installation and setup 16
3.1 Preparing your system for Compose 16
Hardware prerequisites 16
Software and network prerequisites 17
Required permissions for the Compose service 17
Reserved system names 17
3.2 Installing or upgrading Compose 17
Installation Instructions 18
Upgrade Instructions 18
3.3 Installing and upgrading Compose silently 19
Silently installing Compose 19
Silently upgrading Compose 20
Silently uninstalling Compose 20
3.4 Determining the required number of database connections 21
3.5 Accessing Qlik Compose 21
4 Security considerations 23
4.1 Setting up HTTPS for the Compose console 23
Checking if an SSL certificate is installed 23
Using the self-signed certificate 24
Replacing the self-signed certificate on Windows 26
4.2 Setting the hostname and changing the HTTPS port 27
To set the hostname: 27
To change the HTTPS port: 27
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
4
4.3 Setting up HSTS on Compose 28
Enabling HSTS 28
Disabling HSTS 28
4.4 Setting Single Sign-On Authentication with Kerberos 29
4.5 Changing the master user password 29
5 Data Warehouse projects 32
5.1 Defining a Qlik Replicate task 33
Prerequisites 33
Limitations and considerations 33
Setting up the task 34
5.2 Adding and managing data warehouse projects 35
Adding data warehouse projects 35
Managing and monitoring projects 37
Project settings 37
Resetting projects 43
Project deployment 44
Migrating objects as CSV files 46
Exporting and importing projects using the CLI 77
Working with environment variables 87
Generating projects using the CLI 97
Exporting project documentation 98
Viewing and downloading DDL scripts 99
Project versioning 100
Creating a diagnostics package 102
5.3 Getting started with Data Warehouse projects 103
High-level flow 103
Console elements 103
Data warehouse project tutorial 106
5.4 Setting up a data warehouse connection 110
Using Microsoft SQL Server as a data warehouse 111
Using Oracle as a data warehouse 114
Using Snowflake as a data warehouse 117
Using Amazon Redshift as a data warehouse 121
Using Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a data warehouse 124
Using Google Cloud BigQuery as a Data Warehouse 128
Managing databases 131
5.5 Setting up Landing Zone and Data Source connections 131
Reserved column names and suffixes 131
Permissions 132
Data type mappings 133
Defining landing zones 140
Defining Replicate data source connections 147
Managing databases 154
5.6 Creating and managing the model 154
Reserved column names 155
Generating the model 155
Model limitations 163
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
5
Validating the model 163
Displaying the model 164
Managing the model 167
Creating expressions 184
Opening the expression builder 185
Defining reusable transformations 191
5.7 Creating and managing the data warehouse 192
Data warehouse tasks 193
Managing tasks 203
Viewing and exporting task statements 219
Modifying task settings 220
Validating the data warehouse 226
Clearing the data warehouse metadata cache 227
5.8 Creating and managing data marts 228
Adding data marts and star schemas 229
Displaying data in a pivot table 235
Managing data marts 237
Example of a Valid Table Creation Modifier 245
Example of a Valid Table Creation Modifier 250
Creating and managing custom ETLs 254
Viewing and exporting task statements 256
Validating and adjusting the data mart 256
Reloading the data mart 258
Modifying data mart settings 260
The "Obsolete" indicator 262
5.9 Creating and managing command tasks 263
Defining command tasks 263
Managing command tasks 264
Controlling and monitoring command tasks 264
5.10 Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows 265
Viewing information in the monitor 265
Viewing missing references 267
Controlling tasks 269
Notifications 272
Workflows 274
Monitoring and controlling Qlik Replicate tasks 279
6 Data Lake projects 282
6.1 Defining a Qlik Replicate task 282
Prerequisites 282
Limitations and Considerations 283
Setting up the task 283
6.2 Adding and managing Data Lake projects 284
Prerequisites 284
Data Lake project guidelines 286
Adding data lake projects 288
Managing and monitoring projects 290
Project settings 291
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
6
Resetting projects 296
Project deployment 297
Exporting and importing projects using the CLI 298
Generating projects using the CLI 306
Viewing and downloading DDL scripts 307
Project versioning 308
Creating a diagnostics package 310
6.3 Getting started with Data Lake projects 311
High-level flow 311
Console elements 311
6.4 Setting up landing and storage connections 314
Defining a Storage Zone 314
Defining Landing Zones 323
Managing Landing and Storage connections 325
6.5 Selecting source tables and managing metadata 325
Reserved column names 326
Selecting and adding the source tables 326
Validating the metadata and storage 330
Managing the metadata 332
Schema evolution 337
Creating transformations 339
Reusable transformations 345
6.6 Creating and Managing Storage Zone Tasks 347
Defining and running data storage tasks 348
Managing task definitions 351
Clearing the metadata cache 361
Viewing and exporting task statements 362
Modifying task settings 363
6.7 Creating and managing command tasks 363
Defining Command tasks 364
Managing Command tasks 365
Controlling and monitoring Command tasks 365
6.8 Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows 365
Viewing information in the monitor 366
Running and controlling tasks 368
Notifications 370
Workflows 372
Monitoring and controlling Replicate tasks 376
7 Managing Compose 378
7.1 License settings 378
License enforcement 378
Registering a license 378
7.2 Viewing a license 379
7.3 Logging settings 379
Setting the logging level 379
Setting automatic roll over and cleanup 380
Viewing and downloading Compose log files 381
Contents

Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
7
7.4 Mail server settings 382
7.5 Running tasks on a remote Compose server 382
7.6 Replicate Server settings 382
7.7 User permissions 384
Default user permissions according to role 384
Granular access control 386
Managing user and group roles using the Compose CLI 388
Managing user permissions 389
7.8 Audit trails 392
Audit trail information 393
Exporting Audit Trail files 393
Configuring Audit Trail size and retention 394
Decoding an encoded payload 395
8 Setting up Compose on a Windows HA cluster 396
8.1 Step 1: Installing Compose in the cluster 396
Preparation 396
Primary node setup 397
Secondary node setup 397
8.2 Step 2: Adding the Compose service 398
8.3 Step 3: Defining the service dependencies 398
8.4 Step 4: Defining the URLfor the cluster 399
8.5 Upgrading Compose on the cluster 400
A Impact of DST change on Qlik Compose 401
B Support matrix 402
B.1 Supported Windows platforms 402
B.2 Supported browsers 402
B.3 Supported Qlik Replicate and Enterprise Manager versions 402
B.4 Supported Databases for Data Warehouse Projects 402
Supported data sources 402
Supported data warehouses 403
B.5 Supported hive distributions for Data Lake projects 404
C Cron format and examples 405
C.1 Cron format 405
C.2 Special characters 405
C.3 Usage examples 406
D Supported characters 408
E Glossary 409
Contents

1 What's new?
1 What's new?
This section describes the new and enhanced features in Compose November 2023 and Compose
November 2023 SR1.
In addition to these release notes, customers who are not upgrading from the latest GA
version are advised to review the release notes for all versions released since their
current version.
Customers should also review the Replicate release notes in ≤ Qlik Community for information
about the following:
l
Migration and upgrade
l
End of life/support features
l
Newly supported versions and third-party software
l
Resolved issues
l
Known issues
1.1 Features and enhancements introduced in
Compose November 2023 Service Release 1
Support for bulk generation of data warehouse and workflow
tasks
In previous versions, there was no way to generate multiple data warehouse tasks or workflow
tasks in a single operation. Now, you can select the tasks you want to generate in the new Bulk
Generate dialog, as well as the validation level (basic or all) for all selected tasks.
Generating data warehouse tasks (page 196)
Generating workflow tasks (page 278)
Support for basic validations when generating data mart tasks
In the past, data mart tasks were generated with All Validations by default and there was no option
to choose Basic Validations. As All Validations access the database to verify the existence of
columns used in expressions and lookups, they could take a long time to complete are often not
required. From this version, the default task generation has now been changed to Basic Validations
with an option to choose All Validations.
Adding data marts and star schemas (page 229)
Support for editing data warehouse tasks
From this version it is now possible to edit the task type (Full Load or Change Processing) as well as
other task properties.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
8

1 What's new?
Adding, editing, and duplicating tasks (page 203)
Other enhancements
Compose CLI data mart processing enhancement
Support for the --timeout -1 parameter was added to the Compose CLI mark_reload_
datamart_on_next_run command. This parameter overrides the server call's default timeout in
seconds and can be used to prevent timeouts when processing very large data marts.
UI enhancement
You can now sort columns in the Manage Data Storage Tasks and Monitor Details windows.
Snowflake enhancements
l
To align with the updated behavior of Snowflake on AWS auto-increment columns, newly
added auto-increment columns will use the new ORDERED modifier, as needed.
l
It is now possible to limit the number of data warehouse task runs checked by the data mart
task. To do this, set the following Compose environment variable:
qlk__MissingSatIDsLatestRuns
This might improve performance in certain scenarios.
Using inner joins with Transactional data marts
When working with Transactional data marts, it is now possible to use inner joins for dimensions
instead of sub-queries.
To turn on this feature, set the following environment variables to "true":
qlk__PersistDenormForFctT
qlk__PersistPreselForFctT
1.2 Features and enhancements introduced in
Compose November 2023 Initial Release
Support for choosing the task mode for new data warehouse
tasks
In previous versions, users needed to duplicate the Full Load task in order to configure a Change
Processing task. From this version, you can now choose whether to run the data warehouse task in
Full Load mode or in Change Processing mode.
See:
Adding, editing, and duplicating tasks (page 203)
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
9

1 What's new?
Support for using a separate schema for data mart tables in
Amazon Redshift
The option to configure a separate schema for data mart tables has been extended to support
Amazon Redshift.
Azure Synapse Analytics enhancements
Some of the enhancements described below require setting a Windows environment
variable. If you set or unset an environment variable, the change will only take effect
after you restart the Qlik Compose service.
l
HEAP staging tables support: Two environmental variables have been added: "qlk__
FullLoadStagingTablesAsHeap" and "qlk__CDC_StagingTablesAsHeap". Set these variables
to 'true' or '1', to create the staging tables as HEAP tables for Full Load or CDC tasks
respectively.
l
Added the ability to set the statistics threshold for data mart ETL: Now there are two
statistics thresholds for Synapse that can be set by the user using the following system
environment variables:
1. For the data warehouse ETL, use "qlk__UpdateStatisticsPercentageDwh"
This is used for updating the statistics of the Hub and satellite tables.
2. For the data mart ETL, use "qlk__UpdateStatisticsPercentageDma"
This is used for updating the statistics for the fact and dimension tables.
Notes:
l
Values should be between 0 and 100. A value less than 0 will be converted to 0; in this
case, the command to update the statistics will be skipped.
l
A value exceeding 100 will be converted to 100.
l
If a value cannot be interpreted as an integer, the default value (20) will be used.
l
If this variable is not present, then the default value (20) will be used.
l
The "UpdateStatisticsPercentage" system environment variable is no longer
supported.
l
The JDBC and ODBC additional properties will no longer be overridden: On the first
deployment, Compose copies all the connection parameters including JDBC and ODBC
additional properties. On subsequent deployments, the parameters will not be overridden in
the target environment.
l
Improved performance: Revised ELT statements to reduce number of statements and
improve performance running against Synapse including:
l
Skipping statements when not needed (based on run-time metadata)
l
Combining multiple statements into a single one
l
Managing Staging table (create/insert/index) based on runtime metadata
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
10

1 What's new?
Snowflake enhancements
Some of the enhancements described below require setting a Windows environment
variable. If you set or unset an environment variable, the change will only take effect
after you restart the Qlik Compose service.
l
Data mart performance improvement: Each SELECT is replaced by SELECT DISTINCT to
improve Snowflake's performance with data mart tasks.
In some environments, using the 'DISTINCT' keyword for Snowflake might cause
performance degradation. If this is the case, you can suppress the 'DISTINCT'
keyword by setting the environmental variable "qlk__DisableCteDistinct" to either
'1' or 'true'.
l
Reduced Snowflake storage costs by adding support for Transient Tables: In previous
versions, Compose would create TSTG and TTMP objects in Snowflake during ELT
processes, which would increase customers' data storage costs. From this version, Compose
will create Snowflake Transient Tables for temporary data storage during ETL processes,
thereby significantly reducing costs.
l
Key pair authentication: Snowflake key pair authentication is now supported.
Key pair authentication is supported in both standard and advanced mode, and
with both JDBC and ODBC.
See:
Defining the connection parameters (page 119)
Other enhancements to Data Warehouse projects
Some of the enhancements described below require setting a Windows environment
variable. If you set or unset an environment variable, the change will only take effect
after you restart the Qlik Compose service.
l
Data mart obsolete indication:Optimized implementation of the data mart obsolete
indication.
l
Transactional data mart performance:Performance improvements were made to
transactional data marts.
l
Optimized the method for updating Type 2 dimensions: Before generating the ETL for
this, you first need to set the environmental system variable 'qlk__NewPreselectDim' to either
'1' or 'true'.
l
Expressions: Added the option to evaluate NULL when testing an expression.
l
Migration performance: Improved performance with Qlik Compose migration operations.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
11

1 What's new?
l
Data mart export/import: Exporting and importing data marts now includes the "Table
Creation Modifiers" column. This will enable you to customize the fact or dimension table
creation modifiers.
Notes:
l
If the column value is empty, the project default will be used.
l
The project default value is not included in the export/import.
l
Optimization of dropping and creating tables in an empty schema: From this version,
when a schema does not exist, Compose will try to create it (and return an error if it fails).
Additionally, if the new schema is empty, Compose will not try to drop tables from the
previous schema.
l
Mappings for target columns not mapped to source: A new option has been added to the
Task Settings: When a data warehouse column is unassigned. The new option enables you
to set unassigned columns to NULL or to use a previous column value.
This setting will be ignored if "backdating" is used.
See:
Modifying task settings (page 220)
l
CLItask generation: Added the ability to generate tasks using the Compose CLI at project,
task, data warehouse, and data mart level.
See:
Generating tasks using the CLI (page 270)
l
Logging: The logging (for DWH and Data marts) can now be controlled by the following
environmental system variable:
qlk__LoggingType
The following options are possible:
l
None - No logging at all
l
Deferred - All logging info will be stored in runtime variables, which will be used to add
the logging information in a single statement at the end of the task. When this variable
is not available or when it has other values, the logging will be as usual.
l
Compose CLI in Data Warehouse projects: Added the ability to update custom ETLs in Data
Warehouse projects using the Compose CLI. This functionality can be incorporated into a
script to easily update Custom ETLs.
See:
Creating and managing custom ETLs (page 199)
Enhancements to Data Lake projects
l
Apache Impala views in Data Lakes projects: The header__batch_modified column will now
be cast as varchar(32) for the outbound Apache Impala views. To leverage this
enhancement, you need to set an environment variable.
l
Databricks: Added support for Unity Catalog.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
12

2 Introduction
2 Introduction
Qlik Compose provides an all-in-one purpose built automation solution for creating an agile data
warehouse and/or ingesting data from multiple sources to your data lake for further downstream
processing. To this end, Qlik Compose offers two project types: Data Warehouse and Data Lake.
This introduction will take a closer look at how these projects can help your organization overcome
the hurdles typically faced when confronted with the challenge of setting up and maintaining an
agile data warehouse, or when faced with challenge of ingesting data from multiple source to a
single analytics-ready storage system.
2.1 Data warehouse projects
Traditional methods of designing, developing, and implementing data warehouses require large
time and resource investments. The ETL stand-up development effort alone – multi-month and
error-prone with prep times of up to 80 percent and expertise from specialized developers – often
means your data model is out of date before your BI project even starts. Plus, the result of a
traditional data warehouse design, development, and implementation process is often a system
that can’t adapt to continually changing business requirements. Yet modifying your data warehouse
diverts skilled resources from your more innovation-related projects. Consequently, your business
ends up with your data warehouse becoming a bottleneck as much as an enabler of analytics.
Qlik Compose data warehouse projects allows you to automate these traditionally manual,
repetitive data warehouse tasks: design, development, testing, deployment, operations, impact
analysis, and change management. Qlik Compose automatically generates the task statements,
data warehouse structures, and documentation your team needs to efficiently execute projects
while tracking data lineage and ensuring integrity. Using Qlik Compose, your IT teams can respond
fast – in days – to new business requests, providing accurate time, cost, and resource estimates.
Then once projects are approved, your IT staff can finally deliver completed data warehouses, data
marts, and BI environments in far less time.
Data warehouse projects architecture
The process is illustrated in the following diagram and described below:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
13

2 Introduction
Key features
The comprehensive set of automation features in our Qlik Compose solution simplifies data
warehousing projects. It eliminates the cumbersome and error-prone manual coding required by
legacy data warehouse design and implementations’ many repetitive steps. In addition, our solution
includes the operational features your business needs for ongoing data warehouse and data mart
maintenance.
Automation Features Operational Features
l
Optimized for either model-driven
or data-driven data warehousing
approaches
l
Real-time source data integration
l
Automated ETL generation
l
Physical data warehouse
management
l
Data mart generation
l
Monitoring
l
Workflow designer and scheduler
l
Notifications
l
Data profiling and quality enforcement
l
Lineage and impact analysis
l
Project documentation generation
l
Migration between environments
2.2 Data lake projects
Leverage Qlik Compose data lake projects to automate your data pipelines and create analytics-
ready data sets. By automating data ingestion, schema creation, and continual updates,
organizations realize faster time-to-value from their existing data lake investments.
Easy data structuring and transformation
An intuitive and guided user interface helps you build, model and execute data lake pipelines.
Automatically generate schemas and Hive Catalog structures for operational data stores (ODS) and
historical data stores (HDS) without manual coding.
Continuous updates
Be confident that your ODS and HDS accurately represent your source systems.
l
Use change data capture (CDC) to enable real-time analytics with less administrative and
processing overhead.
l
Efficiently process initial loading with parallel threading.
l
Leverage time-based partitioning with transactional consistency to ensure that only
transactions completed within a specified time are processed.
Historical data store
Derive analytics-specific data sets from a full historical data store (HDS).
l
New rows are automatically appended to HDS as data updates arrive from source systems.
l
New HDS records are automatically time-stamped, enabling the creation of trend analysis
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
14

2 Introduction
and other time-oriented analytic data marts.
l
Supports data models that include Type-2, slowing changing dimensions.
Data lake project architecture
The flow is as follows:
1. Land: The source tables are loaded into the Landing Zone using Qlik Replicate or other third-
party replication tools.
When using Qlik Replicate to move the source table to the Landing Zone, you can define
either a Full Load replication task or a Full Load and Store Changes task to constantly
propagate the source table changes to the Landing Zone in write-optimized format.
2. Store: After the source tables are present in the Landing Zone, Compose auto-generates
metadata based on the data source(s). Once the metadata and the mappings between the
tables in the Landing Zone and the Storage Zone have been finalized, Compose creates and
populates the Storage Zone tables in read-optimized format, ready for consumption by
downstream applicaitons.
It should be noted that even though setting up the initial project involves both manual and
automatic operations, once the project is set up, you can automate the tasks by designing a
Workflow in Compose and/or utilizing the Compose scheduler.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
15

3 Qlik Compose installation and setup
3 Qlik Compose installation and setup
This section describes how to install and set up Qlik Compose.
Note that as Qlik Replicate serves as a data (and metadata) provider for Qlik Compose, you also
need to install Replicate in your organization. For a description of the Replicate installation
procedure, refer to the
Qlik Replicate Setup and User Guide.
In this section:
l
Preparing your system for Compose (page 16)
l
Installing or upgrading Compose (page 17)
l
Installing and upgrading Compose silently (page 19)
l
Determining the required number of database connections (page 21)
l
Accessing Qlik Compose (page 21)
3.1 Preparing your system for Compose
Compose should be installed on a Windows Server machine that is able to access the data
warehouse and optionally the source database(s) defined in your Compose project. Note that
Compose only needs to access the source database if you plan to discover the source database
when generating your model. For more information on discovery, see
Discovering the Source
Database or Landing Zone (page 156)
.
Before installing Compose, make sure that the following prerequisites have been met:
Hardware prerequisites
The following table lists the required hardware for varied deployment scales:
Component
Basic
System
Large
System
Extra-
Large
System
Processor
Additional cores may improve performance
when several ETL processes are running
concurrently.
Quad
core
Quad
core base
8-core
base
Hardware component requirements
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
16

3 Qlik Compose installation and setup
Component
Basic
System
Large
System
Extra-
Large
System
Memory
Additional memory may improve performance
when several ETL processes are running
concurrently.
8 GB 16 GB 32 GB
Disk requirements
For all configurations, RAID is recommended
for higher system availability in case of disk
failure.
100 GB
SSD
500 GB
10,000
RPM
RAID
500 GB
15,000
RPM
RAID
Network 1 Gb 10 Gb Two 10 Gb
Software and network prerequisites
l
Firewall ports 80/443 should be open on the Compose machine.
l
.NET Framework 4.8 or later installed on the Compose machine.
l
TLS 1.2 or later must be supported in the underlying OS.
On Windows Server 2012 R2, TLS 1.2 should be turned on by default. If it is not,
refer to the Microsoft online help for instructions on how to turn it on.
For information on supported databases and browsers, see
Support matrix (page 402)
.
Required permissions for the Compose service
Qlik Compose needs to be installed and run as Administrator.
Reserved system names
All database object names (queries, tables, columns, schemas, and indexes) starting with the prefix
qlk__, and regardless of case, are reserved for internal Compose use.
Thus, a table named qlK__MyTable or a column named QLK__MyColumn would not be permitted.
3.2 Installing or upgrading Compose
The following topic describes how to install and upgrade Qlik Compose.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
17

3 Qlik Compose installation and setup
Installation Instructions
For best performance when using cloud-based databases (such as, Snowflake) as your
data source or data warehouse, it is strongly recommended to install Qlik Compose on a
machine (such as Amazon EC2) located in the same region as your database instance.
To install Compose:
1. Run the Compose setup file (
Qlik_Compose_<version.number>.exe
).
The Qlik Compose setup wizard opens.
2. Click Next. Select I accept the terms of the license agreement and then click Next again.
3. Optionally change the installation directory and then click Next.
4. Click Next and then click Next again to start the installation.
5. When the installation completes, click Finish to exit the Wizard.
As part of the installation, a new Windows Service called Qlik Compose is created.
6. Open the Qlik Compose console as described in
Accessing Qlik Compose (page 21)
.
When you first open the Qlik Compose Console, you will be prompted to register
an appropriate license. Register the license that you received from Qlik.
Upgrade Instructions
Depending on your existing Compose version, you may also need to perform additional
version-specific upgrade tasks. It is therefore strongly recommended to review the
release notes for the new version before upgrading.
1. Stop all Compose tasks and services.
2. After the Qlik Compose service has been stopped by the Installer, make sure that all child
processes are also stopped.
Compose runs a check to verify the termination of tasks and processes before
running an upgrade. If any processes are found to be still running, the installation
will be aborted.
3. Run the Qlik Compose setup wizard.
4. Start all Compose tasks and services.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
18

3 Qlik Compose installation and setup
3.3 Installing and upgrading Compose silently
Compose can be installed silently (i.e. without requiring user interaction). This option is useful, for
example, if you need to install Compose on several machines throughout your organization.
Before commencing the installation, make sure that the prerequisites have been met.
See Preparing your system for Compose (page 16).
The following topics describe how silently install, upgrade, and uninstall Compose:
l
Silently installing Compose (page 19)
l
Silently upgrading Compose (page 20)
l
Silently uninstalling Compose (page 20)
Silently installing Compose
The installation process consists of two stages: creating a response file, and running the silent
install.
Creating a response file
Before starting the installation, you need to create a response file.
To create the response file:
1. From the directory containing the Compose setup file, run the following command(note that
this will also install Compose):
Qlik_Compose_<version.number>.exe /r /f1<my_response_file>
where:
<my_response_file> is the full path to the generated response file.
Example:
Qlik_Compose_<version.number>.exe /r /f1C:\Compose_install.iss
2. To change the default installation directory, open the response file in a text editor and edit
the
first
szDir value as necessary.
3. To change the default data directory, edit the
third
szDir value as necessary.
4. Save the file as <name>.iss, e.g. Compose_install_64.iss.
Running the silent install
To silently install Compose, open a command prompt and change the working directory to the
directory containing the Compose setup file. Then issue the following command (where <response
file> is the path to the response file you created earlier):
Syntax:
<Compose_setup_file> /s /f1<my_response_file> [/f2<LOG_FILE>]
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
19

3 Qlik Compose installation and setup
Example:
C:\>Qlik_Compose_<version.number>.exe /s /f1C:\temp\1\Compose_install.iss /f2C:\temp\1\silent_
x64_install.log
If the installation was successful, the log file should contain the following rows:
[ResponseResult]
ResultCode=0
Silently upgrading Compose
Before starting the silent upgrade:
1. Create a response file. See Step 1 of "Creating a Response File" in Silently
installing Compose (page 19)
2. It is strongly recommended to back up the Compose "Data" folder.
3. All tasks and java processes must be terminated. Compose runs a check to verify
the termination of tasks and processes before running the upgrade. If any
processes are found to be still running, the upgrade will be aborted.
To silently upgrade Compose:
1. Open a command prompt and change the working directory to the directory containing the
Compose setup file.
2. Issue the following command (where
<my_response_file>
is the path to the response file you
created earlier):
Syntax:
<COMPOSE_KIT> /s /f1<my_response_file> [/f2<LOG_FILE>]
Example:
C:\>Qlik_Compose_<version.number>.exe /s /f1C:\temp\1\Compose_upgrade.iss /f2C:\temp\1\silent_
x64_up.log
If the upgrade was successful, the log file should contain the following rows:
[ResponseResult]
ResultCode=0
Silently uninstalling Compose
Silently uninstalling Compose is also comprised of creating a response file and running the silent
uninstall.
The process is the same as for silently installing Compose. For instructions, see
Silently installing
Compose (page 19)
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
20

3 Qlik Compose installation and setup
3.4 Determining the required number of database
connections
As a rule of thumb, the higher the number of database connections opened for Compose, the more
tables Compose will be able to load in parallel. It is therefore recommended to open as many
database connections as possible for Compose. However, if the number of database connections
that can be opened for Compose is limited, you can calculate the minimum number of required
connections as described below.
To determine the number of required connections:
1. For each task, determine the number of connections it can use during runtime. This value
should be specified in the Advanced tab in the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks Settings
window (Data Warehouse projects) or in the Manage Storage Tasks Settings window (Data
Lake projects). When determining the number of required connections, various factors need
to be taken into account including the number of tables, the size of the tables, and the
volume of data. It is therefore recommended to determine the required number of
connections in a Test environment.
2. Calculate the number of connections needed by all tasks that run in parallel. For example, in a
Data Lake project, if three data storage tasks run in parallel, and each task requires 5
connections, then the number of required connections will be 15.
Similarly, in a Data Warehouse project, if a workflow contains two data warehouse tasks that
run in parallel and each task requires 5 connections, then the minimum number of required
connections will be 10. However, if the same workflow also contains two data mart tasks
(that run in parallel) and the sum of their connections is 20, then the minimum number of
required connections will be 20.
3. Factor in the connections required by the Compose Console. To do this, multiply the
maximum number of concurrent Compose users by three and then add to the sum of Step 2
above. So, if the number of required connections is 20 and the number of concurrent
Compose users is 4, then the total would be:
20 + 12 = 32
3.5 Accessing Qlik Compose
You can use a Web browser to access the Qlik Compose Console from any computer in your
network. For information on supported browsers, see
Preparing your system for Compose (page
16)
.
The person logged in to the computer where you are accessing the Console must be an
authorized Qlik Compose user. For more information, see Managing user permissions
(page 389).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
21

3 Qlik Compose installation and setup
To access the Qlik Compose Console:
1. To access the Qlik Compose Console from the machine on which it is installed, select All
Programs > Qlik Compose > Qlik Compose Console from the Windows Start menu. To
access the Qlik Compose Console from a remote browser, type the following address in the
address bar of your Web browser
https://<ComputerName>/qlikcompose/
Where
<ComputerName>
is the name or IP address of the computer on which Compose is
installed.
2. If no server certificate is installed on the Compose machine, a page stating that the
connection is untrusted will be displayed. This is because when Compose detects that no
server certificate is installed, it installs a self-signed certificate. Since the browser has no
way of knowing whether the certificate is safe, it displays this page. For more information,
see
Setting up HTTPS for the Compose console (page 23)
.
3. When prompted for your password, enter your domain username and password.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
22

4 Security considerations
4 Security considerations
During normal operation, Qlik Compose needs to access databases and storage systems for the
purpose of reading and writing data and metadata.
This section describes the procedure you should follow to ensure that any data handled by Qlik
Compose will be completely secure.
In this section:
l
Setting up HTTPS for the Compose console (page 23)
l
Setting the hostname and changing the HTTPS port (page 27)
l
Setting up HSTS on Compose (page 28)
l
Setting Single Sign-On Authentication with Kerberos (page 29)
l
Changing the master user password (page 29)
4.1 Setting up HTTPS for the Compose console
Industry-standard security practices dictate that web user interface for enterprise products must
use secure HTTP (HTTPS). Qlik Compose enforces the use of HTTPS and will not work if HTTPS is
configured incorrectly.
As Compose uses the built-in HTTPS support in Windows, it relies on the proper setup of the
Windows machine it runs on to offer HTTPS access. In most organizations, the IT security group is
responsible for generating and installing the SSL server certificates required to offer HTTPS. It is
strongly recommended that the machine on which Compose is installed already has a valid SSL
server certificate installed and bound to the default HTTPS port (443).
Checking if an SSL certificate is installed
To check whether an SSL certificate is installed, you can use the following command:
netsh http show sslcert | findstr /c:":443 "
If an SSL certificate is installed, the output should look like this:
netsh http show sslcert | finds
tr /c:":443 "
IP:port : 192.168.1.13:443
IP:port : 192.168.1.11:443
IP:port : [fe80::285d:599c:4a55:1092%11]:443
IP:port : [fe80::3d0e:fb1c:f6c3:bc52%23]:443
With a valid SSL certificate installed, the Qlik Compose web user interface will automatically be
available for secure access from a web browser using the following URL:
https://<ComputerName>/qlikcompose/
Where <ComputerName> is the name or IP address of the computer on which Compose is installed.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
23

4 Security considerations
Using the self-signed certificate
Due to the way the HTTPS protocol works, there is no way for Compose to automatically provide
and install a valid SSL server certificate. Still, in the event that no SSL server certificate is installed,
Compose automatically generates and installs a self-signed SSL server certificate (as a temporary
measure). This certificate is generated on the Compose machine and cannot be exported or used
elsewhere.
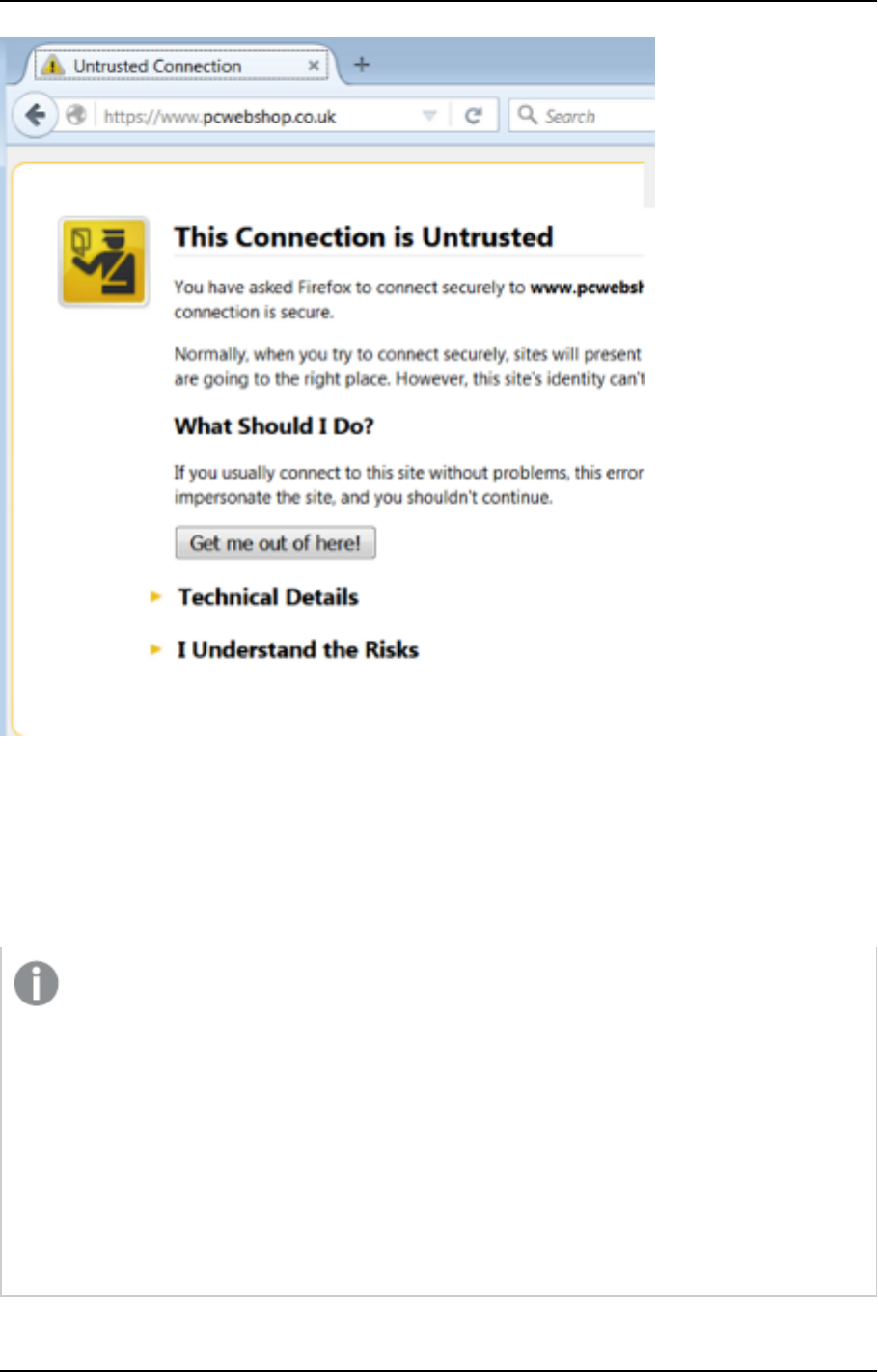
It should be noted that browsers do not consider the certificate to be valid because it was not
signed by a trusted certificate authority (CA). When connecting with a browser to a server that uses
a self-signed certificate, a warning page is shown such as this one in Chrome:
Or this one in Firefox:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
24
4 Security considerations
The warning page informs you that the certificate was signed by an unknown certificate authority.
All browsers display a similar page when presented with a self-signed certificate. If you know that
the self-signed certificate is from a trusted organization, then you can instruct the browser to trust
the certificate and allow the connection. Instructions on how to trust the certificate vary between
browsers and even between different versions of the same browser. If necessary, refer to the help
for your specific browser.
Some corporate security policies prohibit the use of self-signed certificates. In such
cases, it is incumbent upon the IT Security department to provide and install the
appropriate SSL server certificate (as is the practice with other Windows products such
as IIS and SharePoint). If a self-signed certificate was installed and needs to be
removed, then the following command can be used:
composeCtl.exe certificate clean
Note that after the self-signed certificate is deleted, connections to the Qlik Compose
machine will not be possible until a valid server certificate is installed. Should you want
to generate a new self-signed certificate (to replace the deleted certificate), simply
restart the Qlik Compose service.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
25

4 Security considerations
Replacing the self-signed certificate on Windows
The instructions below are intended for organizations who wish to replace the self-signed
certificate generated by the Compose Server on Windows with their own certificate. The process,
which is described below, involves removing the self-signed certificate and then importing the new
certificate.
See also
Setting up HTTPS for the Compose console (page 23)
.
Before starting, make sure that the following prerequisites have been met:
l
The replacement certificate must be a correctly configured SSL PFX file containing both the
private key and the certificate.
l
The common name field in the certificate must match the name browsers will use to access
the machine.
To remove the self-signed certificate created by Qlik Compose:
1. Stop the Qlik Compose service.
2. Open a command prompt (using the "Run as administrator" option) and change the path to
the Compose bin directory. The default path is
C:\Program Files\Qlik\Compose\bin
.
3. Run the following command:
composeCtl.exe certificate clean
To import your own certificate:
1. Run
mmc.exe
to open the Microsoft Management Console.
2. From the File menu, select Add/Remove Snap-in. The Add or Remove Snap-ins window
opens.
3. In the left pane, double-click Certificates. The Certificates snap-in wizard opens.
4. Select Computer account and then click Next.
5. In the Select Computer screen, make sure that Local computer is selected and then click
Finish.
6. Click OK to close the Add or Remove Snap-ins window.
7. In the left pane, expand the Certificates folder. Then, right-click the Personal folder and
select All Tasks > Import.
8. In the File to Import screen, select your PFX certificate file. Note that by default the Open
window displays CER files. In order to see your PFX files, you need to select Personal
Information Exchange from the drop-down list in the bottom right of the window.
9. Click Next and enter the private key password.
10. Continue clicking Next until you reach the Completing the Certificate Import Wizard
screen. Then click Finish to exit the wizard.
11. In the Personal > Certificates folder, double-click the newly imported certificate. The
Certificate window opens.
12. Scroll down the Details tab until you see the Thumbprint details and copy them to the
clipboard.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
26

4 Security considerations
13. Open a command prompt and run the following commands:
Syntax:
¢ netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=[YOUR_CERTIFICATE_THUMBPRINT_
WITHOUT_SPACES] appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}
Example:
netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443
certhash=5f6eccba751a75120cd0117389248ef3ca716e61 appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-
59fc669b0914}
Syntax:
¢ netsh http add sslcert ipport=[::]:443 certhash=[YOUR_CERTIFICATE_THUMBPRINT_WITHOUT_
SPACES] appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}
Example:
netsh http add sslcert ipport=[::]:443 certhash=5f6eccba751a75120cd0117389248ef3ca716e61
appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}
14. Close the command prompt and Microsoft Management Console.
15. Start the Qlik Compose service.
4.2 Setting the hostname and changing the HTTPS port
After installing Qlik Compose, you can use the Compose CLI to set the hostname and HTTPS port
for accessing the Qlik Compose server machine.
Under normal circumstances, you should not need to set the hostname. However, on some
systems, connecting using HTTPS redirects to localhost. If this occurs, set the hostname of the
Compose machine by running the command shown below.
To set the hostname:
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --address
address
Where:
--address is the hostname of the Compose server machine.
Example
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --address MyHostName
To change the HTTPS port:
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --https_port
port_number
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
27

4 Security considerations
Where:
--https_port is the HTTPS port number of the Compose server machine. The default HTTPS port is
443.
Example
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --https_port 442
4.3 Setting up HSTS on Compose
HSTS is a web security policy mechanism that helps to protect websites against man-in-the-middle
attacks such as protocol downgrade attacks and cookie hijacking. It allows web servers to declare
that web browsers (or other complying Dilqam) should automatically interact with it using only
HTTPS connections, which provide Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL).
You can force the Compose Web UI and/or the Compose REST API connections to use HSTS (HTTP
Strict Transport Security). To do this, run the commands described below.
All commands should be run from as Admin from the product bin folder.
Enabling HSTS
Command syntax
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers
header_list
--rest_http_headers
header_
list
Parameters
Parameter Description
--static_http_headers The headers required to connect to the Compose Web UI.
--rest_http_headers The headers required to connect using the API.
Headers should be specified using the following format:
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers "header1:value1" "header2:value2" --
rest_http_headers "header1:value1" "header2:value2"
Example
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers "Strict-Transport-Security:max-
age=31536000; includeSubDomains;" --rest_http_headers "Strict-Transport-Security":"max-
age=31536000; includeSubDomains;"
Disabling HSTS
You can also revert to regular HTTPS connections.
Command syntax
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers ""|--rest_http_headers ""
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
28

4 Security considerations
Parameters
Parameter Description
--static_http_headers Use this parameter to revert the headers required to connect to
the Compose Web UI.
--rest_http_headers Use this parameter to revert the headers required to connect using
the API.
Example
Disable static_http_headers
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --static_http_headers ""
Disable rest_http_headers
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --rest_http_headers ""
4.4 Setting Single Sign-On Authentication with
Kerberos
Kerberos is an enterprise authentication protocol that uses the concept of tickets and three-way
authentication to enable users and computers to identify themselves and secure access to
resources.
Using Kerberos SSO, users can seamlessly log into Compose and administrators can completely
externalize and centrally manage users or group memberships using their existing Kerberos
infrastructure.
To set the authentication method to single sign-on with Kerberos, run:
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --authentication_method sso-kerberos
To revert the authentication method to standard single sign-on, run:
ComposeCtl.exe configuration set --authentication_method sso
If the Kerberos protocol fails, Compose will try to log in using NTLM authentication. If
NTLM authentication is not enabled in the system, an error will be returned.
4.5 Changing the master user password
All passwords are encrypted using a one-time randomly generated master key. The master key is
stored automatically in the root repository of Compose (
<product_
dir>\data\projects\GlobalRepo.sqlite
).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
29

4 Security considerations
The master key is encrypted by a user key, which in turn, is derived from a master password
entered by the user. By default, the Master User Password is randomly generated by Compose. The
best practice, however, is to change the Master User Password, as this will allow Compose projects
and configuration settings to be imported to another machine without needing to re-enter the
project credentials.
It may also be convenient to use the same Master User Password within a trusted environment. In
other words, if the same administrators control both the production and the testing environments,
using the same Master User Password in both environments will facilitate the transfer of projects
with credentials between the testing and production environments.
The user key is stored in the muk.dat file located in
<product_dir>\data\
.
The Master User Password must be a minimum of 32 characters. You can either use your
own password or run the genpassword utility described below to generate a password for
you. Note also that the password can only contain alphanumeric characters (i.e. it
cannot contain special keyboard characters such as # or @).
All of the commands listed below must be run as Admin from:
<product_dir>\bin
To generate a random 32 character password:
Issue the following command:
ComposeCtl.exe utils genpassword
To change the randomly generated master user password:
1. Issue the following command:
ComposeCtl.exe masterukey set --password <new_master_password>
If you add the --prompt parameter to the command and omit the --password
parameter, the CLI will prompt you for the password. When you enter the
password, it will be obfuscated. This is especially useful if you do not want
passwords to be retained in the command prompt history.
Syntax:
ComposeCtl.exe masterukey set --prompt
2. Restart the Compose service.
To change a user-defined master user password:
1. Issue the following command:
ComposeCtl.exe masterukey set --current-password <current_master_password> --password
<new_master_password>
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
30
4 Security considerations
If you add the --prompt parameter to the command and omit the --password and --
current-password parameters, the CLI will prompt you for the required passwords.
When you enter the passwords, they will be obfuscated. This is especially useful if
you do not want passwords to be retained in the command prompt history.
Syntax:
ComposeCtl.exe masterukey set --prompt
2. Restart the Compose service.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
31

5 Data Warehouse projects
5 Data Warehouse projects
This section explains how to set up data warehouse projects.
In this section:
l
Defining a Qlik Replicate task (page 33)
l
Adding and managing data warehouse projects (page 35)
l
Getting started with Data Warehouse projects (page 103)
l
Setting up a data warehouse connection (page 110)
l
Setting up Landing Zone and Data Source connections (page 131)
l
Creating and managing the model (page 154)
l
Creating and managing the data warehouse (page 192)
l
Creating and managing data marts (page 228)
l
Creating and managing command tasks (page 263)
l
Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows (page 265)
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
32

5 Data Warehouse projects
5.1 Defining a Qlik Replicate task
In order to work with Compose, you first need to define a Qlik Replicate task that replicates the
source tables from the source endpoint to a landing zone in the data warehouse (defined as the
target endpoint in the Replicate task). The landing zone should then be defined as the data source
for the Compose project.
For information on which endpoints can be used in a Replicate task that lands data for Compose,
see
Supported data warehouses (page 403)
.
Configuring multiple Replicate tasks with the same landing zone is not supported.
The steps below highlight the settings that are required when using Qlik Replicate with Compose.
For a full description of setting up tasks in Qlik Replicate, please refer
to the
Qlik Replicate Help
.
Prerequisites
l
When Oracle is defined as the source endpoint in the Replicate task, full supplemental
logging should be defined for all source table columns that exist on the target and any source
columns referenced in filters, data quality rules, lookups, and expressions.
l
When using Replicate November 2023 or later and Amazon Redshift as your data warehouse,
you must define a global transformation rule in Replicate that converts BOOLEAN data types
to VARCHAR(1). Otherwise, an error will occur during the data warehouse task. For
information on defining global transformation rules, see Starting the Global Transformation
Rules wizard in the Replicate help.
Limitations and considerations
l
Replicate allows you to define global transformations that are applied to source/Change
tables during task runtime. The following global transformations, however, should not be
defined (as they are not compatible with Compose tasks):
l
Rename Change Table
l
Rename Change Table schema
l
The Create target control tables in schema option in the Replicate task settings' Control
Table tab is not supported.
l
Support for the JSON and XML data types is limited to the Snowflake VARIANT data type.
Therefore, apart from the Snowflake VARIANT data type, columns that are usually created
with these data types (by the Replicate target endpoint) should be created as STRINGs
instead. Therefore, columns that are usually created with these data types (by the Replicate
target endpoint) should be created as STRINGs instead. This can be done automatically
within Replicate using a data type transformation. For information on which target endpoints
support JSON and XML data types as well as instructions on how to create a data type
transformation, please refer to the Replicate Help.
l
As Compose does not use the before-image for UPDATEoperations, it is recommended to
set On UPDATE in the Store Changes Settings tab of the Replicate task settings to Store
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
33

5 Data Warehouse projects
after image only. Note that this should only be done if the Replicate task is dedicated for use
with Compose.
l
As Compose requires a full after-image to be able to perform Change Processing, the
following Replicate source endpoints are not directly supported (as they do not provide a full
after-image):
l
SAP HANA (log based)
l
Salesforce
Setting up the task
To define the task:
1. Open Qlik Replicate and in the New Task dialog, do one of the following:
l
To enable Full Load and Change Processing replication, enable the Full Load and
Store Changes options (the Apply Changes option should not be enabled).
l
To enable Full Load only replication, enable the Full Load replication option only.
l
To enable Change Processing replication only, make sure that only the Store Changes
option is enabled. Note that this option should only be selected if the Full Load tables
and data already exist in the landing zone.
l
To enable Change Processing for lookup tables that already exist in the landing zone
and are not part of the Compose model, enable the Apply Changes option only. Note
that such a task should be defined in addition to the Full Load and Store Changes
replication task described above. For more information on updating standalone lookup
tables, see
Using lookup tables that do not have a task for CDC mapping (page 211)
.
2. Open the Manage Endpoint Connections window and define a source and target endpoint.
The target endpoint must be the database where you want Compose to create the data
warehouse.
3. Add the endpoints to the Qlik Replicate task and then select which source tables to replicate.
4. This step is not relevant if you selected the Apply Changes or Full Load replication option
only. In the Task Settings' Store Change Setting tab, make sure that Store Changes in is set
to Change tables.
5. In the Task Settings’ Target Metadata tab, specify a Target table schema name.
6. If a Primary Key in a source table can be updated, it is recommended to turn on the DELETE
and INSERT when updating a primary key column option in Replicate's task settings'
Change Processing Tuning tab. When this option is turned on, history of the old record will
not be preserved in the new record. Note that this option is supported from Replicate
November 2022 only.
7. Run the task. Wait for the Full Load replication to complete and then continue the workflow in
Compose as described in the
Data warehouse project tutorial (page 106)
below and in
Adding
and managing data warehouse projects (page 35)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
34

5 Data Warehouse projects
Replicate allows you to define global transformations that are applied to source/Change
tables during task runtime. The following global transformations, however, should not be
defined (as they are not compatible with Compose tasks):
l
Rename Change Table
l
Rename Change Table schema
5.2 Adding and managing data warehouse projects
This section describes how to add and manage a data warehouse project.
In this section:
l
Adding data warehouse projects (page 35)
l
Managing and monitoring projects (page 290)
l
Project settings (page 37)
l
Resetting projects (page 43)
l
Project deployment (page 44)
l
Migrating objects as CSV files (page 46)
l
Exporting and importing projects using the CLI (page 77)
l
Generating projects using the CLI (page 97)
l
Exporting project documentation (page 98)
l
Viewing and downloading DDL scripts (page 99)
l
Project versioning (page 308)
l
Creating a diagnostics package (page 310)
Adding data warehouse projects
Adding a new project is the first task you need to undertake in order to work with Qlik Compose.
There are two types of project:
l
Data Warehouse - for ingesting data from multiple sources and creating analytics-ready data
marts.
l
Data Lake - for ingesting data from multiple sources and moving it to a storage system for
analytics.
This topic guides you through the steps required to set up a data warehouse project. For
instructions on setting up a Data Lake project, see
Adding data lake projects (page 288)
.
You can set up as many projects as you need, although the ability to actually run tasks is
determined by your Compose license.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
35

5 Data Warehouse projects
Adding a Data Warehouse project
To add a new Data Warehouse project:
1. Click the New Project toolbar button.
The New Project wizard opens.
2. In the Project Name tab, specify the following and then click Next:
l
Name: The project name.
Project names cannot contain the following characters:
/\,&#%$@=^*+"'`~?<>:;[]{} as well as all non-printable characters (below
0x20). The project name can contain a single dot, but it cannot be the first
or last character.
l
Environment Type: Optionally, change the default environment type.
l
Environment Title: Optionally, specify an environment title.
For information about the environment settings, see
Environment tab (page 40)
.
The following names are reserved system names and cannot be used as project
names: CON, PRN, AUX, CLOCK$, NUL, COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, COM5, COM6, COM7,
COM8, COM9, LPT1, LPT2, LPT3, LPT4, LPT5, LPT6, LPT7, LPT8 and LPT9.
3. Select Data Warehouse as your project type and then click Finish.
4. The project panels will be displayed.
5. Add at least one source database and a data warehouse as described in
Setting up Landing
Zone and Data Source connections (page 131)
and
Setting up a data warehouse connection
(page 110)
respectively.
6. Create a model as described in
Creating and managing the model (page 154)
.
7. Set up the data warehouse as described in
Creating and managing the data warehouse
(page 192)
.
8. Set up the data mart as described in
Creating and managing data marts (page 228)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
36

5 Data Warehouse projects
Managing and monitoring projects
The table below describes the available project management options.
Project management actions are performed in the main Compose window. To switch
from a specific project to the main window, click the downward arrow to the right of the
project name and then select All Projects from the drop-down menu.
To Do this
Edit a project Any of the following:
l
Double-click the project.
l
Right-click the project and select Designer.
l
Select the project and then click the Open toolbar button.
Monitor a project Any of the following:
l
Right-click the project and select Monitor.
l
Double-click the project and select the Monitor tab on the right of
the console.
Create a
deployment
package
Any of the following:
l
Right-click the project and select Create Deployment Package.
l
Select the project and then select Create Deployment Package
from the Deployment toolbar menu.
See also:
Project deployment (page 44)
(Data Warehouse projects) and
Project deployment (page 297)
(Data Lake projects).
Delete a project Any of the following:
l
Right-click the project and select Delete.
l
Select the project and then click the Delete toolbar button.
View or change
user permissions
Right-click the project and select User Permissions.
Relevant for Data Warehouse projects only.
See also:
User permissions (page 384)
.
Project management procedures
Project settings
You can change the project settings according to your needs.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
37

5 Data Warehouse projects
To access the project settings:
1. Open your project as described in
Managing and monitoring projects (page 290)
.
2. Click the downward arrow to the right of the project name and select Settings from the drop-
down menu.
The Settings window opens, displaying the following tabs:
l
General tab (page 38)
l
Naming tab (page 39)
l
Environment tab (page 40)
l
Table creation modifiers tab (page 42)
General tab
In this tab, the following settings are available:
Miscellaneous
l
Generate DDL scripts but do not run them: By default, Compose executes the CREATE,
ADJUST and DROP statements immediately upon user request. When you select this option,
Compose will only generate the scripts but not execute them. This allows you to review and
edit the scripts before they are executed.
For example, if you want your data warehouse/storage tables to contain partitions, you will
need to edit the CREATE statement to create the partitions.
You can view, copy and download the DDL scripts as described in
Viewing and downloading
DDL scripts (page 99)
.
When this option is selected, you need to do the following to see the results:
l
After running the scripts, clear the metadata cache as described in Clearing
the data warehouse metadata cache (page 227).
l
When this option is selected, you need to press [F5] (i.e. refresh the page)
in order for the web console to display the updated list of tables. This can
be done either before running the scripts (recommended) or after running
the scripts. Note that until you refresh the browser, the information in the
web console will only be partially updated.
l
Ignore Mapping Data Type Validation: By default, Compose issues a validation error when a
landing table is mapped to a logical entity with a different data type. You can select this
option to allow the mapping of different data types. Note that you should only select this
option if you need to map landing table data types to compatible (though not identical)
logical entity data types.
l
Write metadata to the TDWM tables in the data warehouse:
When this option is selected (the default unless Amazon Redshift is the data warehouse),
Compose writes the metadata for the data warehouse tables to the following tables:
<schema>.TDWM_Tables and <schema>.TDWM_COLUMNS.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
38

5 Data Warehouse projects
Centralizing the metadata in two dedicated tables makes it easier for external metadata tools
to analyze the metadata. The metadata is also written to the local Compose repository, so
clearing this option (if performance issues are encountered) will not affect Compose
functionality in any way.
l
Do not display the default workflows in the monitor: Select this option if you want to
prevent the default workflows from being executed.
Dates
l
Lowest Date: The value stored in the "From Date" column. This is the date when the version
started.
l
Highest Date: The value stored in the "To Date" column. This is the date when the version
ended.
Current Time Convention
When a source record’s timestamp cannot be determined, select one of the following to use
instead:
l
Current time in UTC (the default for new projects)
To preserve backward compatibility when upgrading or deploying old projects,
local server time is the default.
Before changing this option, make sure that existing data will not be impacted.
l
Current time in server local time
For existing objects, Compose will not be able to determine a source record's timestamp if both of
the following are true:
l
The "From Date" columns are not mapped
l
The task is set up to perform Incremental Load
Naming tab
In this tab, you can change the default "From Date" and "To Date" column names, as well as the
prefixes and suffixes used to identify tables, views, and columns.
If you change the prefix or suffix of existing tables (e.g. data warehouse tables), you
need to drop and create the data warehouse and data mart tables.
Name Description
Suffix for Replicate
Change Tables
The suffix used to identify Replicate Change Tables in the landing
zone of the data warehouse.
Name management options
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
39

5 Data Warehouse projects
Name Description
Prefix for data
warehouse tables
The prefix used to identify tables in the Data Warehouse.
Prefix for data
warehouse views
The prefix used to identify views in the Data Warehouse.
Suffix for archived
Replicate Change Tables
The suffix used to identify archived Change Tables in the specified
database.
For more information on archiving Change Tables, see After applying
changes.
Prefix for data mart
tables
The prefix used to identify tables in the data mart.
Suffix for exception mart
tables
The suffix used to identify error tables in the data warehouse. These
tables contain data that was rejected by a data quality rule.
Suffix for hub tables The suffix used to identify hub tables in the Data Warehouse. Hub
tables contain History Type 1 columns. History Type 1 column do not
contain any version history as opposed to History Type 2 columns
that do.
Suffix for satellite tables The suffix used to identify satellite tables in the Data Warehouse.
Satellite tables contain History Type 2 columns. History Type 2
columns keep a history of the data version by adding a new row
whenever the data is updated.
"From Date" column
name
The name of the "From Date" column. This column is added to tables
that contain attributes (columns) with a History Type 2. The column
is used to delimit the range of dates for a given record version.
This name cannot be used in other columns.
"To Date" column name The name of the "To Date" column. This column is added to tables
that contain attributes (columns) with a History Type 2. The column
is used to delimit the range of dates for a given record version.
This name cannot be used in other columns.
Environment tab
In this tab, you can:
l
Specify information about your environment, part of which will be displayed as a banner at
the top of the window when you open the project.
l
Determine the number of database connection to open concurrently.
After providing the following information, click OK to save your settings:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
40

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Environment type:Select one of the following types according to your environment type:
Development, Test, Acceptance, Production, Other. This information will not be displayed
in the banner.
l
Environment title: Specify a title for your environment. The title will be displayed in the
banner at the top of the console.
l
Project title: Specify a title for your project. The project title will be shown in the console
banner. If both an Environment Title and a Project Title are defined, the project title will be
displayed to the right of the environment title.
l
The Project title option requires Compose August 2021 Patch Release 12 or
later.
l
When a project is deployed to a new environment, the environment title and
environment type in the new environment will not be overridden.
The following image shows the banner with both an Environment title and a Project title:
The banner text is shown without the Environment title and Project title labels.
This provides greater flexibility as it allows you add any banner text you like,
regardless of the actual label name. For example, specifying
Project
owner: Mike Smith
in the Project title field, will display that text in the banner.
Creating or Dropping Data Warehouse Tables
Limit the number of database connections to: The higher the number of database connections,
the more data warehouse tables Compose will be able to create or drop in parallel. While increasing
the default should improve performance, it might also impact other database applications. It is
therefore not recommended to increase the default unless you encounter performance issues.
The environment properties can be
exported and imported
to a new project, but cannot
be imported to an existing project.
Task recovery
You can set SQL state classes and error codes, on the occurrence of which, a task will be retried.
You can set the following parameters:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
41

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Maximum retry count: The number of times to retry a task before exiting with failure.
Increasing the number of retries will impact system resources. Therefore, only increase the
default value if you expect tasks to recover after the default number of retries.
l
Interval between retry attempts (sec): The time to wait between retry attempts. Increasing
the interval will consume more system resources. Therefore, only increase the default value
if it is critical that the task recover as soon as possible.
l
Retry on these SQL state classes: The default is 08 (connection exceptions). You can add
additional classes as desired. Classes should be separated with a comma.
Example: 08,22,2F
l
Retry also on these error codes: The default is 1205 (which occurs when a table is locked
by another process). You can add additional error codes as desired. Error codes should be
separated with a comma.
Example: 1205,2020,233
Limitations and considerations:
l
ODBC statements comprise a small part of the task execution sequence. However, as the
task retry mechanism is JDBC-based, ODBC statements will not be retried even if the
specified SQL state/error code is encountered.
Task and Workflow Information Retention
You can set the maximum number of runs to keep task and workflow logs and messages. The
default is 100. Task information includes logs, the number of inserted/updated rows per table,
errors, and various other runtime messages. If you find that the number of accumulated logs and
messages is degrading performance, reducing this value might help.
Table creation modifiers tab
By default, Compose creates tables in the data warehouse using the standard CREATE TABLE
statement. However, organizations often need tables to be created with custom properties for
better performance, special permissions, custom collation, and so on. For example, in Microsoft
Azure Synapse Analytics, it’s possible to create a table as a HEAP, which is optimized for smaller
tables. By default, Compose creates tables in Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a CLUSTERED
COLUMNSTORE INDEX, which offers the best overall query performance for large tables.
In the Table creation modifiers tab, you can append table creation modifiers as SQL parts to the
CREATE TABLE statement. You can set table creation modifiers for both data warehouse tables and
for data mart tables. In the data warehouse, separate modifiers can be set for Hub and Satellite
tables while in the data mart, separate modifiers can be set for fact and dimension tables. Once set,
all tables will be created using the specified modifiers, unless overridden at the entity level.
To set table creation modifiers:
1. Select the Custom option for any of the available table types.
2. Click the Edit button to open the Table Creation Modifier editor.
3. Enter the SQL parts you want to append to the CREATE TABLE statement.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
42

5 Data Warehouse projects
4. Optionally, but strongly recommended, validate the SQL in an external validation tool that
supports your specific database and version.
Compose does not provide any way of validating your SQL. Therefore, make sure
to validate the SQL before deploying in a production environment.
5. Click OK to close the editor and save your SQL.
Limitations
If you change an existing table creation modifier, you will not be prompted to adjust affected tables
when validating the model. If you want to apply the change to existing tables, dropping and
recreating all tables might not be an issue in a development environment. However, in a production
environment (where dropping and recreating all tables might not be a viable option), you will need
to adjust the tables outside of Compose.
Example of a Valid Table Creation Modifier
In the following example, the Compose CREATE TABLE statement (rows 1-5) is appended with an
SQL part instructing Compose to create the table as a HEAP (row 6).
CREATE TABLE MyTable
(
column1 integer,
column2 varchar(50),
)
WITH (HEAP)
For an explanation of how to define table creation modifiers for individual data warehouse tables,
see
Defining Table Creation Modifiers (page 181)
For an explanation of how to define table creation modifiers for individual fact tables, see
Example
of a Valid Table Creation Modifier (page 245)
.
For an explanation of how to define table creation modifiers for individual dimension tables, see
Example of a Valid Table Creation Modifier (page 250)
.
Resetting projects
You can reset projects as required. This can be useful in the project development stage as it allows
you to easily delete unwanted project elements.
Be careful not to reset a project and delete data in a production environment.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
43

5 Data Warehouse projects
To reset a project:
1. Open your project as described in
Managing and monitoring projects (page 290)
.
2. Click the downward arrow to the right of the project name and select Reset Project from the
drop-down menu.
The Reset Project window opens.
3. Select which elements to reset according to your project type.
l
Model (Entities, Relationships, Attribute Domains), mappings, and data mart
definitions
For more information on models, see
Creating and managing the model (page 154)
.
l
Reusable transformations
For information on the reusable transformations, see
Defining reusable
transformations (page 191)
.
l
Global mappings
For more information on global mapping, see
Managing global mappings (page 161)
.
l
Data warehouse and data mart tables
For more information on data warehouses and data marts, see
Creating and managing
the data warehouse (page 192)
and
Creating and managing the data warehouse (page
192)
respectively.
l
Command tasks
For more information on data warehouses and data marts, see
Creating and managing
command tasks (page 263)
.
l
DDL Scripts
For more information on DDL scripts, see
Project settings (page 37)
and
Viewing and
downloading DDL scripts (page 99)
.
l
Drop Archive Tables
For more information on Archive Tables, see
Defining landing zones (page 140)
4. Click Reset Project and then click Yes when prompted to confirm your request.
Project deployment
Project deployment packages can be used to back up projects or migrate projects between
different environments (e.g. testing to production). As a deployment package is intended to be
deployed in a new environment, it contains the Data Warehouse and data source definitions, but
without any passwords. The deployment package also does not contain any data from the Data
Warehouse or data mart, only the metadata. The deployment package also contains the project
metadata and mapping information, which should be consistent with the landing zone tables in the
new environment.
For a complete list of objects contained in the deployment package, see
Exporting a project (page
78)
.
Project deployment should always be unidirectional (for example, from test to
production), and not the other way around.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
44

5 Data Warehouse projects
Creating deployment packages
This section explains how to create a project deployment package.
To create a deployment package
1. Choose one of the following methods:
l
In the main Compose window, right-click the desired project and select Create
Deployment Package from the context menu.
l
In the main Compose window, select the desired project. Then, click the Deployment
toolbar button and select Create Deployment Package from the drop-down menu.
l
In the project window, select Deployment > Create Deployment Package from the
project drop-down menu.
The Create Deployment Package - <Project_Name> window opens.
2. Select Exclude environment variable values to exclude all of the environment specific
settings from the deployment package (the default). Leave this option selected if the project
you are exporting includes environment variables and the settling in the target environment
are significantly different from the source environment. The variables will be replaced with
their default values (either empty or the default Boolean value).
See also:
Working with environment variables (page 87)
3. Provide a Version number and a Description in the designated fields and then click OK.
A ZIP file containing a JSON file (i.e. the project settings) and a readme.txt file will be saved to your
browser's default download location. The ZIP file name is in the following format: <Project_Name>_
deployment_<Date>__<Time>.zip
The readme.txt file contains the following information about the deployment package: project
name, export date, exporter user name, deployment version, and description.
Deploying packages
This section explains how to deploy a project deployment package. This section explains how to
deploy a project deployment package. You can only deploy packages to an existing project.
Therefore, before deploying a project, create a new project with the user name and password
required for connecting to the Data Warehouse database and the Landing Zone database (if
defined) in the new environment. In addition, the Landing Zone databases in the target project must
have the same display name (defined in the Compose console) as the corresponding databases in
the source project. Note that as database settings are usually environment specific, the database
settings in the target project will not be overwritten by those of the source project.
Deploying a project between different database types is not supported. For example,
you cannot create a package in SQL server and deploy it to an Oracle database.
When deploying, Compose does not override existing connection parameters. This enables you to
easily migrate projects from test to production, for example, without needing to change user
names, passwords or IP addresses.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
45

5 Data Warehouse projects
If preferred, you can create an empty project and provide the required credentials after
the deployment completes. In this case, an error message prompting you for the missing
credentials will be displayed after the deployment completes.
To deploy a project:
1. Copy the ZIP file created in
Creating deployment packages (page 45)
to a location that is
accessible from the Compose machine.
2. Open Compose and choose one of the following methods:
l
In the main Compose window, select the desired project. Then, click the Deployment
toolbar button and select Deploy from the drop-down menu.
l
In the project window, select Deployment > Deploy from the project drop-down
menu.
The Deploy window opens.
3. Either drag and drop the file on the window.
OR
Click Select and browse to the location of the deployment package. In the Open window,
either double-click the deployment package ZIP file or select the file and click OK.
The package details will be displayed.
4. Click Deploy to deploy the package. When prompted to replace the existing project, confirm
the operation. The project will be deployed.
When deploying a project defined with multiple Replicate Servers to any of the following:
l
A project without any Landing Zone databases
l
A project which is missing one or more Landing Zone databases defined in the
source project
Then the Landing Zone settings from the source project will be used, but the missing
databases will be created without a password and Replicate Server. These will need to
be configured manually.
Migrating objects as CSV files
Relevant to Data Warehouse projects only.
Migrating Compose objects as CSV files, provides a level of granularity that is not available when
using the standard project export and deployment options. Instead of importing the entire project,
you can import specific objects and then apply periodic updates as needed.
The following objects can be migrated:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
46

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Model objects: Entities, Attributes, Attributes Domain, Relationships, Reusable
transformations, and Reusable transformation parameters
l
Mappings and Mapping Metadata
l
Data Mart objects: Fact tables, Fact attributes, Star schemas, Dimensions, and Dimension
attributes
In this section:
l
Overview (page 47)
l
Migrating models (page 49)
l
Migrating mappings (page 55)
l
Migrating tasks (page 58)
l
Migrating data marts (page 63)
l
Migrating reusable transformations (page 69)
l
Commands for exporting/importing objects (page 70)
l
Commands for comparing and applying objects (page 73)
Overview
The ability to export object definitions to a CSV file and then import them to another environment
provides many benefits, enabling:
l
Migration of data from a custom database table and/or Excel sheets to Compose
l
Data to be reviewed by business analysts who are not able to (or do not want to) access
Compose
l
Synching with third-party tools that output data in CSV format
l
Comparison of versions in order to review changes
l
Resolving of object-specific issues in a development environment and then deploying to the
production environment, even when they are not completely in sync
l
Sharing of resources between projects in the same environment
l
Granular version management of specific objects such as mappings
Manually typing these definitions into Compose would be a laborious and time-consuming
undertaking; using the CLI however, this can be done in a matter of minutes. Following the initial
import, customers who need to apply selective updates to the target environment (such as adding
attributes with their descriptions), can do so using the Compare and Apply CLI commands.
A typical workflow would be as follows:
1. Run the export command to output the source object(s) (to CSV files).
2. Run the import command to bring the objects into the target environment.
3. Following changes to the source environment, run the export command to output the source
object(s) to (CSV files).
4. Run the Compare command to see the differences between the exported objects and the
corresponding target objects.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
47

5 Data Warehouse projects
Alternatively, run the Compare command on the source environment to see the differences
between previous and current source project versions; then determine which changes needs
to be migrated to the target project. This approach is useful if changes were made directly to
the target project as it allows you to retain the custom changes while still applying changes
to other objects.
5. Review the changes and make any edits as necessary.
6. Run the Apply command to apply the changes to the target environment.
7. Periodically repeat steps 3-6 as necessary.
An understanding of the CSV file structure and their impact on the target environment is crucial, not
only for customers who wish to create these files manually, but also for ensuring the import/apply
operations succeed with the expected results. For this reason, this section first discusses the CSV
file structure of the supported objects and only then provides instructions for performing the actual
CLI operations.
l
Only import of new objects is supported.
l
UPDATEs and DELETEs will be ignored by the Apply command (which supports
ADD operations only), but can still be applied manually if needed.
Valid CSV file formats
CSV files must be in a valid format; otherwise, the import/compare/apply operation will fail.
CSV formatting rules:
l
Fields must be separated with a comma.
l
The first line must be a header line which contains the column names.
l
The escaping convention is similar to Excel:
l
If a field contains a comma, then the comma must be wrapped with quotation marks, for
example: "a,b"
l
If the value contains a quotation mark, then ithe quotation mark must be doubled. For
example:
"Mike ""The Hammer"" Smith"
l
If the value contains a new line, then it must be wrapped with double quotes. For example:
"Field owned by Mike.
Comment added by Shelley."
Stored objects
Several objects may have multi-lines, commas, and other such complexities.
Expressions, for example, are stored as two fields:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
48

5 Data Warehouse projects
First field - expression value:
Example:
${x1}*${x2}
Note: The expression may need to be escaped.
Second field - semicolon parameters mappings:
Example:
x1:unit price;x2:quantity
Migrating models
Migrating a Compose Model allows you to:
l
Import existing column definitions (i.e. definitions stored independently of Compose) to a
Compose project
l
Reuse the same Model across several projects or Compose installations
Model objects
A Compose Model consists of the following objects:
l
Entities (
entities.csv
)
l
Attributes (
attributes.csv
)
l
Attributes Domain (
attributesDomain.csv
)
l
Relationships (
relationships.csv
)
During the export process, each of these objects is exported to a separate CSV file.
You can either import the Model in its entirety or only specific elements, according to your needs.
You can also manually create a CSV file containing a Model element (or edit an existing file) and
then import it to a Compose project.
l
The Model must be valid before you can export it to or import it from a CSV file.
For details, see Validating the model (page 163).
l
CSV files must be in a valid format. For details, see
Valid CSV File Formats
.
l
Only a user with Model privileges can import the Model.
Non-privileged users can import just the mappings. For details, see the SCOPE
parameter in the
command for importing a model
.
l
Replacing an existing object is not supported. For example, if the Products entity
already exists in the Model, you cannot import an entities.csv file that contains an
entity called Products.
Guidelines for exporting a Compose model
Note the following:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
49

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
For Boolean fields, accepted values are True/False
l
Data type is the Compose logical type
l
The order of writing the attributes is according to the ordinal in the entity. Primary Keys will
be shown first, even if they were not first in the source model
l
Attribute domain and entity order is alphabetical in the CSV
l
Relationship order is by entity name (alphabetical) and according to their order in the entity
Guidelines for importing a Compose model
Note the following:
l
For boolean fields, accepted values are True/False
l
Column order has no meaning; only column names, which are case insensitive, unless
defined differently
l
If the
entities.csv
file is missing, the entities can be inferred from the
attributes.csv
file (with
no description). In such cases, duplicate objects are verified to be the same and added only
once. For example, if there are several rows with entity name myEntity, the entity will only be
added once
l
Data type is the Compose logical type
l
Relationship details override the underlying attributes information (e.g. history type, is key,
etc.)
l
When importing the
attributes.csv
file, a new entity will not be created if wasn’t already
created in the
entities.csv
file, and its attributes all have relationships to other entities. In
such cases, you should create the entity manually or add it to the
entities.csv
file
l
When importing the
relationships.csv
file, existing attributes will be replaced if:
child attribute prefix+attribute name = relationship_prefix+parent_attribute_name_
prefix+parent_attribute_name
For example, the attribute named CustomerDesignatedID will be replaced by the relationship
where:
l
ID is the name of the attribute in the parent entity and
l
Customer is the prefix of the relationship and
l
Designated is the prefix of the parent attribute.
Note that attributes marked as relationships will be skipped when imported from
attributes.csv
as they must derive their data type from the Attributes Domain.
Entities CSV file format
Column Name Required If column/value is missing Comments
Entity Name Yes Reject Case insensitive
Entity Description No Empty -
Entity CSV mapping rules
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
50

5 Data Warehouse projects
Attributes CSV file format
If Attribute Domain is missing in the attributes.csv file, there must be a data type.
Attribute domains that differ but have the same name will be appended with the suffix _
01.
Column Name Required
If column is
missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Entity Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Attribute Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Description No Empty Accept -
Is Key No No attributes will
be defined as
keys. In such a
case, validation
will fail as at least
one key needs to
be defined.
No Key On import, Compose
does
not
validate that each entity
has at least one key attribute
(required). If you import
entities without key
attributes, then you must
define a key attribute in
Compose after importing the
entity. Otherwise, Model
validation will fail.
Attribute
Domain
No If it is missing,
Data Type must
exist and
attribute
domains will be
built or used the
same as they are
during discovery.
Reject The Attribute Domain name
or the word "Relationship"
Data Type No If it is missing,
the Attribute
Domain must
exist. An error
will be returned if
the data type
does not match
the attribute
domain or if both
exist.
Reject Use combined syntax:
Varchar(50)
Decimal(10,2)
Attribute CSV mapping rules
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
51

5 Data Warehouse projects
Column Name Required
If column is
missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Prefix No Empty Accept (an
empty feld
means there
will be no
prefix)
-
History Type No Key - Type 1, Not
key - type 2
Reject Values are Type 1 or Type 2.
Yes (Type 2) and No (Type 1)
are also allowed.
Satellite/Hub No Key is Hub; other
attributes are
SAT 1
Reject Hub/1/2/3
Expression No No expressions
in any attribute
No
expression in
any attribute
-
Expresssion
Params
No All attribute-
parameter
mappings are
trivial (same
name)
All attribute-
parameter
mappings
are trivial
(same name)
-
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
52

5 Data Warehouse projects
Column Name Required
If column is
missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Add after No Not relevant. Not relevant. Instructs Compose to add
the attribute after a specific
attribute. The column is only
relevant when adding
attributes. When the column
is empty, the corresponding
attributes should be added
at the end (according to their
order in the CSV file).
Note that it may refer to any
attribute that is defined
above the current row.
For example, assuming a
record contains the
attributes address, height,
and weight, specifying the
following:
school, add after=weight
ID, add after=school
email, add after=empty
Will result in the following
order: address, height,
weight, school, ID, email
Attributes Domain CSV file format
Column
Name
Required
If column is
missing
If value is missing Comments
Name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Description No Empty The specific attribute value may
be empty as well.
-
Data Type No Reject Reject Use combined
syntax:
Varchar(50)
Decimal(10,2)
Attributes Domain CSV mapping rules
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
53

5 Data Warehouse projects
Relationships
Column Name Required If column is missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Child Entity Yes Reject Reject This is the more
detailed entity
(e.g.
OrderDetails).
Case insensitive.
Parent Entity Yes Reject Reject This is the less
detailed entity
(e.g. Products).
Case insensitive.
Prefix No Empty
If there are several
relationships from the
same source to the same
target, a prefix must be
added.
If all the
originating
attributes
have the same
prefix, use it
here.
A relationship
may not have
a prefix to its
underlying
attributes.
The specific
attribute value
may be empty
as well.
-
Position After No Add the relationships to
the end. Relationships are
ordered according to their
order in the file.
Same as
missing
column
The attribute
name or
relationship to
position it after or
”0” to position it
first.
Description No Empty Specific
attribute may
have empty
value as well
-
Relationships CSV mapping rules
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
54

5 Data Warehouse projects
Column Name Required If column is missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Is Key No No attributes will be
defined as keys. In such a
case, validation will fail as
at least one key needs to
be defined.
No key -
History Type No Key: Type 1
Non-key: Type 2
Reject Values are Type 1
or Type 2.
Yes (Type 2) and
No (Type 1) are
also allowed.
Satellite/Hub No Key: Hub
Other attributes: SAT 1
Reject Hub/1/2/3
Migrating mappings
Migrating mappings allows you to:
l
Export mapping metadata and mappings from a Compose project to CSV files. Mapping
metadata will be exported to
mappingsMetadata.csv
while mappings will be exported to
mappings.csv
. The former shows the table mappings while the latter show the column
mappings.
l
Import new mappings that do not exist in the current Compose project.
l
Reuse the same mappings across several projects or Compose installations.
Mappings export guidelines
When exporting mappings and mapping metadata from Compose, it is important to note the
following:
l
The export of mappings is allowed for users with the Viewer security role.
l
The order of writing the mapping metadata is according to metadata name alphabetically
(e.g. Map_Orders appears after Map_Customers).
l
The order of writing a mapping is according to target columns (same as Model ordinal).
l
Source columns which are not mapped to anything will not appear in the exported file.
l
All target columns will appear in the mappings even if they were not mapped.
Mappings import guidelines
When importing mappings and metadata to the Model, it is important to note the following:
l
If required, you can import one CSV file at a time:
mappingsMetadata.csv
or
mappings.csv
.
l
Column order has no meaning; only column names (case insensitive).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
55

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
When importing metadata, Compose validates that the targets exist in the Model. Source
columns are not validated on import.
l
If the source schema, table, view or query don't exist, they will be validated after the import.
l
Importing mappings will fail in the following scenarios:
l
If the target entity doesn't exist in the Model.
l
If the compose database object doesn't exist.
l
If the mapping attribute doesn't exist in the Model.
Valid CSV file formats
The CSV files must be in a valid format. For more detailed information, see the notes in
Valid CSV
file formats (page 48)
.
Mapping metadata CSV file format
Column
Name
Required
If column is
missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Landing
Zone
Database
Yes Reject Reject The Compose "source database"
name (excluding the word "landing")
Schema No If there is no
Schema
column,
either the
default
schema will
be used or
none (as
some
databases
do not have
separate
schemas)
If no schema
is specified,
either the
default
schema will
be used or
none (as
some
databases
do not have
separate
schemas)
-
Source Type No Table Reject Table/View/Query
Source
Object
Yes Reject Reject If Source Type is Table or View, the
Source Object is its name.
If Source Type is Query, the rules
and limitations described in
Valid
CSV file formats (page 48)
will be
applied.
CSV metadata mapping rules
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
56

5 Data Warehouse projects
Column
Name
Required
If column is
missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Target
Entity
Yes Reject Reject -
Filter No No filter No filter
Filter
Params
No Same name
for
attribute-
parameter,
like
expression
below
Same name
for attribute-
parameter,
like
expression
below
Example of Semicolon parameters
mappings:
x1:unit >price;x2:quantity
Mapping
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Target
Column
Yes Reject No mapping
if there is
also no
expression
or lookup.
Case insensitive
Mapping
Type
No Field
mapping
Allow the
field to be
empty if
there is no
field
mapping, no
expression,
and no
lookup.
Field Mapping /Expression/Lookup
Field
Mapping
No Reject No mapping
to this
attribute.
The name of the source field, or
empty if this field is not mapped.
Expression No No
expression
No
expression in
this
attribute.
Example of an expression value:
${x1}*${x2}
Expression
Params
No All attribute-
parameter
mapping is
trivial (same
name)
No
expression in
that attribute
Example of Semicolon parameters
mappings:
x1:unit >price;x2:quantity
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
57

5 Data Warehouse projects
Column
Name
Required
If column is
missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Lookup
Landing
Database
No No lookups No
expression in
that attribute
Lookup Landing Database name
Example:
Northwind on MySQL
Lookup
Table
No No lookups No
expression in
that attribute
Lookup table or view name in schema
table format.
Example:
Schema1.Orders
Lookup
Type
No No lookups No
expression in
that attribute
Table or View
Lookup
Condition
Value
No No lookups No
expression in
that attribute
-
Lookup
Condition
Params
No No lookups No
expression in
that attribute
Include Lookup/Landing.
Example:
x:$Lookup$.a;y:$Landing$.CustomerID
Lookup
Result Value
No No lookups No
expression in
that attribute
-
Lookup
Result
Params
No No lookups No
expression in
that attribute
Same format as the lookup condition
parameters.
Migrating tasks
You can migrate data warehouse tasks, data mart tasks, and custom ETLs (tasks) from one
environment to another, while preserving custom objects in the target environment. This is
especially useful for customers who wish to incrementally updated production environments with
new versions from the test environment.
The following files will be exported:
For the data warehouse:
l
<specified export folder>/customEtl.csv - Contains details of any (enabled or disabled)
custom ETLs defined for the task.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
58

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
<specified export folder>/taskCustomEtl.csv - Lists any
enabled
custom ETLs defined for
the data warehouse task.
l
<specified export folder>/taskSettings.csv - Contains details of the task settings defined
for each of the data warehouse tasks.
l
<specified export folder>/tasks.csv - Lists the data warehouse tasks.
l
<specified export folder>/taskDataWarehouseTables.csv - Lists the data warehouse tables
and properties.
l
<specified export folder>/taskMappings.csv - Lists the mappings used in the task.
l
<specified export folder>/SQL/DW_Custom_ETL_<custom ETL name>.SQL - One SQL file
for each custom ETL.
For each data mart:
l
<specified export folder>/<data mart name>/customEtl.csv - Contains details of any
custom pre-loading or post-loading ETLs defined for the data mart task
l
<specified export folder>/<data mart name>/taskSettings.csv - Contains details of the task
settings
l
<specified export folder>/<data mart name>/SQL/DM_Custom_ETL_<custom ETL
name>.SQL - One SQL file for each custom ETL
Considerations
Export considerations
l
Parameters will be written to CSV files in alphabetical order (as they appear in the web
console).
Import considerations
l
Importing tasks or custom ETLs will override any existing objects with the same names.
l
Importing logical entities or mappings that do not exist in the target project will result in
failure.
Valid CSV file formats
The CSV files must be in a valid format. For more detailed information, see the notes in
Valid CSV
file formats (page 48)
.
Data warehouse CSV file formats
Tasks file
The tasks.csv file consists of one row per task.
Header
name
Mandatory
If column is
missing
If column exists but value
is empty
Comments
Task name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Tasks
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
59

5 Data Warehouse projects
Header
name
Mandatory
If column is
missing
If column exists but value
is empty
Comments
Description No Empty Empty -
Type No Full Load Only Reject Full Load Only
or
Change Tables
Only
Task settings file
The taskSettings.csv file consists of one row per setting.
Header
name
Mandatory
If column is
missing
If column exists but value is
empty
Comments
Task Name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Setting
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Setting
Value
Yes Reject Reject -
Data warehouse task settings
Task entities file
The taskDataWarehouseTables.csv file consists of one row per entity.
Header name Mandatory
If column
is missing
If column
exists but
value is
empty
Comments
Task Name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Entity Name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Handle duplicates Yes Reject Reject Boolean
Task logical entities
Task mappings file
The taskMappings.csv consists of one row per task for each mapping that is used in the task.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
60

5 Data Warehouse projects
Header
name
Mandatory
If column is
missing
If column exists but value is
empty
Comments
Task Name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Mapping
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Task mappings
Custom ETL file
The customEtl.csv consists of one row for each custom ETL defined for the task (Pre-Loading,
Multi-Table, Single Table, or Post-Loading), regardless of whether or not the ETL is enabled.
Header name Mandatory
If column
is missing
If column
exists but
value is empty
Comments
Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Description No Empty Empty -
Type Yes Reject Reject Pre Loading ETL, Multi Table
ETL, Single Table ETL or Post
Loading ETL
Entity Yes Reject Reject Relevant only for single table
ETL
Sequence
Number
Yes Reject Reject Valid values are positive integer
numbers
Execute as
Stored
Procedure
Yes Reject Reject Boolean
Data warehouse custom ETL
l
For each custom ETL, Compose will export/import an SQL file to:
<specified export folder>/SQL
l
The file name will be DW_Custom_ETL_<custom ETL name>.SQL
l
If you wish to edit the file name, make sure that it only contains the following
characters: A-Z, 0-9, underscore (_), or space. On import, any other character will
be replaced with an underscore.
Task custom ETL file
The taskCustomEtl.csv file consists of one row for each enabled custom ETL used in the data
warehouse task.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
61

5 Data Warehouse projects
Header name Mandatory
If column
is missing
If column
exists but
value is
empty
Comments
DWH Task Name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Custom ETL Name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Data warehouse task custom ETL
Data mart CSV file formats
Task settings file
The taskSettings.csv file consists of one row per setting.
Header
name
Mandatory
If column is
missing
If column exists but value is
empty
Comments
Setting
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Setting
Value
Yes Reject Reject -
Data mart task settings
Custom ETL file
The customEtl.csv file consists of one row per custom ETL (Pre Loading ETL or Post Loading ETL).
Header name Mandatory
If column
is missing
If column exists
but value is empty
Comments
Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Description No Empty Empty -
Type Yes Reject Reject Pre Loading ETL or
Post Loading ETL
Active Yes False False Boolean
Sequence
Number
Yes Reject Reject Valid values are
positive integer
numbers
Execute as
Stored
Procedure
Yes Reject Reject Boolean
Data mart custom ETL
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
62

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
For each custom ETL, Compose will export/import an SQL file to:
<specified export folder>/<data mart name>/SQL
l
The file name will be DM_Custom_ETL_<custom ETL name>.SQL
l
If you wish to edit the file name, make sure that it only contains the following
characters: A-Z, 0-9, underscore (_), or space. On import, any other character will
be replaced with an underscore.
Migrating data marts
You can migrate data marts from one environment to another, while preserving custom objects in
the target environment.
The following diagram shows a data mart model:
Exporting data marts
When you export data marts, a separate folder containing the CSV files will be created for each
data mart:
Example:
datamarts.csv
datamart1\facts.csv
datamart1\FactDimensionsLinks.csv
datamart1\dimensions.csv
datamart1\factattributes.csv
datamart1\dimensionattributes.csv
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
63

5 Data Warehouse projects
datamart2\facts.csv
datamart2\factdimensions.csv
datamart2\dimensions.csv
datamart2\factattributes.csv
datamart2\dimensionattributes.csv
Data marts CSV
The
datamarts.csv
consists of one row per data mart.
Header
name
Required
If column is
missing
If column exists but
value is empty
Comments
Data Mart
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Description No Empty Empty -
Table Prefix No Empty Empty Default for future fact and
dimension creation
View Prefix No Empty Empty Default for future fact and
dimension creation
Data marts CSV metadata mapping
When exporting a data mart, the following objects will not be included: View schema,
database name, and schema name. As these objects are environment-specific, they
need to be set them up manually after importing the data mart to the target environment
(unless you wish to user the defaults from the data warehouse).
Facts CSV
The
facts.csv
consists of one row per fact table.
Header
name
Required
If column is
missing
If column
exists but
value is
empty
Comments
Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
The name corresponds to the fact
dimension name
Description No Empty Empty -
Facts CSV metadata mapping
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
64

5 Data Warehouse projects
Fact Type No On ADD:
Transactional
On ADD:
Transactional
Transactional, Aggregated, or State
Oriented
Fact Table
Name
Yes Reject Reject -
Fact View
Name
No Empty Empty Empty means that no view is created
Transaction
Date
*No If mandatory,
reject
If mandatory,
reject
Mandatory for transactional and
aggregated facts
Ignored for state-oriented facts
Includes full path with dot notation;
for example, in AdventureWorks it
might be:
OrderDetail.OrderHeader.ModifiedD
ate
Source Filter No No filter No filter Filter on the source columns (which
would eventually translate to an SQL
"where" statement)
Must be formatted as an expression
Source Filter
Params
No Same name
for attribute-
parameter,
similar to
expression
below
Same name
for attribute-
parameter,
similar to
expression
below.
-
Aggregation
Filter
No No filter No filter Filter on the aggregated columns
(which would eventually translate to
an SQL "having" statement)
Must formatted as an expression
Aggregation
Filter
Params
No Same name
for attribute-
parameter,
like
expression
below
Same name
for attribute-
parameter,
like
expression
below
-
Root entity Yes Reject Reject The root entity used. For example, if
the fact is a denormalization of order
details and orders, it will contain
"orders"
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
65

5 Data Warehouse projects
Fact As
Type 1
No Enable the
option
Enable the
option
Boolean: Accepts the values TRUE
or FALSE
For an explanation of this option,
see
Editing star schemas (page
241)
.
Dimensions CSV
The
dimensions.csv
consists of one row per dimension.
Header
name
Required
If column is
missing
If column
exists but
value is
empty
Comments
Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Description No Empty Empty -
Dimension
Table Name
Yes Reject Reject -
Dimension
View Name
No Empty Empty Empty means that no view is
created
History Type No Type 2 Type 2 Type 1/ Type 2
Source Filter No No filter No filter Filter on the source columns
(which would eventually
translate to an SQL "where"
statement)
Must be formatted as an
expression
Source Filter
Params
No Same name for
attribute-
parameter, like
expression
below
Same name for
attribute-
parameter, like
expression
below
-
Root entity Yes Reject Reject The root entity used. For
example, if the fact is a
denormalization of order
details and orders, it will
contain "orders"
Dimensions CSV metadata mapping
Fact dimensions CSV
The
FactDimensionsLinks.csv
consists of one row per dimension usage in the fact.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
66

5 Data Warehouse projects
Header name Required If column is missing
If column exists
but value is
empty
Comments
Fact Name Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Dimension
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case
insensitive
Referenced
data mart
No The data mart does not
contain a referenced
dimension.
Means that it is not
a referenced
dimension.
-
Referenced
dimension
name
Only for
referenced
dimensions.
The data mart does not
contain a referenced
dimension.
Means that it is not
a referenced
dimension.
Name in the
referencing
data mart.
Fact dimensions CSV metadata mapping
Fact attributes CSV
The
factattributes.csv
consists of one row per attribute and includes the OID attributes as well.
On export, the order is determined by the attributes order. On import, the order is determined by
the read order.
Header name Required
If column is
missing
If column
exists but
value is
empty
Comments
Star schema
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Attribute
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Entity Path No Treat as empty Treat as
empty
Case insensitive.
If the column is directly
mapped to a data
warehouse, the field will
contain the model entity path
(for example:
Orders.Customers).
An empty field means that
the entity path should be
calculated using an
expression
Fact attributes CSV metadata mapping
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
67

5 Data Warehouse projects
Header name Required
If column is
missing
If column
exists but
value is
empty
Comments
Description No Empty A specific
attribute may
have empty
value as well.
-
Data Type Yes Reject Reject Use combined syntax:
Varchar(50) Decimal(10,2)
Aggregation No No aggregation
columns (this
will return an
error if the Fact
is aggregated).
No
aggregation
columns.
Empty or
SUM/COUNT/MAX/MIN/COUNT_
DISTINCT
Expression No No expressions
in any attribute.
No expression
in that
attribute.
See
Stored objects (page
48)
.
Expression
Params
No All attribute-
parameter
mapping is
trivial (same
name)
All attribute-
parameter
mapping is
trivial (same
name)
See
Stored objects (page
48)
.
Dimension attributes CSV
The
dimensionattributes.csv
consists of one row per dimension attribute in a fact dimension. These
may also include Date or Time dimensions (e.g. Customer.ModifiedDate).
On export, the order is determined by the attributes order. On import, the order is determined by
the read order.
Header
name
Required
If column is
missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Dimension
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Attribute
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Dimension attributes CSV metadata mapping
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
68

5 Data Warehouse projects
Header
name
Required
If column is
missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Entity Path No Treat as
empty
Treat as
empty
Case insensitive.
If the column is directly mapped
to a data warehouse, the field will
contain the model entity path (for
example:
Orders.Customers
)
Am empty field, means that the
entity path should be calculated
using an expression
Description No Empty Specific
attribute
may have
empty value
as well
-
Data Type Yes Reject Reject Use combined syntax: Varchar
(50) Decimal(10,2)
Expression No No
expressions in
any attribute
No
expression in
that
attribute.
See
Stored objects (page 48)
.
Expression
Params
No All attribute-
parameter
mapping is
trivial (same
name)
All attribute-
parameter
mapping is
trivial (same
name)
See
Stored objects (page 48)
.
Migrating reusable transformations
You can migrate reusable transformations from one environment to another, while preserving
custom objects in the target environment.
For information on reusable transformations, see
Defining reusable transformations (page 191)
.
Reusable transformations
The
ReusableTransformation.csv
file includes a row per reusable transformation parameter and is
described in the table below. Note that some reusable transformations may have no parameters.
Header name Required If column is missing If value is missing Comments
Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Reusable transformations CSV mapping rules
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
69

5 Data Warehouse projects
Header name Required If column is missing If value is missing Comments
Category No On ADD: General On ADD: General Case sensitive
Description No Empty Empty
Expression No On ADD: Empty On ADD: Empty
Reusable transformations parameters
The
ReusableTransformationParams.csv
file is described in the table below.
Header
name
Required
If column
is missing
If value is
missing
Comments
Reusable
Transformation
Name
Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Parameter Name Yes Reject Reject Case insensitive
Data Type No On ADD:
VarChar
On ADD:
VarChar
According to reusable
transformation data types (i.e. no
length and scale)
Description No Empty Empty
Reusable transformations parameters CSV mapping rules
General guidelines
It's important to take note of the following:
l
On export:
l
The order in which the parameters will be written is determined by their order in the
web console
l
The order of reusable transformations in the CSV file is alphabetical
l
Reusable transformations are considered part of the model, which means users need
the import model permission in order to import them.
l
Column order has no meaning; only column names (case insensitive)
l
All CSVs are optional
l
The CSV files do not contain or rely on internal object IDs, rather, they rely on object
names.
l
On import, existing reusable transformations
will be overridden by the information from the
CSV file
.
Commands for exporting/importing objects
You can export and import Compose objects using the export_csv and import_csv CLI
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
70

5 Data Warehouse projects
To import specific entities, use the CSV mechanism described in Migrating models (page
49).
Compose CLI requires Administrator permission. To grant Administrator permission,
select "Run as administrator" when opening the command prompt. All commands should
be run from the Compose
bin
directory (C:\Program Files\Qlik\Compose with a default
installation).
Exporting objects
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe export_csv --project project_name --outfolder folder
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--outfolder The name of the target folder for the CSV files.
Example
ComposeCli.exe export_csv --project myproject --outfolder c:\MyCFDWProject
Importing objects
As CSV files do not have versions, Compose cannot know which Compose version the
CSV file being imported originated from. If the default behavior has changed between
versions, the rule is that the default of the new version will always be applied. For
example, in the Compose May 2021 version, the option to update the fact with changes
to Type 2 data warehouse entities is now enabled by default. In previous versions, facts
were not updated with changes to Type 2 data warehouse entities and there was no
option to change this behavior. Therefore, continuing with our example, if you want this
option to be disabled by default, you would need to add the column for that setting (Fact
As Type 1) to the fact.csv file and set the value to "FALSE" before importing.
Before performing any import operations, it is strongly recommended to review the topic(s) that
discuss CSV file structure and the impact of missing columns and/or values on the target
environment. For example, before importing Data Marts, review the Migrating Data Marts topic.
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
71

5 Data Warehouse projects
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe import_csv --project
project_name
[--infolder
folder
] [--scope
model|mappings|datawarehouse|DatawarehouseTasks|datamarts] [–-filetype
objecttype
] [–-infile
filename
]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--infolder The full path to the folder containing the CSV files. This parameter
is only required if you want to import all files.
--scope Use this parameter to allow non-privileged users to import specific
objects. When this parameter is omitted, all objects will be
imported.
Possible values are:
l
--scope model - Imports the model objects (Attributes
Domain, Entities, Attributes, Relationships, Reusable
Transformations, and Reusable Transformation Parameters)
l
--scope mappings - Imports the mappings metadata and the
actual mappings.
l
--scope datawarehouse - Imports the mappings as well as all
objects included in the DatawarehouseTasks described below.
l
--scope DatawarehouseTasks - Imports the data warehouse
tasks and related objects (Tasks, Task Settings, Task
Mappings, Task Data Warehouse Tables, Task Custom
ETLs, and Custom ETLs).
l
--scope datamarts - Imports the data mart objects (Data
Marts, Facts, Star Schemas, Fact Attributes, Dimension
Attributes, Task Settings, and Custom ETLs).
The --scope parameter cannot be included in the same
command as the --filetype parameter
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
72

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--filetype The type of CSV file to import. When this parameter is omitted, all
objects will be imported.
Possible values are:
l
AttributesDomain
l
Entities
l
Attributes
l
Relationships
l
MappingsMetadata
l
Mappings
l
ReusableTransformation
l
ReusableTransformationParams
l
DataMarts
l
Tasks
l
TaskSettings
l
TaskMappings
l
TaskDataWarehouseTables
l
TaskCustomETLs
l
CustomETLs
The --filetype parameter cannot be included in the
same command as the --scope parameter
--infile The full path to the file to import when using non-default file
names. This must be specified together with the --filetype
parameter described above.
Examples
Import all CSV files
ComposeCli.exe import_csv --project myproject --infolder c:\composecfdw_csv
Import a specific CSV file with a custom Name
ComposeCli.exe import_csv --project myproject --filetype AttributesDomain --infile
c:\myattributesdomain.csv
Commands for comparing and applying objects
You can compare and apply Compose objects using the compare_csv and apply_csv CLI. Before
performing any of these operations, it is strongly recommended to review the topic(s) that discuss
CSV file structure and the impact of missing columns and/or values on the target environment. For
example, before applying changes to a Model, review the "Migrating the Model" topic.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
73
5 Data Warehouse projects
Comparing objects
Comparing the model to be imported with the existing project model allows you to view and
optionally edit the proposed changes before applying them.
When you run the Compare command, the structure of the CSV output files will be identical to the
export output files, but with the addition of Change Type and Action columns at the end. Note that
as the Apply command only supports ADD operations, the only value in the Change Type column
will be ADD.
If a column or value was deleted in the source environment, the Action column will contain the
value "IGNORE". This tells Compose not to delete the corresponding column/value in the target
environment when the Apply command is run. You can delete the "IGNORE" before running the
Apply command to force the deletion of the corresponding column/value in the target environment.
However, as the Apply command
does not support DELETE operation
s, deleting the "IGNORE"
before running the Apply command will have no effect.
Compare guidelines:
l
Unchanged objects will not be written to the output file(s).
l
If there was no changes at all to any of the object types, an empty output file will only be
created if you include the --create_files_even_when_no_diff parameter in the command (see
below).
l
For Boolean fields, values are True/False
l
Data type is Compose's logical type.
l
For model, the attributes writing order is according to the new ordinal in the entity.
l
Mapping metadata, attributes domain and entity order is alphabetical in the CSV file.
l
Relationship order is by entity name (alphabetical) and according to their order in the entity.
l
For mapping, the listed order is:
l
Alphabetical for mapping names (e.g. Map_Orders follows Map_Customers)
l
According to target columns (model ordinal) within a mapping.
l
Within a mapping, FD (From Date) could be one of the rows.
l
Source columns which are not mapped to anything will not be included in the output file.
l
If the model is not valid, the Compare command may fail.
Compose CLI requires Administrator permission. To grant Administrator permission,
select "Run as administrator" when opening the command prompt. All commands should
be run from the Compose
bin
directory (C:\Program Files\Qlik\Compose with a default
installation).
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe compare_csv --project project_name --infolder folder --changes_folder folder [-
-create_files_even_when_no_diff]
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
74

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of
the project.
--infolder The folder
containing the
exported CSV
files.
--changes_folder The folder to
where the
change files
will be written.
The file names
will be identical
to the exported
CSV files, but
with a _
changes suffix
(e.g. entity_
changes.csv).
--create_files_even_when_no_diff Use this
parameter if
you want a
template
output file to
be created
when there are
no differences
(e.g. an empty
entity_
changes.csv
file containing
only the header
columns). This
may be useful,
for example, if
you wish to
manually
create a
changes file.
Example
ComposeCli.exe compare_csv --project ProjectEmpty --infolder "C:\1" --changes_folder "C:\2" --
create_files_even_when_no_diff
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
75

5 Data Warehouse projects
Applying objects
Once you are satisfied with the proposed changes, you can then apply them to your project.
Apply guidelines:
l
If a column is missing on ADD, then the action will be as described in the topic discussing the
object elements.
l
By default, all changed object definitions will be added. To filter out rows or columns, edit the
outputted CSV file as needed. For example, to only apply changes to a specific Data Mart,
delete all of the other Data Marts' rows.
l
Any non-standard field name headings, should be renamed in the CSV to the Compose
standard.
l
Column order is insignificant as the columns will be ordered by name (case insensitive).
l
For Boolean fields, accepted values are Yes/No, True/False, 1/0 (case insensitive)
l
Data type is Compose's logical type.
l
Relationship details override the underlying attributes information (e.g. History Type, Is Key,
etc.).
Attributes that are marked as relationships will be skipped on import as they
derive their data type from the relationship.
l
All CSV files are optional in the folder.
l
For mappings, the apply operation will fail in the following scenarios:
l
The model is not valid.
l
The target does not exist in the model.
l
The mapping attribute does not exist in the model (after applying attributes.csv)
l
The Compose database object does not exist.
l
If the source schema, table, view or query does not exist, it will be validated after the Apply
operation .
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe apply_csv --project
project_name
--changes_folder
folder
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--changes_folder The folder containing the change files
written by the compare command.
Example
ComposeCli.exe apply_csv --project ProjectEmpty --changes_folder "C:\1"
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
76

5 Data Warehouse projects
Exporting and importing projects using the CLI
Compose CLI requires Administrator permission. To grant Administrator permission,
select "Run as administrator" when opening the command prompt. All commands should
be run from the Compose
bin
directory (C:\Program Files\Qlik\Compose with a default
installation).
Under normal circumstances, use the deployment options described in
Project deployment (page
44)
to export and import projects. For deployment automation or control by another tool, you can
use the command line interface (CLI) to perform such tasks.
To export or import a project or project configuration, you first need to change the
default Master User Password.
For more information on changing the master user password, see Changing the master
user password (page 29).
See also: Moving projects from the test environment to the production environment
(page 85) and Import/export scenarios - When is a password required? (page 86)
Before running any command, you must run the
Connecting to Qlik Compose server (page 77)
command.
To get help when using the command line, you can run the Help command. For example, for help
about exporting a project, issue the following command:
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository --help
This brings up a list of help parameters.
In this section:
l
Connecting to Qlik Compose server (page 77)
l
Exporting a project (page 78)
l
Importing a project (page 80)
l
Exporting the project configuration (page 83)
l
Importing the project configuration (page 84)
l
Moving projects from the test environment to the production environment (page 85)
Connecting to Qlik Compose server
Run the Connect command to establish a connection to the Qlik Compose Server. You must run this
command before running any other command.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe connect [--url connection_url]
Where:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
77

5 Data Warehouse projects
--url is the connection URL to the system where the server is running.
Example
ComposeCli.exe connect --url https://mymachine.mydomain/qlikcompose
Exporting a project
You can use the export_project_repository CLI to export a project.
Exported projects include the following:
l
Databases
l
Model definitions (entities and attributes)
l
Mappings
l
Custom ETLs
l
Data warehouse tasks
l
Data mart definitions
Existing data warehouse tables and generated tasks are not exported. Notifications and
schedules are also not exported as they are considered to be environment-specific.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository --project
project_name
--outfile
output_file
[--is_
without_credentials or --without_environment_specifics] [--password
password
] [--master_user_
password
master_user_password
]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--outfile The path to and name of the output file. This file is in
JSON format (e.g.
C:\file.json
).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
78

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--is_without_credentials Use this parameter to specify that you want to export
the project settings without the encrypted fields.
When importing to a new project, you will need to
manually enter the project passwords (in the
Compose database connection settings) after the
import completes. In addition to eliminating the need
to specify a password when exporting or importing
the project, the is_without_credentials parameter
also allows the project to be used in every Compose
installation, regardless of its master user password. It
is also useful in the event that you would like to keep
the existing passwords in the target environment (e.g.
when exporting from a testing environment to an
existing project in the production environment).
--password The password for encrypting the credentials in the
exported project. When used, this parameter must be
used together with the master_user_password
parameter described below. Use the password >
parameter if you want to encrypt the credentials in the
exported project, but do not want the source master
password to be used in a different environment. The
specified password must be at least 32 characters in
length and can either be user-devised or generated
using the genpassword utility described in
Changing the
master user password (page 29)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
79

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--master_user_password The master user password defined for the source
machine. When used, this parameter must be used
together with the password parameter. Use the master_
user_password > parameter if you want to encrypt the
credentials in the exported project, but do not want
the source master password to be used in a different
environment. In such a case, when you import the
project to an environment that has a different master
password, you will only need to specify the password
qualifier.
For instructions on changing the master user
password, see
Changing the master user password
(page 29)
.
See also:
Moving projects from the test environment
to the production environment (page 85)
and
Import/export scenarios - When is a password
required? (page 86)
--without_environment_specifics Use this parameter to exclude all of the environment
specific settings from the export. This is useful if the
project you are exporting includes environment
variables and the settling in the target environment
are significantly different from the source
environment. The variables will be replaced with their
default values (either empty or the default Boolean
value).
See also:
Working with environment variables (page
87)
Example
Export project without a password
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository --project MyProject --outfile file.json --is_without_
credentials
Export project with a password
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository --project MyProject --outfile file.json --password
MyPassword --master_user_password MyMasterUserPassword
Importing a project
You can use the import_project_repository CLI to import a project. If you import to an existing
project, all of the project settings, except the project configuration items will be overridden. For
information on the project configuration items, see
Exporting the project configuration (page 83)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
80
5 Data Warehouse projects
Imported projects include the following:
l
Databases
l
Model definitions (entities and attributes)
l
Mappings
l
Custom ETLs
l
Data warehouse tasks
l
Data mart definitions
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe import_project_repository --project
project_name
--infile
input_file
[--
password
password
] [--is_without_credentials] [--override_configuration] [--dont_backup_
existing_project] [--autogen]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--infile The full path to the input file, including the file name.
This file is in JSON format (e.g.
C:\file.json
).
--password The password specified with the password parameter
during export.
For instructions on changing the master user
password, see
Changing the master user password
(page 29)
.
See also:
Moving projects from the test environment
to the production environment (page 85)
and
Import/export scenarios - When is a password
required? (page 86)
--is_without_credentials Use this parameter to specify to import the project
settings without the encrypted fields. In this case, you
will need to manually enter the project passwords in
the Compose database connection settings.
--override_configuration Use this parameter to override the existing project
configuration. When importing a project, the default
setting is not to override the existing project
configuration.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
81

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--dont_backup_existing_project Use this parameter to specify not to back up the
existing project. By default, existing projects are
backed up to the following location (and automatically
restored if the import fails):
<product_dir>\data\projects\<project_name>_
backup_<timestamp>
--autogen Use this paramter to automatically generate the
imported project. If the project is imported
successfully, Compose will:
l
Validate the model and adjust the data
warehouse if needed
l
Create the data warehouse tables if they do not
exist
l
Validate the data warehouse
l
Adjust the data warehouse if needed.
If the "Adjust" cannot be performed
automatically, the "autogen" process will be
stopped.
l
Generate all data warehouse tasks.
If Compose encounters an error while
generating a data warehouse task, it will skip
the problematic task and continue with the
remaining tasks.
l
Create, adjust and generate all data marts
If an error is encountered during the
"Create" or "Generate" operations, it is
recommended to switch to the Compose
Console and perform these operations
manually. Doing so will generate a more
detailed error message and enable you to
resolve the issue.
For information on validating the data warehouse and
generating the task, see
Creating and managing the
data warehouse (page 192)
. For information on
generating the data mart task, see
Creating and
managing data marts (page 228)
.
Example
ComposeCli.exe import_project_repository --project MyProject --infile file.json --password
MyPassword --override_configuration --autogen
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
82

5 Data Warehouse projects
Exporting the project configuration
You can use the export_project_repository_config CLI to export the configuration settings
of an existing project. This includes database definitions, scheduling jobs, and notifications. This is
helpful, for example, when you need to migrate configuration settings from a test environment to
the production environment.
For information about migrating projects, see
Moving projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 85)
.
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository_config --project
project_name
--outfile
output_file
[--is_without_credentials] [--password
password
] [--master_user_password
master_user_password
]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--outfile The path to and name of the output file. This file is in JSON format
(e.g.
C:\file.json
).
--is_without_credentials Use this parameter to specify that you want to export the project
settings without the encrypted fields. When importing to a new
project, you will need to manually enter the project passwords (in
the Compose database connection settings) after the import
completes. In addition to eliminating the need to specify a
password when exporting or importing the project, the is_without_
credentials parameter also allows the project to be used in every
Compose installation, regardless of its master user password. It is
also useful in the event that you would like to keep the existing
passwords in the target environment (e.g. when exporting from a
testing environment to an existing project in the production
environment).
--password The password for encrypting the credentials in the exported
project. When used, this parameter must be used together with the
master_user_password parameter described below. Use the password
> parameter if you want to encrypt the credentials in the exported
project, but do not want the source master password to be used in
a different environment. The specified password must be at least
32 characters in length and can either be user-devised or
generated using the genpassword utility described in
Changing the
master user password (page 29)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
83

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--master_user_password The master user password defined for the source machine. When
used, this parameter must be used together with the password
parameter. Use the master_user_password > parameter if you want
to encrypt the credentials in the exported project, but do not want
the source master password to be used in a different environment.
In such a case, when you import the project to an environment that
has a different master password, you will only need to specify the
password qualifier.
For instructions on changing the master user password, see
Changing the master user password (page 29)
.
See also:
Moving projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 85)
and
Import/export scenarios -
When is a password required? (page 86)
Example
Export project configuration without a password
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository_config --project MyProject --outfile file.json --is_
without_credentials
Export project configuration with a password
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository_config --project MyProject --outfile file.json --
password MyPassword --master_user_password MyMasterUserPassword
Importing the project configuration
You can use the Compose CLI to import the configuration settings of an existing project. This
includes database definitions, scheduling jobs, and notifications. This is helpful, for example, when
you need to migrate configuration settings from a test environment to the production environment.
For information about migrating projects, see
Moving projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 85)
.
Before you can import the project configuration, you must first run the import_project_
repository command described in Importing a project (page 80).
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe import_project_repository_config --project
project_name
--infile
input_file
[--
password
password
] [--is_without_credentials]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
84

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--infile The full path to the input file, including the file name. This file is in
JSON format (e.g.
C:\file.json
).
--password The password specified with the password parameter during
export.
For instructions on changing the master user password, see
Changing the master user password (page 29)
.
See also:
Moving projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 85)
and
Import/export scenarios -
When is a password required? (page 86)
--is_without_credentials Use this parameter to specify to import the project settings without
the encrypted fields. In this case, you will need to manually enter
the project passwords in the Compose database connection
settings.
Example
ComposeCli.exe import_project_repository_config --project MyProject --infile file.json --
password MyPassword
Moving projects from the test environment to the production environment
After successfully creating and testing projects in the test environment, you now want to move
those projects to the production environment. You also need to propagate updates from the testing
environment to the production environment as necessary. Although it sounds complicated, moving
new and updated projects from the test environment to the production environment is actually
quite straightforward, as explained below.
See also
Import/export scenarios - When is a password required? (page 86)
.
The data source and data warehouse display names must be identical in both the testing
and the production environments.
To perform the initial migration from the testing environment to the production environment:
1. Export the project from the test environment as described in
Exporting a project (page 78)
.
2. Import the test project to the production environment as described in
Importing a project
(page 80)
.
3. Edit the connection settings to point to the production data source and data warehouse.
For more information, see
Setting up Landing Zone and Data Source connections (page
131)
and
Setting up a data warehouse connection (page 110)
respectively.
4. Configure notifications and scheduling as needed.
For more information, see
Scheduling tasks (page 270)
and
Notifications (page 272)
respectively.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
85

5 Data Warehouse projects
To propagate updates from the testing environment to the production environment:
1. Export the project from the test environment as described in
Exporting a project (page 78)
.
2. Import the test project to the production environment as described in
Importing a project
(page 80)
.
Import/export scenarios - When is a password required?
The following section describes which of the various export/import scenarios require a password to
be specified.
In all scenarios, if you import a project to an existing project, the credentials of the
existing projects are preserved (as they are part of the project configuration).
Example 1: Moving a project or project configuration between two Compose machines without
retaining the project credentials.
This is useful when importing to a new project that will have different project credentials.
In such a scenario, simply add the is_without_credentials parameter to either the export or the
import command.
Example 2: Moving a project or project configuration between two Compose machines that
have the same Master User Password.
In such a scenario, neither the export command nor the import command need to include a
password. If you do not want the source and target projects to have the same credentials (for
database connectivity, etc.), then you also need to specify the is_without_credentials parameter in
either the export or the import command.
Example 3: Moving a project or project configuration between two Compose machines that
have a different Master User Password, but without revealing the Master User Password of
the source machine.
In such a scenario, the export command must include the password and master_user_password
parameters while the import command must include the password parameter. The same password
(specified with the password parameter) must be used for both export and import.
Example 4: Moving a project or project configuration between two Compose machines that
have a different Master User Password.
In such a scenario, the export command does not need to include a password, but the import
command should specify the Master User Password of the source machine (using the password
parameter).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
86

5 Data Warehouse projects
Working with environment variables
Requires Compose August 2021 Service Release 03 or later.
Environment variables allow developers to build more portable expressions, custom ETLs, and
Compose configurations, which is especially useful when working with several environments such
as DTAP (Development, Testing, Acceptance and Production). Different environments (for example,
development and production) often have environment-specific settings such as database names,
schema names, and Replicate task names. Variables allow you to easily move projects between
different environments without needing to manually configure the settings for each environment.
This is especially useful if many settings are different between environments. For each project, you
can use the predefined environment variables or create your own environment variables.
Database and schema name variables are supported with the following objects:
l
Reusable transformations
l
Custom ETLs (Data warehouse and Data marts)
l
Mappings lookups
l
Mappings and model expressions
l
Data mart settings
In this section:
l
Limitations and considerations (page 87)
l
Locations and names of predefined variables (page 88)
l
Compose environment_variables CLI guidelines (page 91)
l
Working with predefined variables only (page 91)
l
Working with user-defined variables only (page 92)
l
Working with both user-defined and predefined variables (page 94)
l
Removing environment variables (page 96)
l
Manually editing the JSON file (page 96)
Limitations and considerations
l
Values for predefined variables will be shown in the Compose user interface, but user-
defined variables will be shown in variable format (for example, $$${myVariable}).
l
Variable names are case sensitive and can include alphanumeric characters, underscores,
and periods only.
l
User-defined variable definitions will not be included in projects exported as JSON files or in
projects exported as CSV files. However, user-defined variable names will be included in the
relevant places in the exported files.
See also:
Exporting and importing projects using the CLI (page 77)
and
Migrating objects as
CSV files (page 46)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
87

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Exported CSV objects that are associated with predefined environment variables (for
example, a mapping database and schema) cannot contain user-defined environment
variables.
For instance, this is not allowed:
Name Landing Zone Database Schema
MyMapping $$${MyDatabase} $$${MySchema}
See also:
Migrating objects as CSV files (page 46)
.
Locations and names of predefined variables
Predefined variables are located in the following places:
Predefined data warehouse variables
The following predefined data warehouse connection variables can be set:
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.connectionInputModeStandard} - The value can be "True" or
"False". "False" means that Advanced will be used.
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.serverName}
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.port}
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.authenticationMethodSQLServer} - The value can be "True"
or "False".
Relevant for Microsoft SQL Server only.
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.userName}
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.encryptedPassword}
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.odbcString}
Only relevant when the Advanced connection option is set.
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.jdbcString}
Only relevant when the Advanced connection option is set.
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.warehouse}
Relevant for Snowflake only.
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.database}
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.datawarehouseSchema}
l
$$${database.Data Warehouse.datamartSchema}
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
88

5 Data Warehouse projects
For an explanation of data warehouse settings, see
Setting up a data warehouse connection (page
110)
Predefined landing zone variables
The following predefined landing zone connection variables can be set:
As there can be several landing zones, the middle part of the variable name (landing1
below) is the landing zone name and should be replaced with the actual name of your
Landing Zone.
l
$$${database.landing1.contentType} - Values can be "Full Load Only", "ChangeProcessing",
or "Full Load and Change Processing"
l
$$${database.landing1.designatedBy} - The value can be "database" or "schema".
l
$$${database.landing1.database}
l
$$${database.landing1.schema}
l
$$${database.landing1.errorMartSchema}
l
$$${database.landing1.afterApplyingChanges} - Values can be "Delete" (the default) or
"Archive".
l
$$${database.landing1.archiveDatabase}
Only relevant if "Archive" is set.
l
$$${database.landing1.archiveSchema}
Only relevant if "Archive" is set.
l
$$${database.landing1.isAssociatedWithReplicateTask} - The value can be "True" or "False".
l
$$${database.landing1.replicateServer}
Only relevant if the Associate with Replicate task option is set.
l
$$${database.landing1.replicateTask}
Only relevant if the Associate with Replicate task option is set.
l
$$${database.landing1.source.isSourceDefined} - The value can be "True" or "False".
l
$$${database.landing1.source.connectionInputModeStandard} - The value can be "True" or
"False". "False" means that Advanced will be used.
l
$$${database.landing1.source.serverName}
l
$$${database.landing1.source.port}
l
$$${database.landing1.source.authenticationMethodSQLServer} - The value can be "True"
or "False".
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
89

5 Data Warehouse projects
Relevant for Microsoft SQL Server only.
l
$$${database.landing1.source.userName}
l
$$${database.landing1.source.encryptedPassword}
l
$$${database.landing1.source.odbcString}
Only relevant when the Advanced connection option is set.
l
$$${database.landing1.source.jdbcString}
Only relevant when the Advanced connection option is set.
l
$$${database.landing1.source.database}
l
$$${database.landing1.source.datawarehouseSchema}
For an explanation of landing zone settings, see
Defining landing zones (page 140)
.
Predefined data mart variables
The following predefined data mart connection variables can be set:
As there can be several data marts, the middle part of the variable name (datamart1
below) is the data mart name and should be replaced with the actual data mart name.
l
$$${datamart.datamart1.databaseDefault} - The value can be "True" or "False".
l
$$${datamart.datamart1.database}
l
$$${datamart.datamart1.tablesSchemaDefault} - The value can be "True" or "False".
l
$$${datamart.datamart1.tablesSchema}
l
$$${datamart.datamart1.viewsSchemaDefault} - The value can be "True" or "False".
l
$$${datamart.datamart1.viewsSchema}
For an explanation of data mart settings, see
Modifying data mart settings (page 260)
.
Predefined lookup variables
The following predefined lookup variables can be set:
As there are usually multiple mappings and columns, the middle part of the variable
name (mapping1.column1 below) are the mapping and column names and should be
replaced with the actual mapping and column name.
l
$$${mapping.mapping1.column1.lookup.schema}
For an explanation of lookup settings, see
Using lookup tables (page 210)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
90

5 Data Warehouse projects
Predefined mappings variables
The following predefined mapping variables can be set:
As there are usually multiple mappings, the middle part of the variable name (mapping1
below) is the mapping name and should be replaced with the actual mapping name.
l
$$${mapping.mapping1.schema}
For an explanation of mappings settings, see
Editing column mappings (page 205)
.
Compose environment_variables CLI guidelines
The procedures below describe how to manage environment variables using the Compose CLI.
When using the Compose CLI, make sure to adhere to the following guidelines:
l
Before running any environment_variables commands, run the Connect command to establish
a connection to the Compose Server. For more information on this command, see
Connecting to Qlik Compose server (page 77)
.
l
Variable names should be specified in the CLI without dollar signs or curly brackets. So, for
example, assuming the name of your landing database is MyLanding,
$$${database.MyLanding.database} should be specified as database.MyLanding.database.
l
When setting a variable with the Compose CLI, any variable names and values with spaces
(both user-defined and predefined) must be specified in quotation marks. This means, for
example, that all data warehouse variables must be specified with quotation marks as their
names always contain a space (for example, "database.Data Warehouse.serverName").
l
When setting a Boolean value, use --boolVal instead of --val. For example, to set
database.Data Warehouse.connectionInputModeStandard to "True", specify:
--var "database.Data Warehouse.connectionInputModeStandard" --boolVal true
Working with predefined variables only
When working with predefined environment variables only, the flow is as follows:
1. In the source environment:
a. Configure your project as desired.
b. Run the following command to write the predefined environment variables to a JSON
file (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project and
JsonFileLocation
with the full path of your JSON file):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command writePredefined --project
projectName
--jsonFile
JsonFileLocation
For security reasons, Compose never writes encrypted passwords to files.
1. a. Create a deployment package or export the project using the Compose CLI.
See also:
Project deployment (page 44)
and
Exporting a project (page 78)
.
2. In the target environment:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
91

5 Data Warehouse projects
a. Deploy the project if you created a deployment package or import the project if you
exported it using the Compose CLI.
See also:
Project deployment (page 44)
and
Importing a project (page 80)
.
b. Copy the JSON file created in the source environment to your preferred location.
c. Edit the JSONfile and replace the variable values with the values you want to
propagate to the target environment.
See also:
Working with environment variables (page 87)
.
d. Run the following command to propagate the JSON file variables to the Compose user
interface (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project and
JsonFileLocation
with the full path of your edited JSON file):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command setALL --project
projectName
--
jsonFile
JsonFileLocation
Example:
ComposeCli environment_variables --command setALL --project analytics --jsonFile
C:\compose\compose-variables.json
Running the setAll command will remove any existing environment
variables that are not included in the JSON file. Therefore, if you want to
make sure that such variables are not removed when setAll is run, add them
to the JSON file.
You can also set any variable by running the set command. This is
especially useful if you do not want the JSON file to include passwords. In
this case, you would need to run the following command (shown as an
example):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command set --project MyProject --
var encryptedPassword --val g56g56y563%
When you set a password with the CLI, Compose encrypts the password
first and then sets it.
e. Run the following command to apply the predefined environment variables and
complete the process (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command applyPredefined --project
projectName
Working with user-defined variables only
When working with user-defined environment variables only, the flow is as follows:
User-defined variables should have the following format in the Compose user interface:
$$${myVariable}
You can use user-defined variables in the following places:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
92

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Expressions - in model, mappings (column expressions, data quality and filters) or data mart
l
Lookup conditions and expressions
l
Custom ETLs
To set user-defined variables:
1. In the source environment:
a. In the Compose user interface, include your variable in an object that supports user-
defined variables (for example, a Custom ETL in a data warehouse task or an
expression), and save your settings.
Example: User-defined variable in a Custom ETL
UPDATE
"ROSIE"."DWH2"."TSTG_Employees"
SET
"Title" = $$${myVar}
WHERE "EmployeeID" < 150
b. For user-defined variables, use one of the following methods:
Method 1:
Set each variable individually by running the following command (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project,
varName
with the variable name,
and
value
with the variable value):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command set --project
projectName
--var
varName
--val
value
Example:
ComposeCli environment_variables --command set --project MyProject --var myVar --
val Manager
Method 2:
Add the user-defined variables directly to the JSON file as described in
Manually
editing the JSON file (page 96)
below.
c. Generate the task(s) with the user-defined variables.
d. If you set the user-defined variables with the CLI, run the following command to write
the user-defined variables to a JSON file (replacing
projectName
with the name of your
Compose project and
JsonFileLocation
with the full path of your JSON file):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command writeCLISet --project
projectName
--
jsonFile
JsonFileLocation
e. Create a deployment package or export the project using the Compose CLI.
See also:
Project deployment (page 44)
and
Exporting a project (page 78)
.
2. In the target environment:
a. Deploy the project if you created a deployment package or import the project if you
exported it using the Compose CLI.
See also:
Project deployment (page 44)
and
Importing a project (page 80)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
93

5 Data Warehouse projects
b. Copy the JSON file created in the source environment to your preferred location.
c. Edit the JSONfile and replace the variable values with the values you want to appear
in the target environment.
See also:
Working with environment variables (page 87)
.
d. Run the following command to propagate the JSON file variables to the Compose user
interface (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project and
JsonFileLocation
with the full path of your edited JSON file)::
ComposeCli environment_variables --command setALL --project
projectName
--
jsonFile
JsonFileLocation
Running the setAll command will remove any existing environment
variables that are not included in the JSON file. Therefore, if you want to
make sure that such variables are not removed when setAll is run, add them
to the JSON file.
e. Generate the relevant tasks as well.
Working with both user-defined and predefined variables
Each time Compose writes to the JSON file, it overwrites the existing content. Therefore,
when working with both user-defined and predefined variables, you need to specify the
path to two different JSON files. For convenience, you can then merge the two files into
a single JSON file while taking care to use the format described in Manually editing the
JSON file (page 96) below.
When working with both user-defined and predefined environment variables, the flow is as follows:
1. In the source environment:
a. Configure your project as desired.
b. Run the following command to write the predefined environment variables to a JSON
file (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project and
predefinedJsonFileLocation
with the full path of the JSON file that you want to contain
your predefined variables):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command writePredefined --project
projectName
--jsonFile
predefinedJsonFileLocation
For security reasons, Compose never writes encrypted passwords to files.
c. In the Compose user interface, add user-defined variables to supported objects (for
example, a Custom ETL in a data warehouse task), and save your settings.
Example: User-defined variable in a Custom ETL
UPDATE
"ROSIE"."DWH2"."TSTG_Employees"
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
94

5 Data Warehouse projects
SET
"Title" = $$${myVar}
WHERE "EmployeeID" < 150
d. For user-defined variables, use one of the following methods:
Method 1:
Set each variable individually by running the following command (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project,
varName
with the variable name,
and
value
with the variable value):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command set --project
projectName
--var
varName
--val
value
Example:
ComposeCli environment_variables --command set --project MyProject --var myVar --
val Manager
Method 2:
Add the user-defined variables directly to the JSON file as described in
Manually
editing the JSON file (page 96)
below.
e. Generate the task with the user-defined variable(s).
f. If you set the user-defined variables with the CLI, run the following command to write
the user-defined variables to a JSON file (replacing
projectName
with the name of your
Compose project and
JsonFileLocation
with the full path of the JSON file that you want
to contain your user-defined variables):):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command writeCLISet --project
projectName
--
jsonFile
userDefinedJsonFileLocation
g. Create a deployment package or export the project using the Compose CLI.
See also:
Project deployment (page 44)
and
Exporting a project (page 78)
.
2. In the target environment:
a. Deploy the project if you created a deployment package or import the project if you
exported it using the Compose CLI.
See also:
Project deployment (page 44)
and
Importing a project (page 80)
.
b. Copy the JSON file created in the source environment to your preferred location.
c. Edit the JSONfile and replace the variable values with the values you want to appear
in the target environment.
See also:
Working with environment variables (page 87)
.
d. Run the following command to propagate the JSON file variables to the Compose user
interface (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project and
JsonFileLocation
with the full path of your edited JSON file)::
ComposeCli environment_variables --command setALL --project
projectName
--
jsonFile
JsonFileLocation
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
95

5 Data Warehouse projects
Running the setAll command will remove any existing environment
variables that are not included in the JSON file. Therefore, if you want to
make sure that such variables are not removed when setAll is run, add them
to the JSON file.
e. Generate all tasks with user-defined variables.
f. Run the following command to apply the predefined environment variables and
complete the process (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command applyPredefined --project
projectName
Removing environment variables
Run the "Remove" command if you set a variable that you no longer want to use in the target
environment.
Removing a predefined variable will reset it to its previous value. To prevent errors, make
sure when you remove user-defined variables, to also edit or remove the custom ETL or
expression where the variable is located.
1. Run the following command:
ComposeCli environment_variables --command remove --var
VarName
--project
projectName
Example:
ComposeCli environment_variables --command remove --var MyVariable --project MyProject
2. Generate any task(s) configured with user-defined variables.
Manually editing the JSON file
Before you propagate the JSON file variables to the Compose user interface in the target
environment, you need to edit the file and replace the source variable values with the target
variable values. It might also be more convenient to create, edit and maintain the JSON file manually
instead of (or in addition to) using the writeCLISet and writePredefined commands described above.
The JSON file is split into two sections: “predefinedVariables” and “userDefinedVariables”. When
you edit the JSON file, make sure to put predefined variables in the “predefinedVariables” section
and user-defined variables in the “userDefinedVariables” section. In addition, make sure to use
standard JSON escaping conventions, as shown in the following example:
{
“predefined”: {
"databases.Data Warehouse.serverName": "myhostname"
},
“userDefined”: {
"variable": "value",
"var2": "val2"
}
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
96

5 Data Warehouse projects
Editing and saving the JSON file does not automatically set and apply the variables. To
do this, run the 'SetAll' and 'ApplyPredefined' commands. If the JSON file also contains
user-defined variables, you will need to generate the associated tasks as well. See
below for details.
Propagating the JSON file variables to the Compose user interface
After you have prepared your JSON file and copied it to your preferred location, perform the
following procedure to propagate the variables to the Compose user interface:
1. Run the following command to propagate the JSON file variables to the Compose user
interface (replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project and
JsonFileLocation
with the full path of your edited JSON file):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command setALL --project
projectName
--jsonFile
JsonFileLocation
Example:
ComposeCli environment_variables --command setALL --project MyProject --jsonFile
C:\composeVariables\myVariables.json
Running the setAll command will remove any existing user-defined environment
variables from the user-interface, and reset any modified predefined environment
variables that are not included in the JSON file to their previous values.
2. If the JSON file contains predefined environment variables, run the following command
(replacing
projectName
with the name of your Compose project):
ComposeCli environment_variables --command applyPredefined --project projectName
3. If the JSON file contains user-defined environment variables, generate the associated task
(s).
Generating projects using the CLI
The instruction below explain how to automatically generate projects using the CLI. This can be
especially useful when deploying projects between different environments.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe generate_project --project
project_name
[--database_already_adjusted] [--
stopIfDatamartsNeedRecreation]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--database_already_adjusted This should only be included if the data warehouse and
data marts were adjusted outside of Compose.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
97

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--stopIfDatamartsNeedRecreation Stops the process if any data marts cannot be
automatically adjusted and need to be recreated.
Example
ComposeCli.exe generate_project --project MyProject --stopIfDatamartsNeedRecreation
When the command is run, Compose will:
l
Validate the model.
l
Create any data warehouse tables that do not exist.
l
Validate the data warehouse.
l
Adjust the data warehouse if needed.
If an Adjust script is needed and --database_already_adjusted is included in the
command, the script (DDL) will not be run as it is assumed that the user ran it
manually.
l
Generate all data warehouse tasks.
If Compose encounters an error while generating a data warehouse task, it will
skip the problematic task and continue with the remaining tasks.
l
Create, adjust and generate all data marts.
If the "Adjust" cannot be performed automatically and --
stopIfDatamartsNeedRecreation is included in the command, the process will stop.
Certain limitations apply when adjusting the data mart. For more information, see
Auto-adjust
limitations and considerations (page 258)
.
Exporting project documentation
Relevant to Data Warehouse projects only.
You can export a project to a zip file for record keeping and sharing offline. The project is exported
as HTML files which can be easily printed to PDF using the print toolbar button in the HTML page.
To export the project documentation:
1. Open the project as described in
Managing and monitoring projects (page 290)
.
2. Click the downward arrow to the right of the project name and select Generate Project
Documentation from the drop-down menu.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
98

5 Data Warehouse projects
A zip file with the name of the project and a timestamp of when the documentation was
generated will be created (e.g.
MyComposeProject_documentation_03_22_2016__15_01_
10.zip
). Depending on your browser settings, the file will either be automatically downloaded
to your browser’s Downloads folder or you will be prompted to save it.
3. To view the documentation, extract the contents of the zip file and then open the index.html
file.
A browser tab will open displaying the documentation categories in the left pane.
4. Navigate through the documentation using the tree in the left pane and the breadcrumbs
above the documentation.
Viewing and downloading DDL scripts
In the DDL Script Files window, you can view and download the data warehouse DDL script files.
By default, Compose executes the Create, Adjust and Drop statements immediately upon user
request. However, when the Generate DDL scripts but do not run them option is enabled,
Compose will only generate the scripts but not execute them.
DDL scripts must be run from the data warehouse database and schema or data
warehouse database and data mart schema, depending on the DDL script and the
platform type (for example, in Oracle there are no schemas just the database).
For more information on the Create DDL scripts only option, see
Project settings (page 37)
.
To open the DDL Script Files window:
1. Open your project as described in
Managing and monitoring projects (page 290)
.
2. Click the downward arrow to the right of the project name and select Show DDL Scripts
from the drop-down menu.
The DDL Script Files window opens.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
99

5 Data Warehouse projects
3. To view a script, select the desired script in the Script Files pane on the left. The script will
be displayed on the right.
4. To download a script, select the desired script in the Script Files pane on the left. Then click
the download button in the top right of the window.
5. To search for an element in the script, start to type in the search box. All strings that match
the search query will be highlighted blue.
You can navigate between search query matches using the arrows to the right of the search
box. Use the right and left single arrows to navigate matches sequentially. Use the right and
left double arrows to jump to the last and first match respectively.
6. To reset the search, either delete the search query or click the "x" to the right of the search
box.
Project versioning
Compose provides built-in project version control using the Git engine. Version control enables
Compose developers to commit project revisions to both a local and a remote Git repository. If a
mistake is made, Compose developers can easily roll back to earlier versions of the project while
minimizing disruption to all team members.
Revisions only store metadata and mapping information. After you revert to a saved
revision, you will need to recreate the data warehouse and data mart tables.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
100

5 Data Warehouse projects
Configuring version control settings
To define Version Control Settings:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Version Control > Settings.
The Version Control Settings - Git window opens.
The Local Commits area shows the local root folder where project revisions are committed.
The first time a project revision is committed, Compose creates a JSON file with the current
project settings. The <project_name>.json file is archived to a ZIP file (<project_name>_
deployment.zip), which is located in a project-specific folder under the source-control folder.
2. To enable commits to a remote Git database, select Enable remote commits and then
provide the following information:
l
URL - The address of the remote Git database.
l
User name - Your user name for accessing the remote Git database.
l
Password - Your password for accessing the remote Git database.
Committing projects
You can commit a project using the console or using the CLI:
To commit a project to Version Control using the web console:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Version Control > Commit.
The Commit - <Project_Name> window opens.
2. Enter a message in the Message box and optionally select the Remote push check box.
Note that the Remote push check box will be disabled if the Enable remote commits option
described above is not selected.
To commit a project to Version Control using the CLI:
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe commit --project
project_name
[--message
message
] [--remote]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--message An optional message to accompany the commit.
--remote This parameter is required if you want to commit the project to a
remote Git repository (see above). By default, the project will be
committed locally to
<product_dir>\data\source-control
.
Example
ComposeCli.exe commit --project MyProject --remote
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
101

5 Data Warehouse projects
To revert to a saved revision:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Version Control > Revisions history.
The Revision History - <Project_Name> window opens.
By default, the last 10 revisions are shown. You can change this number by selecting one of
the available options from the Show drop-down list.
2. Optionally, use the Search box to find a specific revision.
3. Select the desired revision and then click the Deploy to Revision toolbar button.
4. When prompted to confirm the operation, click Yes.
The existing project will be replaced.
5. Click Close to close the Revision History - <Project_Name> window.
To download a saved revision:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Version Control > Revisions history.
The Revision History - <Project_Name> window opens.
By default, the last 10 revisions are shown. You can change this number by selecting one of
the available options from the Show drop-down list.
2. Optionally, use the Search box to find a specific revision.
3. Select the desired revision and then click the Download Revision as Package toolbar
button.
The package will be saved as a ZIP file in your browser's default download location.
Creating a diagnostics package
To assist in troubleshooting esoteric issues, a Qlik Support Engineer may ask you for a diagnostics
package. The diagnostics package contains the following information:
l
The project "data" directory
l
Java logs and workflow logs
l
.NET logs
l
Deployment package file
As a prerequisite to creating a diagnostics package, the project must have at least one
database connection configured.
To create a diagnostics package:
1. From the Project menu, select Create Diagnostics Package.
2. A zip file in the following format will either be downloaded to your computer or you will be
prompted to download it (according to your browser settings):
Compose_Diagnostics_<project_name>_<timestamp>.zip
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
102

5 Data Warehouse projects
5.3 Getting started with Data Warehouse projects
This section provides an overview of the Qlik Compose architecture, familiarizes you with its
interface and ends with a short tutorial.
In this section:
l
High-level flow (page 103)
l
Console elements (page 103)
l
Data warehouse project tutorial (page 106)
High-level flow
Setting up data warehouse project typically consists of the following stages (simplified):
1. In Qlik Replicate, define a task that replicates the source tables to a landing zone in the data
warehouse.
2. In Compose:
a. Configure access to your data warehouse.
b. Configure access to your data sources.
c. Use the "Discover" option to auto-generate a model from the source tables or import
an existing model that was created in ERwin. You can even create the model manually
if you prefer.
d. Once your model is ready, create the data warehouse tables and populate them with
the source data.
e. Create a data mart from the data warehouse tables.
f. Populate the data mart tables.
See also
Introduction (page 13)
.
Console elements
This section will familiarize you with the elements that comprise the Qlik Compose UI.
To open Qlik Compose, from the Windows Start menu, select All Programs > Qlik Compose > Qlik
Compose Console.
Management view
The Qlik Compose Console opens in Management view.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
103

5 Data Warehouse projects
In Management view, you can perform the following tasks:
l
Create, edit, and delete projects
For more information, see
Adding and managing data warehouse projects (page 35)
.
l
Access Qlik Compose management options, including:
l
Register and view the product license
l
Manage log levels and cleanup options
l
Manage email settings
For more information, see
Managing Compose (page 378)
.
Designer view
When you add a new project or open an existing project, the console switches to Designer view. If
you are in Monitor view (see below), you can switch back to Designer view by clicking the Designer
tab in the top right of the console.
Designer view comprises the following panels:
l
Databases - Configure access to your source database(s) and data warehouse.
For more information, see
Setting up Landing Zone and Data Source connections (page 131)
and
Setting up a data warehouse connection (page 110)
respectively.
l
Model - Create and edit your model.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
104

5 Data Warehouse projects
For more information, see
Creating and managing the model (page 154)
.
l
Data Warehouse - Create the data warehouse tables, generate the task statements, and run
data warehouse tasks.
For more information, see
Creating and managing the data warehouse (page 192)
.
l
Data Mart - Define data marts, create the data mart tables, generate the task statements,
and run data mart tasks.
For more information, see
Creating and managing data marts (page 228)
.
In Designer view, each of the panels has a bar below the panel name. The bar can be empty, half-
filled or completely filled, according to the current configuration status of the panel properties, as
follows:
l
No fill (gray) - Not configured
l
Half filled - Configuration is not complete
l
Completely filled - Fully configured
Monitor view
To switch to Monitor view, click the Monitor tab in the top right of the console.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
105

5 Data Warehouse projects
In Monitor view, you can view the status of data warehouse and data mart tasks and schedule their
execution, either individually or as a workflow.
For more information, see
Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows (page 265)
.
Data warehouse project tutorial
This short tutorial will walk you through each of the stages required to create a data warehouse
project. For simplicity’s sake, we will be using Microsoft SQL Server as both the source database
server and the target Data Warehouse. You can of course use any of the supported source or target
databases, but instructions for doing so are outside the scope of this tutorial.
What you need:
l
Qlik Compose installed according to the instructions in
Qlik Compose installation and setup
(page 16)
.
l
The Northwind.MDF sample database attached to Microsoft SQL Server.
An easy-to-follow set of instructions for downloading and installing Northwind.MDF can be
found at the following website:
http://businessimpactinc.com/install-northwind-database/
l
Define an empty database on Microsoft SQL Server (e.g. northwind_dwh) and make a note of
its name. This will serve as the target Data Warehouse for the Northwind.MDF source tables.
l
Microsoft SQL Server Native Client 11.0 installed on the Compose machine.
To set up a Compose project:
1. Define and run a replication task in Qlik Replicate as described in
Defining a Qlik Replicate
task (page 33)
.
2. Open Qlik Compose.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
106

5 Data Warehouse projects
3. Add a data warehouse project as described in steps 1-3 of
Adding data warehouse projects
(page 35)
.
4. In the Databases panel, perform the following steps to define your data warehouse:
a. Click Manage. The Manage Databases window opens.
b. Click the Add New Database link or the New toolbar button. The New Data
Warehouse window opens.
c. In the New Data Warehouse window:
l
In the Name field, specify a display name for your data warehouse.
l
From the Type drop-down list, select Microsoft SQL Server.
l
In the Server Name field, specify the Microsoft SQL Server name using the
following format:
l
To connect to a named Microsoft SQL Server instance: computer_name\db_
server_name
l
To connect to the default Microsoft SQL Server instance: computer_name
l
In the User Name and Password fields, enter your credentials for logging in to
the server specified in the Server Name field.
l
In the Database Name field, specify the name of the database specified in the
target endpoint of the Qlik Replicate task.
l
In the Data Warehouse Schema field, specify dbo or your preferred schema.
l
In the Data Mart Schema field, specify dbo or your preferred schema.
You can specify different schemas for the data warehouse and data
mart tables, but for the purpose of this quick start, we’ll use the same
schema.
l
Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection
to the specified database and then click OK to save your settings.
d. Click New. The New Data Source window opens.
e. In the New Data Source window:
l
In the Name field, specify a display name for your data source.
l
From the Content Type drop-down list, choose Full Load and Change
Processing.
l
From the Designate By drop-down list, choose Schema.
l
In the Schema name field, enter the schema name that you specified in the
Target Metadata tab of the Replicate task. For more information, see
Defining a
Qlik Replicate task (page 33)
.
l
In the Error mart schema name field, specify the schema where you want the
data mart exception tables to be created. Data that is rejected by data quality
rules will be copied to tables in the specified schema.
l
Select the Source database connection check box and then provide the
details for connecting to the source database. For the purpose of this tutorial,
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
107

5 Data Warehouse projects
except for the Schema, these should be the same as the data warehouse
connection details.
l
Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection
to the specified database and then click OK to save your settings.
l
Click OK to save your settings.
5. In the Model panel, perform the following steps to create the model for data warehouse
generation:
a. From the drop-down menu in the top right corner of the Model panel, select Discover.
The Discover window opens.
b. Select the source database (i.e. the database without the "_landing" suffix). This is the
source endpoint in the Qlik Replicate task. The Source Table/View Selection -
<
Data_Source_Name
>_Landing window opens.
c. In the Source Table/View Selection window:
l
Select the Tables option.
l
Click the Search button.
l
From the Results list, select which tables to discover and then click OK. The
Generating Model from <db_name> window opens.
d. Wait for the model generation to complete and then click Close.
6. In the Data Warehouse panel, perform the following steps to populate the Data Warehouse
with the source data:
a. Click Create. The Creating Data Warehouse window opens. Wait for the Data
Warehouse to be created and then click Close.
b. Click Manage. The Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window opens.
c. Click Generate. The Generating Statements for Task: <Name> window opens. Wait
for the ETL instruction set to be generated and then click Close.
d. Click Run. The Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window switches to Monitor view and
Qlik Compose starts to populate the Data Warehouse with data (this may take a few
seconds).
e. Wait for the Data Warehouse to be populated and then close the Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window.
7. In the Data Mart panel, perform the following steps to create a data mart with a star schema:
a. Click New. The New Data Mart window opens. Leave the default name.
b. Make sure the Start New Star Schema Wizard check box is selected, and click
OK.The New Star Schema wizard opens. Leave the default name.
c. Select Transactional as the star schema type and then click Next.
d. In the Facts screen, select Order Details. Then click Next.
e. In the Dimensions screen, clear all the check boxes and then select Customers and
Products only, as shown below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
108

5 Data Warehouse projects
f. Then click Next.
g. In the Transaction Date screen, select OrderDate and then click Finish. The star
schema is displayed on the right of the Manage Data Marts window.
h. Click Create Tables. The Creating Data Mart: <Data Mart Name> window opens.
Wait for the Data Mart tables to be created and then close the window.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
109

5 Data Warehouse projects
i. Click Generate. The Generating Statements for Data Mart: <Data Mart Name>
window opens. Wait for the generation of the task statements to complete and then
close the window.
j. Click Run.
The Manage Data Marts window switches to Monitor view and Qlik Compose
populates the Data Mart with data. Leave the Manage Data Marts window open in
Monitor view for now (The two buttons at the top right of the window allow you to
switch between Designer and Monitor views).
8. To display the data in a pivot table:
a. Click the Pivot toolbar button. The Select Columns for Pivot Table window opens.
b. From the drop-down list at the top of the window, select the Pivot Table columns as
follows:
l
In the 1Fct_Order Details table, select Quantity.
l
In the 1Dim_Customers table, select Country.
l
In the 1Dim_Products table, select ProductName.
c. Click OK. A Pivot Table is created with your selected columns.
d. Drag the Quantity box to the space above the table and the ProductName box to the
space on the left.
e. Select Heatmap from the drop-down list below the Customize Columns button.
Your pivot table should now look like this:
5.4 Setting up a data warehouse connection
This section explains how to set up data warehouse connectivity in a Qlik Compose project.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
110

5 Data Warehouse projects
The data warehouse contains the landing zone tables (the target of the Qlik Replicate task), the
logical entities, the actual data warehouse tables and the data mart tables.
For more information on the data warehouse structure in an project Qlik Compose project, see
Introduction (page 13)
.
Note that Qlik Compose will not let you add data sources before you add a data warehouse. This is
because the server connection settings for the source landing zone are derived from the data
warehouse settings.
For all supported data warehouse types, each data warehouse schema (or database if
there are no schemas) should be used exclusively for a single data warehouse. In other
words, using the same schema for different projects, data warehouses and landing
zones is not allowed. Data mart schemas, however, can be shared by different data
marts.
For more information on adding data sources, see
Setting up Landing Zone and Data Source
connections (page 131)
.
For instructions on adding a data warehouse, see the following according to your data warehouse
type.
l
Using Microsoft SQL Server as a data warehouse (page 111)
l
Using Oracle as a data warehouse (page 114)
l
Using Amazon Redshift as a data warehouse (page 121)
l
Using Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a data warehouse (page 124)
l
Using Snowflake as a data warehouse (page 117)
l
Using Google Cloud BigQuery as a Data Warehouse (page 128)
Using Microsoft SQL Server as a data warehouse
Although the procedures in this section specifically refer to Microsoft SQL Server, they
are equally applicable to Microsoft Azure SQL Managed Instance and Microsoft Azure
SQL Database.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 111)
l
Working with Windows authentication (page 150)
l
Microsoft SQL Server data types (page 112)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 113)
Prerequisites
Before you can use Microsoft SQL Server as a data warehouse in a Qlik Compose project, make
sure that the following prerequisites have been met:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
111

5 Data Warehouse projects
Client
Microsoft SQL Server Native Client must be installed on the Qlik Compose machine.
Permissions
To use Microsoft SQL Server as a Data Warehouse a Qlik Compose project, the Compose user must
be granted the following privileges in the Microsoft SQL Server database:
l
The Qlik Compose user must have at least the db_owner user role on the Microsoft SQL Server
database.
l
The Qlik Compose user must be granted the CREATE VIEW permission on the Microsoft SQL
Server database.
l
A Microsoft SQL Server system administrator must provide this permission for all Qlik
Compose users.
Working with Windows authentication
You can configure the Qlik Compose Microsoft SQL Server source to log in to Microsoft SQL Server
using Windows authentication. If you choose this option, you also need to make sure that:
l
The Microsoft SQL Server instance is set up to allow Windows log on.
l
The Compose user is specified as the "Log on as" user for the Qlik Compose Server service
account.
OR
Microsoft SQL Server is configured to allow login for the Qlik Compose Server service
account.
Microsoft SQL Server data types
The following table shows the Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse data types that are supported
when using Qlik Compose and the default mapping from Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped from the source, see the section for
the source database you are using.
Qlik Compose data types Microsoft SQL Server data types
Bigint BIGINT
Decimal NUMERIC (p,s)
Integer INT
Date DATETIME2
Datetime DATETIME2
GUID UNIQUEIDENTIFIER
IntAutoInc INT IDENTITY
Byte VARBINARY (Length)
Data type mappings
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
112

5 Data Warehouse projects
Defining the connection parameters
This section describes how to use a Microsoft SQL Server database as a data warehouse in a Qlik
Compose project. You can also use the Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse settings to specify
connection details to a Microsoft Azure SQL Database.
When using Microsoft Azure SQL Database as the data warehouse, the data warehouse
must be located on the same database as the landing zone, although it should use a
different schema.
To define Microsoft SQL Server as a data warehouse:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the bottom left of the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button or click the Add new database link in the middle of the
window.
The New Data Warehouse dialog box opens.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select the desired data warehouse.
4. Enter the information as described below.
l
Connection input mode: Select Standard or Advanced.
If you selected Standard connection input mode, specify the following:
l
Server Name: The name or IP address of the Microsoft SQL Server server
machine.
l
Port: Optionally, change the default port.
When connecting to a named instance using the instance name, either change
the port to 0 to use the SQL Server Browser service to redirect.
l
Windows authentication / SQL Server authentication: Choose how you want
Compose to log in to the Microsoft SQL Server database. If you choose
Windows authentication, see Working with Windows Authentication below.
l
User Name: The user name for accessing the Microsoft SQL Server database.
The specified user must have read/write privileges on the Microsoft SQL Server
database.
l
Password: The password for accessing the Microsoft SQL Server database.
If you selected Advanced connection input mode, specify the following:
l
Password: The password for accessing the Microsoft SQL Server database.
l
ODBCConnection String: The string of parameters required to connect to the
Microsoft SQL Server ODBCDriver.
l
JDBCConnection String: The string of parameters required to connect to the
Microsoft SQL Server JDBCDriver.
Compose will concatenate the database name to the ODBC/JDBC
connection string.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
113

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Warehouse Properties: Specify the following:
l
Database Name: The name of the Microsoft SQL Server database.
l
Data Warehouse Schema: The schema in which to create the data warehouse
tables.
l
Data Mart Schema: The schema in which to create the data mart.
5. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified data warehouse.
6. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Working with Windows authentication
You can configure Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses to log in to Microsoft SQL Server using
Windows authentication.
If you choose this option, you also need to make sure that:
l
The Microsoft SQL Server instance is set up to allow Windows log on.
l
The Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses user is specified as the "Log on as" user for the Qlik
Compose for Data Warehouses service account.
-OR-
l
Microsoft SQL Server is configured to allow login for the Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses
service account.
Using Oracle as a data warehouse
This section describes how to set up Oracle as a data warehouse in a Compose project.
When loading a huge number of records (i.e. hundreds of millions), the
UNDO/REDO/TEMP tablespace on the Oracle database must be large enough to hold the
data being loaded.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 114)
l
Oracle data types (page 116)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 116)
Prerequisites
Before you can use Oracle as a data warehouse in a Qlik Compose project, make sure that the
following prerequisites have been met:
Client
Before you can use Oracle as a source in a Qlik Compose project, make sure that the following client
prerequisites have been met:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
114

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
The Oracle database should be configured with the required permissions (see below) and
accessible from the Compose machine.
l
Install Oracle Data Access Components (x64) on the computer where Qlik Compose is
located. Then, add the full path of the Oracle Data Access DLL to the system environment
variables.
The default path should be:
<ORACLE_PRODUCT_CLIENT_DIR>\ODP.NET\bin\4\
l
The path to the Oracle Data Access DLL also needs to be specified in both
the machine.conf file and the Global Assembly Cache (GAC). In addition,
make sure that the Oracle.DataAccess.dll file exists in the following
location: C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_64.
For more information, see
Oracle Help Center
.
l
The Qlik Compose service needs to be restarted after installing the
required components.
l
Install Oracle Instant Client for Microsoft Windows (x64) 19.0 or later on the computer where
Qlik Compose is located.
l
If you want to use an Oracle TNS name in the connection settings, you first need to set the
ORACLE_HOME environment variable.
Example:
<ORACLE_PRODUCT_CLIENT_DIR>\product\<version>\client_1
Permissions
To use Oracle as a Data Warehouse a Qlik Compose project, the Compose user must be granted the
following privileges in the Oracle database:
l
grant create session
l
grant create table
l
grant create view
l
grant connect
l
grant resource
l
grant create sequence
l
grant create any directory
l
grant SELECT on SYS.DBA_REGISTRY
l
grant select any table
l
grant delete any table
l
grant drop any table
l
grant unlimited tablespace
l
grant create any table
l
grant insert any table
l
grant update any table
l
grant drop any table
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
115

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
grant alter any table
l
grant create any view
l
grant drop any view
l
grant create any index
Oracle data types
The Oracle database for Qlik Compose supports most Oracle data types. The following table shows
the Oracle data warehouse data types that are supported when using Qlik Compose and the default
mapping from Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped from the source, see the section for
the source database you are using.
Qlik Compose data types Oracle data types
Bigint DECIMAL (19,0)
Date DATE
Datetime DATE
Decimal DECIMAL (p,s)
Integer DECIMAL (10,0)
GUID VARCHAR (38)
IntAutoInc DECIMAL (10,0)
Byte raw (${LENGTH})
Data type mappings
Defining the connection parameters
This section describes how to use an Oracle database as a data warehouse in a Qlik Compose
project.
To define Oracle as a data warehouse:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the bottom left of the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button or click the Add new database link in the middle of the
window.
The New Data Warehouse dialog box opens.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select the desired data warehouse.
4. Enter the information as described below.
l
Connection input mode: Select Standard or Advanced.
If you selected Standard connection input mode, specify the following:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
116

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Server Name: The name or IP address of the Oracle server machine.
l
Port: If you specified a TNS name in the Server Name field, make sure this field
is empty. Optionally, change the default port.
l
User Name: The user name for accessing the Oracle database. The specified
user must have read/write privileges on the Oracle database.
l
Password: The password for accessing the Oracle database.
l
SID: If you specified a TNS name in the Server Name field, make sure this field
is empty. Optionally, specify the Oracle SID.
If you selected Advanced connection input mode, specify the following:
l
Password: The password for accessing the Oracle database.
l
ODBCConnection String: The string of parameters required to connect to the
Oracle ODBCDriver.
l
JDBCConnection String: The string of parameters required to connect to the
Oracle JDBCDriver.
Compose will concatenate the database name to the ODBC/JDBC
connection string.
l
Warehouse Properties: Specify the following:
l
Data Warehouse Schema: The schema in which to create the data warehouse
tables.
l
Data Mart Schema: The schema in which to create the data mart.
l
Maximum length of identifier names is 128: Select this check box to limit the
length of Oracle dimension table identifier names to 128 characters. This should
match your Oracle configuration. This option is available for Oracle versions
starting from 12.2.
5. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified data warehouse.
6. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Using Snowflake as a data warehouse
This section describes how to set up Snowflake as a data warehouse in a Compose project.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 117)
l
Limitations (page 118)
l
Snowflake data types (page 119)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 119)
Prerequisites
Before you can use Snowflake as a data warehouse in a Qlik Compose project, make sure that the
following prerequisites have been met:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
117

5 Data Warehouse projects
Client
l
Download and install Snowflake ODBC driver for Windows 2.18.1 or later.
l
The Qlik Compose machine must be set to the correct time (UTC).
Permissions
The user specified in the Snowflake data warehouse settings must be associated with a role that
grants the following privileges:
l
USAGE on the Snowflake warehouse
l
USAGE or OWNERSHIP on the specified database and its schemas
l
SELECT on the INFORMATION_SCHEMA schemas
l
CREATE SCHEMA on the specified database.
Only required for user-specified schemas that do not yet exist on the target.
l
Tables:
l
CREATE
l
SELECT
l
INSERT
l
UPDATE
l
DELETE
l
TRUNCATE
l
REFERENCES (for current and future tables)
l
DROP (for user-initiated Drop and Create operations)
l
Views:
l
SELECT
l
CREATE (for current and future views)
l
DROP (for user-initiated Drop and Create operations)
l
External functions called by user-defined ETLs:
l
USAGE
Limitations
The following limitations apply when using Snowflake as a data warehouse in a Compose project.
l
Variant, object and array columns are not supported when creating the model using the
discovery method. Compose will ignore such columns during discovery and issue a warning.
l
When discovering the landing zone, Snowflake converts
all
numeric data types to NUMBER
(38,0) and is therefore not recommended. For example, discovering a table with INTEGER i
and DOUBLE d columns in the landing zone would return NUMBER (38,0) for both, whereas
discovering these columns in the source would return more accurate data types.
l
When ingesting data from a Replicate source that may have BIT fields (such as Microsoft SQL
Server), it is recommended to define a global data type transformation in Replicate to
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
118

5 Data Warehouse projects
convert BIT to STRING (1). Otherwise, Compose will convert BIT to VARCHAR (1) (as it does
not support BOOLEAN), which may cause a data type mismatch in the landing zone.
Snowflake data types
The following table shows the Snowflake data warehouse data types that are supported when
using Qlik Compose and the default mapping from Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped from the source, see the section for
the source database you are using.
Qlik Compose data types Snowflake data types
BIGINT INTEGER
INTEGER INTEGER
DECIMAL If column size >38, then:
DOUBLE
If column size <38, then:
DECIMAL (size, scale)
DATE DATE
TIME TIME
DATETIME TIMESTAMP (scale 1-9)
GUID VARCHAR (38)
BIGINTAUTOINC BIGINT IDENTITY
BYTE BINARY
Data type mappings
Defining the connection parameters
This section describes how to add Snowflake as a data warehouse in a Qlik Compose project.
To add Snowflake as a data warehouse:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the bottom left of the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button or click the Add new database link in the middle of the
window.
The New Data Warehouse dialog box opens.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select the desired data warehouse.
4. Enter the information as described below.
l
Connection input mode: Select Standard or Advanced.
If you selected Standard connection input mode, specify the following:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
119

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Server Name: The URL for accessing Snowflake on AWS or Snowflake on
Microsoft Azure.
l
Port: The port through which Snowflake will be accessed (default 443).
l
Authentication method: Choose Username and password or Key pair.
l
Private key: If you selected Key pair authentication, paste the private key file
content into this field.
l
User Name: The user name for accessing the Snowflake database. The
specified user must have read/write privileges on the Snowflake database.
l
Private key password: If you selected Key pair authentication and the private
key file content is encrypted, specify the private key file password in this field.
l
Password: If you selected Username and password authentication, specify
the password for accessing the Snowflake database.
If you selected Advanced connection input mode, specify the following:
l
Authentication method: Choose Username and password or Key pair.
l
Password: If you selected Username and password authentication, enter the
password for accessing the Snowflake database.
l
Private key: If you selected Key pair authentication, paste the private key file
content into this field.
l
User name: If you selected Key pair authentication, specify the user name for
accessing the Snowflake database. The specified user must have read/write
privileges on the Snowflake database.
l
Private key password: If you selected Key pair authentication and the private
key file content is encrypted, specify the private key file password in this field.
l
ODBCConnection String: The string of parameters required to connect to the
Snowflake ODBCDriver.
l
JDBCConnection String: The string of parameters required to connect to the
Snowflake JDBCDriver.
Compose will concatenate the warehouse name to the ODBC/JDBC
connection string.
You can connect to Snowflake with ODBC, using a proxy server and
entering the appropriate ODBC environment parameters. For details,
see
ODBC Configuration and Connection Parameters - Snowflake
Documentation
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
120

5 Data Warehouse projects
You can connect to Snowflake with JDBC, using a proxy server and
entering the appropriate JDBCconnection string:
jdbc:snowflake://<Snowflake server URL>:443/?&user=<snowflake
user name>&warehouse=<Snowflake Warehouse
name>&useProxy=true&proxyHost=<Proxy server
name>&proxyPort=<Proxy server listening port>&proxyUser=<proxy
server user name>&proxyPassword=<proxy server user's password>
l
Warehouse Properties: Specify the following:
l
Warehouse Name: The name of your Snowflake warehouse.
"Warehouse" refers to the Snowflake warehouse and should not be
confused with the data warehouse created by Compose.
l
Database Name: The database in which to create the data warehouse tables.
l
Data Warehouse Schema: The schema in which to create the data warehouse
tables.
l
Data Mart Schema: The schema in which to create the data mart.
5. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified data warehouse.
6. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Using Amazon Redshift as a data warehouse
This section describes how to set up Amazon Redshift as a data warehouse in a Compose project.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 121)
l
Amazon Redshift data types (page 122)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 123)
Prerequisites
Before you can use Amazon Redshift as a data warehouse in a Qlik Compose project, make sure
that the following prerequisites have been met:
Driver
l
Install and configure the latest Amazon Redshift 64-bit ODBC Driver.
l
Install the Amazon Redshift JDBC Driver on the Compose machine. Amazon are working to
resolve a known issue with their latest driver. Until the issue is resolved, JDBC driver 4.1
needs to be used instead.
1. Download the JARfile from:
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.amazon.redshift/redshift-jdbc41/1.2.10.1009
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
121

5 Data Warehouse projects
2. Copy it to:
<Compose_Installation_Folder>\java\jdbc
The Qlik Compose service needs to be restarted after copying the driver.
Amazon Redshift Cluster
If you haven't already done so, set up an Amazon Redshift cluster and make sure that following
information about your Amazon Redshift Cluster is readily available:
l
Amazon Redshift Cluster Name
l
Amazon Redshift Cluster Port
l
Amazon Redshift User Name and Password
l
Amazon Redshift Database Name
Permissions
Qlik Replicate performs the following operations on the replicated tables within Amazon Redshift:
l
SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE
l
Bulk Load
l
CREATE, ALTER, DROP
l
CREATE VIEW
If the user is the 'DB Owner', these permissions are in place by default. Otherwise, the user must be
granted these permissions to achieve successful replication.
Port
Make sure that port 5439 (the Amazon Redshift Cluster port) is open for inbound connections from
Qlik Compose .
Amazon Redshift data types
The following table shows the Amazon Redshift data warehouse data types that are supported
when using Qlik Compose and the default mapping from Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped from the source, see the section for
the source database you are using.
Qlik Compose data types Amazon Redshift data types
INTEGER INT4
BIGINT INT8
DECIMAL NUMERIC (p,s)
DATE DATE
Data type mappings
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
122

5 Data Warehouse projects
Qlik Compose data types Amazon Redshift data types
GUID VARCHAR (38)
DATETIME TIMESTAMP
BYTE VARCHAR (Length in Bytes)
TIME VACHAR (20)
Defining the connection parameters
This section describes how to use an Amazon Redshift database as a data warehouse in a Qlik
Compose project.
To define Amazon Redshift as a data warehouse:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the bottom left of the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button or click the Add new database link in the middle of the
window.
The New Data Warehouse dialog box opens.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select the desired data warehouse.
4. Enter the information as described below.
l
Connection input mode: Select Standard or Advanced.
If you selected Standard connection input mode, specify the following:
l
Server Name: The name or IP address of the Amazon Redshift cluster.
l
Port: Optionally, change the default port.
l
User Name: The user name for accessing the Amazon Redshift database. The
specified user must have read/write privileges on the Amazon Redshift
database.
l
Password: The password for accessing the Amazon Redshift database.
If you selected Advanced connection input mode, specify the following:
l
Password: The password for accessing the Amazon Redshift database.
l
ODBCConnection String: A string of parameters required to connect to the
Amazon Redshift ODBCDriver. After entry, click Test to verify that a connection
was established.
l
JDBCConnection String: A string of parameters required to connect to the
Amazon Redshift JDBCDriver. After entry, click Test to verify that a connection
was established.
You must include the name of the Amazon Redshift database in the
connection string.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
123

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Warehouse Properties: Specify the following:
l
Database Name: The name of the Amazon Redshift database.
l
Data Warehouse Schema: The schema in which to create the data warehouse
tables.
l
Data Mart Schema: The schema in which to create the data mart.
l
More Options: Click to see or hide the following advanced options:
l
Character column size in bytes: This should be calculated according to the
largest value you are likely to store in a VARCHAR column. Tables in the Landing
Zone will be divided by the specified value (and rounded up).
For example, if the value of Character column size in bytes is 3 (the default),
both VARCHAR (12 bytes) and VARCHAR (10 bytes) will be discovered as VARCHAR (4
characters).
See: Use the smallest possible columnsize - Amazon Redshift
If this value is changed, existing tables will not be affected (i.e. the
change will only take effect if new columns are added to the model
and the data warehouse tables are updated accordingly).
5. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified data warehouse.
6. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Using Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a data warehouse
This section describes how to set up Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a data warehouse in a
Compose project.
By default, Compose creates tables in Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a
CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE INDEX, which offers the best overall query performance
for large tables. Depending on your environment though, you might want to override the
default to create all tables or specific tables as a HEAP, for example, which is optimized
for smaller tables. For information on how to accomplish this, see Table creation
modifiers tab (page 42) in the Project Settings section.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 124)
l
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data types (page 125)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 126)
Prerequisites
Before you can use Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a data warehouse in a Qlik Compose
project, make sure that the following prerequisites have been met:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
124

5 Data Warehouse projects
Install the Required Client
Install SQL Server Native Client 11 (for connecting to Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics) on the
Compose machine.
Permissions
The user specified in the Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics connection settings must be granted
the following permissions.
Permission required for the specified target database:
The Compose must be granted the db_owner user role on the specified target database.
Permission required for the master database:
The Compose must be granted SELECT access (by adding the user to the master database and
then to the db_readers role, for example).
Open the Required Firewall Port(s)
l
When Compose runs on a machine outside Azure - Open port 1433 for outbound traffic.
l
When Compose runs on an AzureVM - Open the following ports for outbound traffic:
l
1433
l
11000-11999
l
14000-14999
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data types
The following table shows the Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data warehouse data types that
are supported when using Qlik Compose and the default mapping from Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped from the source, see the section for
the source database you are using.
Qlik Compose data types Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data types
BIGINT BIGINT
DECIMAL DECIMAL (p,s)
INTEGER INTEGER
DATE DATE
DATETIME DATETIME2 (s)
TIME TIME
GUID VARCHAR (38)
BIGINTAUTOINC BIGINT
Data type mappings
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
125

5 Data Warehouse projects
Qlik Compose data types Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data types
BYTE VARBINARY (Length)
VARCHAR (Length) VARCHAR (Length)
NVARCHAR (Length) NVARCHAR (Length)
Defining the connection parameters
This section describes how to use a Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics database as a data
warehouse in a Qlik Compose project.
When using Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as the data warehouse, the data
warehouse database must be the same as the database that you will later define for the
landing zone, although it should use a different schema.
To define Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a data warehouse:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the bottom left of the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button or click the Add new database link in the middle of the
window.
The New Data Warehouse dialog box opens.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select the desired data warehouse.
4. Enter the information as described below:
l
Connection input mode: Select Standard or Advanced.
If you selected Standard connection input mode, specify the following:
l
Server Name: The name of the Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics server you
are using.
l
Port: The port number for the Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics.
l
User Name: The user name of a registered Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics
user.
l
Password: The password for the user entered in the User name field.
If you selected Advanced connection input mode, specify the following:
l
Password: The password for the user entered in the User name field.
l
ODBCConnection String: The string of parameters required to connect to the
Microsoft Azure SQL ODBCDriver.
l
JDBCConnection String: The string of parameters required to connect to the
Microsoft Azure SQL JDBCDriver.
Compose will concatenate the database name to the ODBC/JDBC
connection string.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
126

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Warehouse Properties: Specify the following:
l
Database Name: The name of the target database. This must be the same as
the target endpoint defined in the Qlik Replicate task. For more information, see
Defining a Qlik Replicate task (page 33)
.
l
Data Warehouse Schema: The schema in which to create the data warehouse
tables.
l
Data Mart Schema: The schema in which to create the data mart.
l
More Options: Click to see or hide the following advanced options:
l
Additional JDBC Parameters: Any additional parameters you need to add to
the default JDBC connection string. The parameters should be separated by a
semi-colon.
Format:PARAM1=VALUE1;PARAM2=VALUE2
l
Additional ODBC Parameters: Any additional parameters you need to add to
the default ODBC connection string. The parameters should be separated by a
semi-colon.
Format:PARAM1=VALUE1;PARAM2=VALUE2
5. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified data warehouse.
6. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Identifier labels
Several statements are tagged with an identifier label for troubleshooting 'problem queries' and
identifying possible ways to optimize database settings. The addition of labels to ELT queries
enables fine-grained workload management and workload isolation via Synapse WORKLOAD
GROUPS and CLASSIFIERS.
The identifier labels are as follows:
Table type Tag
Hubs CMPS_HubIns
Satellites CMPS_SatIns
Type1 dimensions CMPS_<data mart name>_DimT1_Init/CMPS_<data
mart name>_DimT1_Incr
Type2 dimensions CMPS_<data mart name>_DimT2_Init/CMPS_<data
mart name>_DimT2_Incr
Transactional facts CMPS_<data mart name>_FctTra_Init/CMPS_<data
mart name>_FctTra_Incr
State-oriented facts CMPS_<data mart name>_FctStO_Init
Aggregated facts CMPS_<data mart name>_FctAgg_Init
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
127

5 Data Warehouse projects
Using Google Cloud BigQuery as a Data Warehouse
This section describes how to set up Google Cloud BigQuery as a data warehouse in a Compose
project.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 128)
l
Limitations and Considerations (page 128)
l
Supported Data Types (page 129)
l
Setting General Connection Properties (page 130)
Prerequisites
Before you can use Google Cloud BigQuery as a data warehouse in a Qlik Compose project, make
sure the prerequisites described below have been met.
Permissions
When you create your Service Account Key for Google Cloud, make sure to select BigQuery >
BigQuery Data Owner as the Role. Leave the default key type (JSON) unchanged.
As part of the Service Account Key creation process, a JSON file containing the connection
information will be downloaded to your computer. You will need to copy the contents of this file to
the Service account key field in the Data Warehouse settings.
Client Prerequisites
Both the Simba ODBC driver and the Simba JDBC driver need to be installed on the Compose
machine.
To do this:
1. Download the following drivers from https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/providers/simba-
drivers:
l
Simba ODBC driver 2.3.0 or later (MSI file)
l
Simba JDBC driver 1.2.2 or later (Zip file)
2. To install the ODBC driver, simply run the installer on the Compose machine.
3. To install the JBDC driver, extract
all
of the files to the <COMPOSE_INSTALL_
DIR>\java\jdbc folder on the Compose machine.
When installing driver versions later than 1.2.22.1026, after extracting the files to
the jdbc folder, you must delete the gson-<version>.jar file from the folder.
Otherwise, an error will occur.
4. Restart the Compose service.
Limitations and Considerations
The following limitations apply when using Google Cloud BigQuery as a data warehouse in a
Compose project.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
128

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
The dataset(s) specified in the connection settings must already exist before loading data
into Google Cloud BigQuery.
l
When ingesting data from a Replicate source that may have BIT columns (such as Microsoft
SQL Server), it is recommended to define a global data type transformation in Replicate to
convert BIT to STRING (1). Otherwise, Compose will convert BIT to VARCHAR (1) (as it does
not support BOOLEAN), which may cause a data type mismatch in the Landing Zone.
l
When discovering from a BigQuery landing database, BOOLEAN and FLOAT columns are not
supported and will be ignored. If you need such columns to be ingested to the data
warehouse, the following workarounds are available:
l
Discover from the source database
l
Convert these data types (which are not supported in Compose) to another type such
as VARCHAR (1) or INT
l
The data warehouse data set and landing data set must be in the same region.
l
As strings do not have length in BigQuery, when discovering from the Landing Zone,
Compose will assume a default length of VARCHAR(32767). From a practical perspective,
since these strings will also be created on BigQuery, they will have no runtime length either.
To keep things orderly however, best practice is to change strings of known length to their
actual expected length.
l
Commonly used BigQuery functions were added to the Compose Expression Builder.
BigQuery SQL commands that are not listed in the Compose Expression Builder can be
entered manually if required.
l
BigQuery does not support altering tables via standard DDL operations. To work around this
limitation, Compose creates a script that copies the data to a new table. After the data is
copied to the new table, make sure to delete the old table.
l
Aggregated fact and state oriented data mart are not supported.
l
Stored procedures in custom ETLs are not supported.
l
Clustering keys are not supported.
Supported Data Types
The following table shows the Google Cloud BigQuery data warehouse data types that are
supported when using Qlik Compose and the default mapping from Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped from the source, see the section for
the source database you are using.
Compose Data Type BigQuery Data Type
BYTES BYTES
DATE DATE
TIME TIME
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
129

5 Data Warehouse projects
DATETIME If scale <=6:
TIMESTAMP If scale >6:
STRING
BIGINT INTEGER
DECIMAL If the data can be stored in 38,9, then:
NUMERIC
If not, then:
STRING with length of original precision +2
VARCHAR STRING
INTEGER INTEGER
Unsupported Data Types
The following Google Cloud BigQuery data types are not supported:
GEOGRAPHY, STRUCT, and ARRAY.
Setting General Connection Properties
This section describes how to use a Google Cloud BigQuery database as a data warehouse in a Qlik
Compose project.
To define Google Cloud BigQuery as a data warehouse:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the bottom left of the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button or click the Add new database link in the middle of the
window.
The New Data Warehouse dialog box opens.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select the desired data warehouse.
4. Enter the information as described in the table below.
l
Connection input mode: Select Standard or Advanced.
If you selected Standard:
l
Paste the contents of the JSON file (including curly brackets) that was
downloaded when you created your BigQuery service account key, into the
Service account key field.
If you selected Advanced, specify the following:
l
ODBCConnection String: Enter a string of parameters required to connect to
BigQuery via the Simba ODBCDriver.
l
JDBCConnection String: Enter a string of parameters required to connect to
BigQuery via the Simba JDBCDriver.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
130

5 Data Warehouse projects
Compose will concatenate the dataset name to the ODBC/JDBC
connection string.
l
Region: Where to upload the dataset created by Compose.
l
Data Warehouse dataset: Specify the dataset in which to create the data warehouse
tables.
l
Data mart dataset: Specify the dataset in which to create the data mart.
5. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified data warehouse.
6. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Managing databases
You can edit and delete databases as required. The table below describes the available options.
To Do this
Edit a
database
In the left side of the Manage Databases window, select the database that you
want to edit and then click the Edit toolbar button.
Delete a
database
In the left side of the Manage Databases window, select the database that you
want to delete and then click the Delete toolbar button.
Click Yes when prompted to confirm the deletion.
Database management options
5.5 Setting up Landing Zone and Data Source
connections
This section explains how to set up landing zone and data source connectivity in a Qlik Compose
project. Note that although you must configure landing zone connectivity, data source connectivity
is only required if you want to discover the source database defined in the Replicate task.
For a list of the pros and cons of discovering the source database as opposed to the landing zone,
see
Discovering the Source Database or Landing Zone (page 156)
.
Reserved column names and suffixes
The following section lists the reserved column names and suffixes. If the any of the discovered
tables contain columns with these names or suffixes, you need to rename them in Compose. For
information on renaming columns, see
Managing attributes (page 169)
.
Reserved column names:
l
ID
l
BIR_MAPPING_NR - internal mapping identifier used in staging tables for ETL
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
131

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
ROWNR - internal row identifier used in staging tables for ETL
l
RUNNO_INSERT - The task run number for INSERT operations.
l
RUNNO_UPDATE - The task run number for UPDATE operations.
l
OBSOLETE__INDICATION - Used to mark OBSOLETE records in data mart objects. See also:
The "Obsolete" indicator (page 262)
l
TR_ID - The unique Transaction ID for a fact table record.
l
BID_OCCS - Internal column used in ETL processing.
l
FD - This column is added to tables that contain attributes (columns) with a History Type 2.
The column is used to delimit the range of dates for a given record version. The column name
can be changed in the project settings.
If you change the "From Date" name in the project settings, the new name will
become a reserved word.
l
TD - This column is added to tables that contain attributes (columns) with a History Type 2.
The column is used to delimit the range of dates for a given record version. The column name
can be changed in the project settings.
If you change the "To Date" name in the project settings, the new name will
become a reserved word.
l
FKNR - Foreign key number column used in logging tables to report missing references
captured via the data warehouse ETL
Reserved suffixes in data darts:
l
_OID
l
_VID
Permissions
This section lists the required permissions for the source landing zone and the source database
defined in a Qlik Replicate task.
l
Landing Zone permissions (page 132)
l
Source database permissions (page 133)
Landing Zone permissions
For proper operation, the user specified in the landing zone database connection settings must be
granted the following permissions:
l
Read metadata
l
Select from tables
l
Create tables (for error marts)
l
Insert to tables (error marts)
For information on the landing zone, see Landing Zone settings.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
132

5 Data Warehouse projects
Source database permissions
To generate the model by discovering the source database in the Replicate task, you need to define
a connection to the source database used in the Replicate task. The user defined in the Source
database connection settings must be granted the following permissions:
l
Read metadata (Columns, Primary Keys and Foreign Keys)
l
Select from tables
For more information, see Source Database Connection.
Data type mappings
This topic lists the data type mappings from the supported source databases or the supported
landing zone databases (where applicable) to the Qlik Compose data types. Note that as MySQL
and IBM DB2 for LUW are not supported as data warehouses in Compose, the mappings in those
sections are applicable to their role as source databases only.
In this topic:
l
Oracle data types (page 133)
l
Microsoft SQL Server data types (page 134)
l
MySQL data types (page 136)
l
Amazon Redshift data types (page 138)
l
IBM DB2 for LUW data types (page 138)
l
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data types (page 139)
l
Google Cloud BigQuery data types (page 140)
Oracle data types
The Oracle database for Qlik Compose supports most Oracle data types. The following table shows
the Oracle source data types that are supported when using Qlik Compose and the default mapping
to Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped in the data warehouse, see the section
for the data warehouse database you are using.
Oracle data types Qlik Compose data types
CHAR Varchar
NCHAR(40) Varchar(80)
VARCHAR(2) VARCHAR
NUMBER Decimal
FLOAT Decimal(38,12)
REAL Decimal(38,12)
Data type mappings
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
133

5 Data Warehouse projects
Oracle data types Qlik Compose data types
DATE Date
TIMESTAMP(6) Date
TIMESTAMP(6) WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE Date
TIMESTAMP(6) WITH TIME ZONE Date
DOUBLE PRECISION Decimal(38,12)
Non-supported data types
Source Oracle tables with columns of the following Oracle data types are not supported and will be
ignored.
l
BLOB
l
CLOB
l
NCLOB
l
BFILE
l
BINARY_FLOAT
l
BINARY_DOUBLE
l
INTERVAL YEAR (2) TO MONTH
l
INTERVAL DAY (6) TO SECOND (5)
l
RAW
l
ROWID
l
UROWID
l
LONG
Microsoft SQL Server data types
The following table shows the Microsoft SQL Server source data types that are supported when
using Qlik Compose and the default mapping to Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped in the data warehouse, see the section
for the data warehouse database you are using.
Microsoft SQL Server data types Qlik Compose data types
char Varchar
nchar Varchar
bit Integer
tinyint Integer
smallint Integer
Data type mappings
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
134

5 Data Warehouse projects
Microsoft SQL Server data types Qlik Compose data types
INT Integer
BIGINT Bigint
decimal Decimal
numeric Decimal
smallmoney Decimal(11,4)
money Decimal(20,4)
float Decimal(38,12)
real Decimal(18,6)
datetime Date
datetime2 Date
smalldatetime Date
BINARY BYTE
date Date
time Varchar(16)
uniqueidentifier GUID
Non-supported data types
Source Microsoft SQL Server tables with columns of the following Microsoft SQL Server data types
are not supported and will be ignored:
l
BLOB
l
CLOB
l
NCLOB
l
VARCHAR(MAX)
l
TEXT
l
NVARCHAR(MAX)
l
NVARCHAR (LENGTH)
l
NTEXT
l
VARBINARY
l
IMAGE
l
DATETIMEOFFSET
l
TIMESTAMP
l
SQL_VARIANT
l
XML
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
135

5 Data Warehouse projects
MySQL data types
The following table shows the MySQL source data types that are supported when using Qlik
Compose and the default mapping to Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped in the data warehouse, see the section
for the data warehouse database you are using.
MySQL data types Qlik Compose data types
BIGINT Bigint
binary BYTE
bit bigint
char Varchar
date Date
datetime Date
DECIMAL Decimal
double Decimal(38,12)
ENUM('x-small', 'small', 'medium', 'large', 'x-large') Varchar(7)
FLOAT Decimal(38,12)
int integer
MEDIUMINT integer
MEDIUMTEXT Varchar(16777215)
nchar(36) Varchar(36)
NUMERIC Decimal
REAL Decimal(38,12)
set('a','b','c','d') Varchar(7)
SMALLINT integer
TEXT Varchar(65535)
time Date
timestamp Date
TINYINT integer
TINYTEXT Varchar(255)
year integer
Data type mappings
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
136

5 Data Warehouse projects
Non-supported data types
Source MySQL tables with columns of the following MySQL data types are not supported and will
be ignored:
l
GEOMETRY
l
GEOMETRYCOLLECTION
l
JSON
l
linestring
l
LONGblob
l
LONGTEXT
l
mediumblob
l
MULTILINESTRING
l
MULTIPOINT
l
MULTIPOLYGON
l
point
l
polygon
l
tinyblob
l
BIT(64)
l
BLOB()
l
BIGBLOB
l
MEDIUMBLOB
l
TINYBLOB
l
BLOB
l
varbinary (20)
Snowflake data types
The following table shows the Snowflake data types that are supported when using Qlik Compose
and the default mapping to Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped in the data warehouse, see the section
for the data warehouse database you are using.
Snowflake data types Qlik Compose data types
NUMBER DECIMAL
FLOAT DECIMAL
VARCHAR VARCHAR
BINARY BYTE
BOOLEAN VARCHAR (5)
DATE DATE
Data type mappings
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
137

5 Data Warehouse projects
Snowflake data types Qlik Compose data types
TIME TIME
TIMESTAMP_NTZ DATETIME(9)
TIMESTAMP_LTZ DATETIME(9)
TIMESTAMP_TZ DATETIME(9)
VARIANT JSON or XML as determined by the data source settings.
OBJECT N/A
ARRAY N/A
Amazon Redshift data types
The following table shows the Amazon Redshift data warehouse data types that are supported
when using Qlik Compose and the default mapping to Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped in the data warehouse, see the section
for the data warehouse database you are using.
Amazon Redshift data types Qlik Compose data types
SMALLINT INTEGER
INTEGER INTEGER
BIGINT BIGINT
DECIMAL DECIMAL
REAL DECIMAL (18,6)
DOUBLE PRECISION DECIMAL (38,12)
BOOLEAN INTEGER
CHAR VARCHAR
DATE DATE
TIMESTAMP DATETIME
Data type mappings
IBM DB2 for LUW data types
The following table shows the IBM DB2 for LUW source data types that are supported when using
Qlik Compose and the default mapping to Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped in the data warehouse, see the section
for the data warehouse database you are using.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
138

5 Data Warehouse projects
IBM DB2 for LUW data types Qlik Compose data types
DATE DATE
TYPE_TIMESTAMP DATE
TIMESTAMP DATE
TYPE_TIME DATE
TYPE_DATE DATE
REAL DECIMAL (18,6)
DOUBLE DECIMAL (18,6)
DECIMAL DECIMAL
SMALLINT INTEGER
INTEGER INTEGER
BIGINT BIGINT
WVARCHAR VARCHAR
CHAR VARCHAR (4000)
WCHAR VARCHAR (4000)
BINARY BYTE
Data type mappings
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data types
The following table shows the Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data warehouse data types that
are supported when using Qlik Compose and the default mapping to Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped to the data warehouse, see the section
for the data warehouse you are using.
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data types Qlik Compose data types
DATE DATE
DATETIME DATETIME
DATETIME2 DATETIME
SMALLDATETIME DATETIME
TIME TIME
CHAR VARCHAR
NCHAR VARCHAR
REAL DECIMAL (18,6)
Data type mappings
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
139

5 Data Warehouse projects
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics data types Qlik Compose data types
FLOAT DECIMAL (38,12)
DECIMAL DECIMAL
MONEY DECIMAL (20,4)
SMALLMONEY DECIMAL (11,4)
BIT INTEGER
TINYINT INTEGER
SMALLINT INTEGER
INT INTEGER
BIGINT BIGINT
VARBINARY BYTE
BINARY BYTE
Google Cloud BigQuery data types
The following table shows the Google Cloud BigQuery data types that are supported when
ingesting data from Google Cloud BigQuery and the default mapping to Qlik Compose data types.
For information on how to view the data type that is mapped in the data warehouse, see the section
for the data warehouse database you are using.
Google Cloud BigQuery data types Qlik Compose data types
DATE Date
TIME Time
TIMESTAMP Datetime
INT64 BigInt
NUMERIC(p,s) Decimal(p,s)
FLOAT64 Decimal(38,12)
STRING Varchar
BOOLEAN Varchar(5) - True or False
Data type mappings
Defining landing zones
In a Compose project, you can define any number of landing zones. Defining multiple landing zones
is necessary if the data that you eventually want to be available in your data mart(s) is located in
several different landing zones.
Before you can define a landing zone in Qlik Compose, you first need to define a data warehouse.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
140

5 Data Warehouse projects
For more information on adding data warehouses, see
Setting up a data warehouse connection
(page 110)
.
To add a landing zone:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button.
The New Data Source window opens.
3. Provide the following information:
Field Description
Content Type Choose whether the content in the landing zone is Full Load, Change
Processing or Full Load and Change Processing (according to the Qlik
Replicate task definition).
See also After applying changes below.
Designated
By
Select whether the landing zone is a Database or a Schema. This should
reflect the target endpoint settings in the Qlik Replicate task.
When Oracle is the Data Warehouse, this field is read-only since the
Oracle landing zone is
always
designated by Schema.
For more information, see
Defining a Qlik Replicate task (page 33)
.
Database
Name
This field is not applicable when Oracle is the Data Warehouse.
If the landing zone is designated by a Database, specify the database
name. This must be the same as the target database defined in the Qlik
Replicate task.
When Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics is the data warehouse, the
landing zone database must be the same as the database defined for the
data warehouse, although it should use a different schema.
For more information, see
Defining a Qlik Replicate task (page 33)
.
Schema
Name
If a schema name was specified in the Qlik Replicate task settings, specify
the same schema name here.
When Oracle is the Data Warehouse, this must be the same as the schema
defined in the Oracle target connection string in the Qlik Replicate task.
For more information, see
Defining a Qlik Replicate task (page 33)
.
Error Mart
Schema
Name
Specify the schema where you want the data mart exception tables to be
created. Data that is rejected by data quality rules will be copied to tables
in the specified schema.
For more information on error marts, see
Defining and managing data
quality rules (page 215)
.
Data source fields
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
141

5 Data Warehouse projects
Field Description
After
applying
changes
Replicate creates Change Tables in the landing zone in which subsequent
changes to the original Full Load data are stored. If you selected Change
Processing or Full Load and Change Processing as the Content Type,
you can determine what to do with the Change Tables after the changes
have been applied to the data warehouse tables:
Choose one of the following:
l
Delete from Change Tables - Deletes the changes from the
Change Tables
l
Keep in Change Tables - Keeps the changes in the Change
Tables. This is useful if you do not want all of the changes to be
applied at the same time.
For more information, see
Working with the Keep in Change Tables
option (page 143)
.
l
Archive the Change Tables - If you select Archive the Change
Tables, you also need to specify a Database name and Schema
name in the relevant fields.
Archived Change Tables do not contain a record of DDL
changes. If DDL changes were applied, you will need to update
the archived tables manually.
Discover the
VARIANT
data type as
(applies to
Snowflake
only)
As Compose does not support mapping directly to the Snowflake
VARIANT data type, you need to choose whether VARIANT columns will
be created as JSON (the default) or XML in the Snowflake database.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
142

5 Data Warehouse projects
Field Description
Associate
with
Replicate
Task
Select this to associate your Compose project with the related Replicate
task. Replicate tasks replicate the relevant tables from the source
database to the landing zone in your data warehouse. Specifying the
Replicate task name will enable you to both discover the source tables'
primary keys, and monitor and control that task from within Compose.
However, before you can specify a Replicate task name, you first need to
define the connection settings to at least one Replicate Server machine.
To do this, click the Replicate Server Settings link below the Associate
with Replicate task field and then configure the settings as described in
Replicate Server settings (page 382)
.
Once you have configured connectivity to at least one Replicate Server,
you can then proceed to select a Replicate task.
To select a Replicate task:
1. Click the browse button to the right of the Associate with
Replicate task field.
The Select Replicate Task window opens.
2. Select a Replicate Server from the Server drop-down list.
The Replicate Tasks list is populated with all tasks defined on the
selected server.
3. Select the task that is replicating the source tables to the landing
zone and then click OK.
The name of the selected task is shown as read-only in the Associate
with Replicate task field.
4. If you want to generate the model by discovering the source database in the Replicate task,
leave the New Data Source window open for now as you will need to define connectivity to
the source database in the Replicate task.
For instructions on how to do this, see
Defining Replicate data source connections (page
147)
.
Otherwise, click OK to save your settings.
Working with the Keep in Change Tables option
When you select the Keep in Change Tables option described earlier, the changes are kept in the
Change Tables after they are applied (instead of being deleted or archived). This is useful as it
allows you to:
l
Use the changes in multiple Compose projects that share the same landing
l
Leverage Change Table data across multiple mappings and/or tasks in the same project
l
Preserve the Replicate data for auditing purposes or reprocessing in case of error
l
Reduce cloud data warehouse costs by eliminating the need to delete changes after every
ETL execution
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
143

5 Data Warehouse projects
To facilitate this functionality, Compose keeps a "watermark" per table as a way of tracking which
data has been consumed and which data is yet to be consumed. The watermarks can be reset if
needed, as described in
Deleting changes and resetting watermarks (page 146)
below.
Use case
I have a table named Inventory in my landing that I would like to load into two separate tables in my
data warehouse for the purpose of tracking and analyzing changes. The tracking table needs to be
updated every 15 minutes while the analysis table needs to be updated once a day.
To accomplish this, I do the following:
1. Set up a connection to my landing zone making sure to select the Keep in Change Tables
option.
2. Discover the source tables from the landing zone as described in
Discovering the Source
Database or Landing Zone (page 156)
.
3. Duplicate the Inventory table in my model so that I have two tables, and then rename the
tables as follows: Inventory_Frequent (for tracking) and Inventory_Snapshot (for analytics).
For instructions on how to duplicate entities, see
Managing entities (page 168)
4. Validate the model as described in
Validating the model (page 163)
.
5. Create the data warehouse tables as described in
Creating the data warehouse tables (page
194)
.
6. Duplicate the Full Load and CDC tasks so that I have one set of tasks that populate and
update the Inventory_Frequent table, and another set of tasks that populate and update the
Inventory_Snapshot table.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
144

5 Data Warehouse projects
Make sure when duplicating the tasks to select Full Load Only as the task type for
Full Load tasks and Change Tables Only as the task type for CDC tasks. See also
Adding, editing, and duplicating tasks (page 203).
7. Verify the correct mappings are selected and delete any redundant mappings that were
created when the tasks were duplicated.
For the source_Frequent and source_Frequent_CDC tasks, the Map_Inventory_
Snapshot mapping should not be selected. Conversely, for the source_Snapshot
and source_Snapshot_CDC tasks, the Map_Inventory_Frequent mapping should
not be selected.
8. Generate and run the source_Frequent and source_Snapshot Full Load tasks.
9. Generate the source_Frequent_cdc and source_Snapshot_cdc tasks.
10. Schedule the source_Frequent_cdc task to run every 15 minutes and schedule the source_
Snapshot_cdc task to run at 20:00 every day.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
145

5 Data Warehouse projects
Deleting changes and resetting watermarks
The following CLIoptions are available for managing watermarks.
Deleting changes from the Change Tables
You can delete the changes from the Change Tables if they are no longer required. Although this is
not required, you might want to incorporate this into your database maintenance plan.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe generate_watermark_scripts --project
project_name
Where:
--project is the name of the project.
Example
ComposeCli.exe generate_watermark_script --project MyProject
Resetting the watermark
Resetting the watermark might be required if you need to reapply changes from an earlier time
period, for example.
After resetting the watermark, on the next CDC run all of the Change Table records will
be processed again.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe reset_watermark --project
project_name
--landing
landing_name
[--table
table_
name
]
Parameters
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
146

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--landing The name of the landing in Compose containing the Change Tables
whose watermarks you want to reset.
--table The logical name (i.e. without the_ct suffix) of a specific Change
Table whose watermark you want to reset. When omitted,
watermarks for all Change Tables will be reset.
Example
ComposeCli.exe reset_watermark --project MyProject --landing northwind_Landing
Limitations and considerations
Switching from Keep in Change Tables to Delete from Change Tables/Archive the Change
Tables or vice versa, requires you to regenerate the affected tasks. If you switch from Keep in
Change Tables to Delete from Change Tables/Archive the Change Tables, Compose need to re-
read the changes and delete/archive the older changes. In such a case, running the CDC tasks
might take longer than usual, depending on the amount of changes.
Defining Replicate data source connections
You can also generate the model by discovering the source database in the Replicate task. In this
case, you will also need to define connectivity to that database.
To define connectivity settings:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the Databases panel. The Manage Databases
window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button. The New Data Source window opens.
3. In the New Data Source window, select the Source database connection option.
4. Continue from one of the following topics as appropriate:
l
Using Oracle as a source (page 147)
l
Using Microsoft SQL Server as a source (page 149)
l
Using MySQL as a source (page 151)
l
Using IBM DB2 for LUW as a source (page 153)
Using Oracle as a source
This section describes how to set up connectivity to the Oracle database defined for the Replicate
task. This is required if you want to discover the tables and/or views from the source database as
opposed to the landing zone. For a list of the pros and cons of each method, see
Discovering the
Source Database or Landing Zone (page 156)
.
It contains the following topics:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
147

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Prerequisites (page 148)
l
Oracle data types (page 133)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 148)
Prerequisites
Before you can use Oracle as a source in a Qlik Compose project, make sure that the following
prerequisites have been met:
l
The Oracle database should be configured with the required
Permissions (page 132)
and
accessible from the Compose machine.
l
Install Oracle Data Access Components (x64) on the computer where Qlik Compose is
located. Then, add the full path of the Oracle Data Access DLL to the system environment
variables.
The default path should be:
<ORACLE_PRODUCT_CLIENT_DIR>\ODP.NET\bin\4\
The path to the Oracle Data Access DLL also needs to be specified in both the
machine.conf file and the Global Assembly Cache (GAC). In addition, make sure
that the Oracle.DataAccess.dll file exists in the following location:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_64.
The Qlik Compose service needs to be restarted after installing the required
components.
l
Install Oracle Instant Client 19.0 or later (Windows x64) on the computer where Qlik Compose
is located.
l
If you want to use an Oracle TNS name in the connection settings, you first need to set the
ORACLE_HOME environment variable.
Example:
<ORACLE_PRODUCT_CLIENT_DIR>\product\<version>\client_1
Defining the connection parameters
You can add an Oracle database to Qlik Compose to use as a source.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
148

5 Data Warehouse projects
To add an Oracle source database to Qlik Compose:
1. In the New Data Source window, enter the information as described in the table below.
Field Description
Type Select Oracle.
Server
Name
Specify the name or IP address of the Oracle server machine.
OR
Specify the TNS name.
Port If you specified a TNS name in the Server Name field, make sure that this
field is empty. Optionally, change the default port.
User Name Specify your user name for accessing the Oracle database.
The specified user must have read/write privileges on the Oracle database.
Password Specify your password for accessing the Oracle database.
SID If you specified a TNS name in the Server Name field, make sure that this
field is empty. Otherwise, specify the Oracle SID.
Schema Specify the schema containing the source tables.
Data source fields
2. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified database.
3. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Using Microsoft SQL Server as a source
This section describes how to set up connectivity to the Microsoft SQL Server database defined as
the source endpoint for the Replicate task. This is required if you want to discover the tables and/or
views from the source database as opposed to the landing zone. For a list of the pros and cons of
each method, see
Discovering the Source Database or Landing Zone (page 156)
.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 149)
l
Working with Windows authentication (page 150)
l
Microsoft SQL Server data types (page 134)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 152)
Prerequisites
Before you can use Microsoft SQL Server as a source in a Qlik Compose project, make sure that the
following prerequisites have been met:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
149

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Microsoft SQL Server should be configured with the required
Permissions (page 132)
and
accessible from the Compose machine.
l
Microsoft SQL Server Native Client must be installed on the Qlik Compose machine.
l
Qlik Compose supports the following Microsoft SQL Server editions.
l
Enterprise Edition
l
Standard Edition
l
Workgroup Edition
l
Developer Edition
Working with Windows authentication
You can configure the Qlik Compose Microsoft SQL Server source to log in to Microsoft SQL Server
using Windows authentication. If you choose this option, you also need to make sure that:
l
The Microsoft SQL Server instance is set up to allow Windows log on.
l
The Compose user is specified as the "Log on as" user for the Qlik Compose Server service
account.
OR
Microsoft SQL Server is configured to allow login for the Qlik Compose Server service
account.
Defining the connection parameters
You can add a Microsoft SQL Server database to Qlik Compose to use as a source. You can also use
the Microsoft SQL Server source to specify connection details to a Microsoft Azure SQL Database.
When using Microsoft Azure SQL Database as the data warehouse, the data warehouse database
must be the same as the database that you will later define for the landing zone, although it should
use a different schema.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
150

5 Data Warehouse projects
To add a Microsoft SQL Server source database to Qlik Compose:
1. In the New Data Source window, enter the information as described in the table below.
Field Description
Type Select Microsoft SQL Server.
Server Name Specify the name or IP address of the Microsoft SQL Server machine.
Port Optionally, change the default port.
Windows
authentication
SQL Server
authentication
Choose how you want Compose to log in to the Microsoft SQL Server
database. If you choose Windows authentication, see Working with
Windows authentication below.
User Name Specify your user name for accessing the Microsoft SQL Server
database.
The specified user must have read/write privileges on the Microsoft
SQL Server database.
Password Specify your password for accessing the Microsoft SQL Server
database.
Database Name Specify the name of the Microsoft SQL Server database.
Schema Specify the schema containing the source tables.
Data source fields
2. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified database and/or landing zone.
3. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Working with Windows authentication
You can configure Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses to log in to Microsoft SQL Server using
Windows authentication.
If you choose this option, you also need to make sure that:
l
The Microsoft SQL Server instance is set up to allow Windows log on.
l
The Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses user is specified as the "Log on as" user for the Qlik
Compose for Data Warehouses service account.
-OR-
l
Microsoft SQL Server is configured to allow login for the Qlik Compose for Data Warehouses
service account.
Using MySQL as a source
This section describes how to set up connectivity to the MySQL database defined as the source
endpoint for the Replicate task. This is required if you want to discover the tables and/or views from
the source database as opposed to the landing zone. For a list of the pros and cons of each
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
151

5 Data Warehouse projects
method, see
Discovering the Source Database or Landing Zone (page 156)
.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 152)
l
MySQL data types (page 136)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 152)
Prerequisites
Before you can use MySQL as a source in a Qlik Compose project, make sure that the following
prerequisites have been met:
l
The MySQL database should be configured with the required
Permissions (page 132)
and
accessible from the Compose machine.
The following MySQL editions are supported:
l
MySQL Community Edition
l
MySQL Standard Edition
l
MySQL Enterprise Edition
l
MySQL Cluster Carrier Grade Edition
l
MySQL ODBC 64-bit client must be installed on the same computer as Qlik Compose.
Cluster prerequisites
To be able to discover clustered (NDB) tables, the following parameters must be configured in the
MySQL my.ini (Windows) file.
Parameter Value
ndb_log_bin Must be:
ndb_log_bin=on
This ensures that changes in clustered tables will be logged to the binary
log.
ndb_log_update_as_
write
Must be:
ndb_log_update_as_write=OFF
This prevents writing UPDATEs as INSERTs in the binary log.
ndb_log_updated_
only
Must be:
ndb_log_updated_only=OFF
Ensures that the binary log will contain the entire row and not just the
changed columns.
Cluster parameters
Defining the connection parameters
You can add a MySQL database to Qlik Compose to use as a source.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
152

5 Data Warehouse projects
To add a MySQL source database to Qlik Compose:
1. In the New Data Source window, enter the information as described in the table below.
Field Description
Type Select MySQL.
Server Name Specify the name or IP address of the MySQL server machine.
Port Optionally, change the default port.
User Name Specify your username for accessing the MySQL database.
The specified user must have read/write privileges on the MySQL
database.
Password Specify your password for accessing the MySQL database.
Database
Name
Specify the name of the MySQL database.
Schema Specify the schema containing the source tables.
Data source fields
2. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified database and/or landing zone.
3. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Using IBM DB2 for LUW as a source
This section describes how to set up connectivity to the IBM DB2 for LUW database defined as the
source endpoint for the Replicate task. This is required if you want to discover the tables and/or
views from the source database as opposed to the landing zone. For a list of the pros and cons of
each method, see
Discovering the Source Database or Landing Zone (page 156)
.
It contains the following topics:
l
Prerequisites (page 153)
l
IBM DB2 for LUW data types (page 138)
l
Defining the connection parameters (page 153)
Prerequisites
Before you begin to work with an IBM DB2 for LUW database as a source in Qlik Compose, make
sure the following prerequisites have been met:
l
The IBM DB2 for LUW database should be configured with the required
Permissions (page
132)
and accessible from the Compose machine.
l
The IBM Data Server Driver for ODBC and CLI version 10.5 must be installed on the Qlik
Compose machine.
Defining the connection parameters
You can add an IBM DB2 for LUW database to Qlik Compose to use as a source.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
153

5 Data Warehouse projects
To add an IBM DB2 for LUW source database to Qlik Compose:
1. In the New Data Source window, enter the information as described in the table below.
Field Description
Type Select IBM DB2 for LUW.
Server Name Specify the name or IP address of the IBM DB2 for LUW server machine.
Port Optionally, change the default port.
User Name Specify your username for accessing the IBM DB2 for LUW database.
The specified user must have read/write privileges on the IBM DB2 for
LUW database.
Password Specify your password for accessing the IBM DB2 for LUW database.
Database
Name
Specify the name of the IBM DB2 for LUW database.
Schema Specify the schema containing the source tables.
Data source fields
2. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified database and/or landing zone.
3. Click OK to save your settings.
The database is added to the list on the left side of the Manage Databases window.
Managing databases
You can edit and delete databases as required. The table below describes the available options:
To Do This
Edit a
database
In the left side of the Manage Databases window, select the database that you
want to edit and then click the Edit toolbar button.
Delete a
database
In the left side of the Manage Databases window, select the database that you
want to delete and then click the Delete toolbar button.
Database management options
5.6 Creating and managing the model
This section describes how to create, import and manage the model.
The model serves as the basis for data warehouse generation in Compose. There are three way of
creating the model: Use Compose to derive a tentative model by reverse engineering the source
database(s) (a process also known as "discovering"); Import a model created in ERwin or create the
model manually in Compose.
In this section:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
154

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Reserved column names (page 155)
l
Generating the model (page 155)
l
Model limitations (page 163)
l
Validating the model (page 163)
l
Displaying the model (page 164)
l
Managing the model (page 167)
l
Creating expressions (page 184)
l
Opening the expression builder (page 185)
l
Defining reusable transformations (page 191)
Reserved column names
The following section lists the reserved column names. If the any of the discovered tables contain
columns with these names, you need to rename them in Compose. For information on renaming
columns, see
Managing attributes (page 333)
.
l
BIR_MAPPING_NR - internal mapping identifier used in staging tables for ETL
l
ROWNR - internal row identifier used in staging tables for ETL
l
RUNNO_INSERT - The task run number for INSERT operations.
l
RUNNO_UPDATE - The task run number for UPDATE operations.
l
OBSOLETE__INDICATION - Used to mark OBSOLETE records in data mart objects. See also:
The "Obsolete" indicator (page 262)
l
TR_ID - The unique Transaction ID for a fact table record.
l
BID_OCCS - Internal column used in ETL processing.
l
FD - This column is added to tables that contain attributes (columns) with a History Type 2.
The column is used to delimit the range of dates for a given record version. The column name
can be changed in the project settings.
If you change the "From Date" name in the project settings, the new name will
become a reserved word.
l
TD - This column is added to tables that contain attributes (columns) with a History Type 2.
The column is used to delimit the range of dates for a given record version. The column name
can be changed in the project settings.
If you change the "To Date" name in the project settings, the new name will
become a reserved word.
l
FKNR - Foreign key number column used in logging tables to report missing references
captured via the data warehouse ETL
Generating the model
This section explains how to generate a Business Model from a source database. You can generate
the model using any of the following methods:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
155

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Use Compose to discover the source database or landing zone
l
Import an ERwin model into Compose
l
Create the model manually in Compose
For information about importing a model created in ERwin, see
Importing the model from ERwin
(page 160)
.
Discovering the Source Database or Landing Zone
Discovery can either be performed on the source database defined for the Qlik Replicate task or in
the landing zone. The decision where to perform the discovery is determined by several factors, as
explained in the following table:
Factor
Discover the
Landing Zone
Discover the
Source Database
defined for the Qlik
Replicate task
The source tables selected in the Qlik Replicate task
contain foreign keys that you want to maintain in the
Compose project.
Qlik Replicate does not support foreign key
replication.
- ✔
The source database defined for the Qlik Replicate task
is not natively supported by Qlik Compose.
✔ -
The selected source tables contain keys that are not
relevant to the data warehouse (e.g. surrogate keys and
business keys)
✔ -
A transformation defined for the Qlik Replicate task
means that not all of the columns will be replicated to
the landing zone. In this case, you should discover the
landing zone since this is the data that you eventually
want to appear in your data warehouse.
✔ -
Discovery factors
To generate the model by discovery:
1. Open your project.
2. To generate the model from within Compose:
1. In the Model panel, select Discover from the drop-down menu in the top right corner.
OR
In the Manage Model window, click the Discover toolbar button.
The Discover window opens.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
156

5 Data Warehouse projects
2. Select whether to discover the source database or the landing zone and then click OK.
Note that the suffix "_landing" denotes the landing zone whereas the actual source
database appears without the suffix.
When discovering directly from Microsoft SQL Server source, TIME will be
discovered as STRING(16). As well as being mapped this way in Replicate,
this will also maintain accuracy when a TIME column is defined with high
precision.
The Source Tables/Views Selection - Name window opens.
3. Choose one of the following Search for options:
l
To list tables only, select Tables.
l
To list views only, select Views.
l
To list tables and views, select All.
4. If you also want the internal Qlik tables to be included in the search results, select the Show
Internal Qlik Tables check box. This may be useful for debugging, but is not usually not
necessary.
5. To display all tables/views, click Search.
6. To only display tables/views whose names contain a specific string, type the string in the
Name field and then click Search.
The tables/views will be displayed in the Results list.
7. In the Results list, select the source tables and/or views on which to base the model or click
the >> button (Add All) to add all of the tables in the schema.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
157

5 Data Warehouse projects
You can select multiple tables/views by holding down the [Shift] (sequential
selection) or {Ctrl] (non-sequential selection) button.
8. To add the selected tables/views, click the > (Add) button.
If you add a table that already exists in the model with the same name, then the
new table is added with the name: source_table_name_01 (or source_table_
name_02 if the name source_table_name_01 already exists, and so on).
If the table contains attribute domains that differ from existing ones but have the
same name, they will also be appended with the _01 suffix.
9. Click OK to generate the model from the selected tables/views.
The Generating Model from [model name] window opens.
A progress bar indicates the current model generation progress. For each stage of the model
generation process, a corresponding message appears in the Messages list.
10. After the model has been generated, click Close.
11. Repeat Steps 2-9 to discover additional sources.
Clearing the Landing Zone metadata cache
To improve performance when reading from the Landing Zone or from the Data Warehouse tables,
Compose caches the metadata from both the Landing Zone and the Data Warehouse tables.
However, synchronization issues may sometimes occur if the metadata structure of the Landing
Zone or the Data Warehouse tables is altered outside of the Compose project.
If you aware of external changes to the metadata or if you notice any data synchronization
anomalies, Compose enables you to clear the metadata cache, either using the UI or using the CLI.
You can clear the Landing Zone metadata cache using either the Compose web console or the
Compose CLI.
Clearing the metadata cache using the web console
When using the web console to clear the metadata cache, the following methods are available:
Method 1:
1. Open the Source Table/View Selection - <Landing_Zone_Name> window as described in
Discovering the Source Database or Landing Zone (page 156)
.
2. Click the Clear Cache button located below the Show internal Qlik tables option.
Method 2:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Data Warehouse panel.
The Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window opens.
2. In the Mappings tab, click Clear Landing Cache.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
158

5 Data Warehouse projects
For information on clearing the Data Warehouse cache, see
Clearing the data warehouse metadata
cache (page 227)
.
Clearing the metadata cache using the CLI
You can also clear the metadata cache using the CLI.
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe clear_cache --project
project_name
[--type landing|storage] [--landing_zone
source_name]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--type Which type of metadata cache to clear. Possible values are:
l
landing
l
storage
If --type
landing
and you want to clear a specific landing
zone, you must set the --landing_zone parameter as well. To
clear the metadata cache in all landing zones, specify --type
landing
and omit the --landing_zone parameter.
--landing_zone the name of the landing zone when --type landing_zone
Example
ComposeCli.exe clear_cache --project MyProject --type landing --landing_zone MySource1
Importing entities and mappings from another project
You can import entities and mappings from another project with the same data warehouse type.
This is especially useful within a development environment if you need to integrate a private
developer's project with the main project.
To import entities and mappings:
1. Open the Manage Model window as described in
Managing the model (page 167)
.
2. In the Entities toolbar, click the Import from Project button.
3. The Import from Project wizard opens.
4. In the Entities tab:
a. Select a project from the Import from Project drop-down list.
b. Optionally, search for specific entities.
c. Select which entities to import or select Select All to import all entities.
5. Click Next to select which mappings to import.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
159

5 Data Warehouse projects
To create new entities and mappings if the selected entities and mappings
already exist, clear the Replace existing entities and mappings check box.
The new entities/mappings will be named <existing_name>_IMPORTED (or <existing_
name>_IMPORTED_<n+> if the entity/mapping is imported more than once).
6. In the Mappings tab:
Either click Finish to import all mappings for the selected entities (the default).
OR
Select which mappings you want to import and then click Finish to import the selected
entities and mappings.
If you do not wish to import any mappings, clear the Mappings check box before
clicking Finish.
Importing the model from ERwin
In order to import a model created in ERwin, you first need to export the model from ERwin to an
XML file and then copy the XML file to the Compose Server machine. Note that when you import a
model from ERwin, you need to create the Mappings ETL scripts manually. You can either do this by
creating global mapping as described in
Managing global mappings (page 161)
below or you can
create the mapping ETL directly in the Data Warehouse panel.
For more information on creating the ETL mapping(s) in the Data Warehouse panel, see
Creating
and managing the data warehouse (page 192)
.
To import the model from ERwin:
1. Open your project.
2. To import a model created in ERwin, in the Model panel, select Import from ERwin from the
drop-down menu in the top right corner.
OR
In the Manage Model window, select Import from ERwin from the Entities drop-down menu.
The Import from ERwin window opens.
3. Specify the full path to the ERwin XML file.
4. If you have set up global mappings, select the Use Global Mappings check box. For details,
see
Managing global mappings (page 161)
.
5. Select one of the following Read entities from options:
l
Logical model - Allows you to import logical entities and attributes.
l
Physical model - Allows you to import physical entities and attributes, exactly as they
appear in the source database.
6. Select a source database and then click OK.
The Select Tables/Views window opens.
7. Continue from Step 4 in
Generating the model (page 155)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
160

5 Data Warehouse projects
Managing global mappings
Before you import a data model from ERwin, you can set up the global mappings from the logical
ERwin model (the entities and attributes) to the physical source database (the tables and columns).
This is useful if numerous entities in your model contain the same attribute. For example, lets
assume that twenty source entities contain an attribute called "BusinessKey". In the physical source
tables however, this column (which also appears in twenty tables) is called "Key". Using the Global
Mappings feature, you only need to define the "Key-to-BusinessKey" mapping once instead of
twenty different times.
When you import from ERwin, you can then select the Use Global Mappings check box to apply
these mappings. See also
Importing the model from ERwin (page 160)
.
You can add, edit, and remove entity and attribute mappings. If needed, you can also change the
source database referenced for the tables (if you have several different sources defined).
To manage global mappings:
1. In the Model panel, from the drop-down menu in the top right, select Global Mappings.
The Global Mappings window opens in the Tables to Entities tab.
2. Import the ERwin entities:
1. Click Import Entities to Mappings toolbar button.
The Import Entities window opens.
2. In the File Path field, enter the full path to the
ERwin.xml
file (on the Compose Server
machine) that includes the entities you want to import.
3. Click OK.
3. Verify that Qlik Compose is using the desired source database. The database name is
displayed in green at the bottom right of the toolbar.
To select a different source database:
1. Click Change Source Database.
2. In the Set Source Database window, select a different database and then click OK.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
161

5 Data Warehouse projects
4. Add new entities, edit existing entities, or remove entities as described in the following table:
To Do This
Add a new
entity
1. In the Tables to Entities tab, click the New toolbar button.
2. Next to the Entity Name field, click the browse button.
The Unmapped Entities window opens, listing only entities that
have not yet been mapped.
3. Select an entity and click OK.
4. Next to the Table Name field, click the magnifying glass icon.
The Find Table for [Entity Name] window opens for the selected
entity.
5. From the Tables drop-down list on the left, select the table to map
to.
6. Click OK. Qlik Compose populates the Table Schema field
automatically, based on the table you selected.
7. Repeat these steps for all unmapped entities.
Edit an entity 1. Move the mouse cursor over the entity and click the Edit button
(pencil icon) that appears on the right.
2. Make the required changes and click OK.
Delete an
entity
1. Select the entity.
2. In the Entities toolbar, click Delete.
3. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes.
Search for an
entity
In the Search look-up field, start typing. Qlik Compose only displays
entities that match the search string.
Entity management options
5. Add, edit, or remove attributes as described in the table below:
To Do This
Add a new
attribute
1. In the Columns to Attributes tab, click the New toolbar button.
2. Provide a name and description (optional) for the attribute and the
column.
3. Click OK.
Attribute management options
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
162

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Search for
an
attribute
In the Search look-up field, start typing. Only attributes that match the
search string will be displayed.
When searching for an attribute based on the attribute name, you
must add the prefix "name:". For example, if you want to search for
an attribute that contains “ar” in its name, type “name: ar” in the
Search look-up field.
Edit an
attribute
1. Move the mouse cursor over the attribute and click the Edit button
(pencil icon) that appears on the right.
2. Make the required changes and click OK.
Remove
an
attribute
1. Select the attribute.
2. Click the Delete toolbar button.
3. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes.
6. Click Close.
Model limitations
l
When Amazon Redshift is the data warehouse type, attribute names that contain the open
parenthesis character "(" are not supported. If any of your attribute names contain the "("
character, you should remove it before creating the data warehouse tables.
For information on renaming attribute names, see
Add an attribute to all Satellite tables and
the Hub table (page 171)
.
l
Discovering new tables does not affect existing entities in the model, even if there is a
relationship between the new entity and one of the existing entities. For example, in the
source database, Table 1 has a Foreign Key that points to Table 2. If Table 1 is added to the
model and then Table 2 is added later, Table 1 will not be updated to contain the required
Foreign Key.
l
The data warehouse needs to be "adjusted" when deleting a relationship/attribute from the
model and then adding the same relationship/attribute back to the model. However, the
"Adjust" operation deletes the data from the corresponding data warehouse column.
Validating the model
Once you have generated the model, you can easily check that it is valid. For example, for a model
to be valid, each of the tables must have a Business Key.
Validating the model does not recalculate expressions for historical data that has
changed. Changes in a dimension expression or lookup of a column in a dimension are
not updated retroactively. In order to update historical data, you would need to reload
the data which could take a long time depending on the number of records and their
history.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
163

5 Data Warehouse projects
To validate the model:
1. Either click the Validate button in the bottom right of the Model panel.
OR
Select Validate from the drop-down menu in the top right of the Model panel.
The Validate Model window opens.
a. If the model is valid, a message will confirm the model’s validity. If the model is not
valid, a list of invalid tables/views will be displayed.
A message indicating why the entity is invalid will be displayed in the Message
column.
b. To resolve the issue, click the Edit Entities button to the right of the entity.
The Edit Model window opens showing the invalid entity.
2. Resolve the issue (in this case, by adding a Business Key) and then click Close.
A message will confirm the model’s validity.
3. Click Close to close the Validate Model window.
Displaying the model
Displaying the model is a good way to see the relationships between the various tables and/or
views in your model.
To display the model:
Either click the Display button in the bottom right of the Model panel.
-OR-
Select Display from the drop-down menu in the top right of the Model panel.
The Display Model window opens showing the Diagram tab.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
164

5 Data Warehouse projects
Diagram tab
In the Diagram tab, the following options are available:
You can select multiple entities by clicking them while holding down the [Ctrl] keyboard
button.
l
Zoom - Increase or decrease the magnification using the slider at the top right of the screen.
Click the button to the right of the slider to restore the default size.
l
Search - The ability to search for entities is particularly useful in a large model. To search for
an entity, type a search string in the Search box. Compose lists the names of entities that
match the search string. Select the desired entity.
l
Drag the diagram - In addition to zooming, you can also drag the diagram by clicking the
space around the diagram and dragging. This is useful for very large diagrams where
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
165

5 Data Warehouse projects
zooming out would render the text unreadable. The guide at the bottom right of the window
shows you which part of the diagram is currently displayed.
l
Show/Hide all attributes for a selected entity - Select an entity and then select/clear the
Attributes check box in the top left of the window.
l
Show/Hide all business keys in the model - Select/Clear the Keys check box in the top left
of the window.
l
Show/Hide relationship attributes - Right-click an entity and select this option to to
show/hide the entity's relationship attributes.
l
Show/Hide business keys - Right-click an entity and select this option to to show/hide the
entity's business keys.
l
Change the Diagram Direction - Select one of the available options from the Direction
drop-down list at the top of the window.
l
Set as relationship source - See
Creating and managing relationships (page 176)
.
l
Hide this node - Right-click an entity and select this option to show/hide the entity. To show
the entity, click the Hidden Nodes box in the left of the window.
l
Hide selected nodes - Right-click an entity and select this option to show/hide selected
entities. To show the hidden entities, click the Hidden Nodes box in the left of the window.
l
Hide non-selected nodes - Right-click an entity and select this option to show/hide non-
selected entities. To show the hidden entities, click the Hidden Nodes box in the left of the
window.
l
Invert selection - Right-click an entity and select this option to highlight all entities except
the selected entity.
l
Select all - Right-click an entity and select this option to highlight all entities in the model.
l
Select path - To highlight the path to which an entity belongs, either hover your mouse
cursor over the entity or right-click the entity and select Select Path.
l
Select path and hide all other nodes - Right-click an entity and select this option to
highlight the entity’s neighbors.
l
Edit - Either double-click the entity or right-click an entity and select the Edit option to edit
the entity’s attributes.
l
Lineage - Right-click an entity and select this option to show/hide the entity’s lineage. For
more information on lineages, see
Lineage and impact analysis (page 179)
.
Tree View tab
In the Tree View tab, the following options are available:
l
Search for an entity or attribute - To search for a specific entity or attribute, enter a part of
the name in the Search box. Entities that match the search string will be highlighted.
l
Expand/Collapse - Click the arrow to the left of a table to see its attributes or related tables.
To show or hide all sub-tables and table attributes, click the Expand All/Collapse All buttons
at the top of the Tree View tab.
l
Lineage - To see an entity or attribute's lineage, hover your mouse over a table or attribute
and then click the button that appears to its right.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
166

5 Data Warehouse projects
For example, clicking the button next to the City attribute (shown in the image above)
will open the following window:
For more information on lineages, see
Lineage and impact analysis (page 179)
.
Managing the model
You can manage the model according to your needs, as described in the following topics:
l
The Manage Model window (page 168)
l
Managing entities (page 168)
l
Creating and managing relationships (page 176)
l
Managing attributes (page 169)
l
Bulk Editing History types and Satellite numbers (page 179)
l
Lineage and impact analysis (page 179)
There are two ways of editing a model in Compose:
l
In the Manage Model window - Editing the model in the Manage Model window is
preferable if you need to make several changes to the model as it provides access to all of
the model’s entities and attributes. To display the results of your changes, open the Model
Display window as described in
Displaying the model (page 164)
.
l
From the Model Display - Editing the model from the Model Display window is convenient if
you only need to edit one or two entities. Another advantage of this method is that it allows
you to see the result of your changes (in the entity relationship diagram) immediately.
To open the Manage Model window from the Model panel:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Model panel or click the Entities link in the
Model panel.
The Manage Model window opens.
2. Edit the model according to the descriptions below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
167

5 Data Warehouse projects
To open the Manage Model window from the Model Display window:
1. Open the Model Display window as described in
Displaying the model (page 164)
.
2. Double-click the entity you want to edit.
The Manage Model window opens.
3. Edit the model according to the descriptions below.
The Manage Model window
The Manage Model window is split into two tabs: The Logical Model tab and the Physical Model
tab. The Logical Model tab shows the entities and attributes as they appear in the model whereas
the Physical Model tab provides a preview of the actual tables (and columns) that will be created in
the data warehouse. So, for example, although the Categories table appears as a single entity in
the Logical Model tab, it will appear as two tables (TDWH_Categories_HUB and TDWH_
Categories_S01) in the Physical Model tab. The reason for this is because the logical Categories
entity contains both Type 1 and Type 2 attributes. Type 1 attributes will be created as columns in
the HUB table while Type 2 attributes will be created as columns in the Satellite table (S01). For
more information on Type 1 and Type 2 attributes, see History.
All editing tasks are performed in the Logical Model tab, except for the following tasks which are
performed in the Physical Model tab:
l
Designate a Distribution Key Column (Amazon Redshift data warehouse only)
l
Designate a Distribution Method (Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics only)
For more information, see
Defining Table Creation Modifiers (page 181)
.
Managing entities
You can add, edit and remove entities from your model as described in the table below.
All of the options available in the toolbar are also available from the drop-down menu in
the toolbar. This is useful when you reduce the window size, since some of the toolbar
buttons - or all of them depending on how small you make the window - will be hidden.
The only button that will not be hidden regardless of the eventual window size is the
drop-down menu button.
To Do This
Add an entity 1. Click the New Entity button in the Entities toolbar.
2. Provide a name and description (optional) for the entity and then
click OK.
Edit an entity 1. Select the entity you want to edit and then click the Edit button in
the Entities toolbar.
2. Edit the entity’s name and description (optional) and then click OK.
Entity management options
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
168

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Remove an entity 1. Click the Delete button in the Entities toolbar.
2. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes.
Duplicate an entity 1. Select the entity you want to duplicate and then select Duplicate
from the drop-down menu in the Entities toolbar.
2. Edit the entity’s name and description (optional) and then click OK.
The duplicated entity is added to the Entities list.
Import entities from
another project
See
Importing entities and mappings from another project (page 159)
.
Import entities from
ERwin
See
Importing the model from ERwin (page 160)
.
Managing attributes
You can add, edit and remove attributes as required. All attributes in the model belong to the
Attributes Domain. When adding a new attribute, you can either select an existing attribute from the
Attributes Domain or create a new Attributes Domain. Both of these options are described in the
table below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
169

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Add an
attribute from
the attributes
domain
1. Click the New Attribute button in the Attributes toolbar.
The New Attribute window opens.
2. To designate the attribute as a business key, select the Key check box.
3. From the Attribute domain drop-down list, select the attribute domain
you wish to add.
4. To edit the selected attribute domain on-the-fly, click the edit button
located after the Attribute domain drop-down list. This will open the Edit
- AttributeDomainName window. Then, continue from Step 2 in Edit an
attribute domain.
5. In the Attribute name field, optionally change the default instance name
for the attribute domain.
You can create multiple instances of a single Attribute Domain. This is
especially useful if you want to use the same Attribute Domain across
multiple tables, with each "instance" having its own unique name. This
also allows you to edit the properties of each attribute without affecting
the other attributes, despite all the Attribute Domain instances sharing a
common Attribute Domain. For example, if the Attribute Domain name is
"ID", you could create one instance for it in the "Categories" entity named
"CategoryID" and another instance in the "Employees" entity named
"EmployeeID". If, however, you edit the parent Attribute Domain attribute,
all instances of that attribute will be updated as well.
6. To add a prefix to the attribute name, enter the desired prefix in the Prefix
field.
Adding a prefix to an attribute name allows you to add multiple instances
of the same attribute domain. For example, the attribute "Employee"
could become two different attributes: "ReportsTo_Employee" and
"HiredBy_Employee".
7. Set the History Type and Satellite number. When the History Type is set
to 2, a new record will be created in the data warehouse each time an
attribute value changes.
8. In the Satellite/Hub field, optionally change the satellite number. Note
that the satellite number can only be changed when the History Type is
set to 2. For an explanation of why this is so, see
The Manage Model
window (page 168)
.
9. To add an expression, click the fx button located after the Expression
field and then continue from
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
10. Click OK to save your settings.
Attribute management options
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
170

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Create a new
attribute
domain and
add it to the
model
1. Click the New Attribute button in the Attributes toolbar.
The New Attribute window opens.
2. To designate the attribute as a business key, select the Key check box.
3. Click the plus sign to the right of the Attribute domain drop-down list.
The New Attribute Domain window opens.
a. Specify a Name for the attributes domain.
b. From the Type drop-down list, select one of the available data
types.
c. If the selected data type requires further configuration, additional
fields will be displayed. For example, when Decimal is selected, the
Length and Scale fields will be displayed. Set the values as
desired.
d. Optionally, specify a Description.
e. Click OK to add the newly created attribute domain to the
Attribute domain field and close the New Attribute Domain
window.
4. Continue from Step 5 in Add an existing attribute domain above.
You can also add new attribute domains via the Manage
Attribute Domains window. For more information, see
Managing the Attributes Domain (page 175)
Add a
relationship
See
Creating and managing relationships (page 176)
.
Add an
attribute to all
Satellite
tables and
the Hub table
You can use the Add to all Satellites and Hub option to define the same Primary
Index for the Hub table and all Satellite tables.
Select the desired attribute and then click the Add to all Satellites and Hub
toolbar button. The attribute is added to the Hub table and to all the Satellite
tables.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
171

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Edit an
attribute
Method 1:
1. Select the attribute you want to edit and then click the Edit button in the
Attributes toolbar.
The Edit - AttributeName window opens
2. Continue from Step 2 of Add an attribute from the attributes domain
above.
Method 2:
1. Double-click the attribute you want to edit.
The values in the attribute row become editable.
2. Continue from Step 2 of Add an attribute from the attributes domain
above.
Bulk edit
history types
and satellite
numbers
See
Bulk Editing History types and Satellite numbers (page 179)
.
Show an
attribute's
lineage
See
Lineage and impact analysis (page 179)
.
Remove an
attribute
1. Select the attribute(s) you want to delete.
2. Click the Delete button in the Attributes toolbar.
3. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes.
Change the
attribute
order
Select the attribute you want to move and use the Move Up/Move to Top and
Move Down /Move to Bottom toolbar buttons to move the attribute.
Search for an
attribute
In the Search lookup field, start typing. Only attributes that match the search
string will be displayed.
When searching for an attribute based on the attribute name, you
must add the prefix "name:". For example, if you want to search for an
attribute that contains “ar” in its name, type “name: ar” in the Search
look-up field.
Manage the
Attributes
Domain
See
Managing the Attributes Domain (page 175)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
172

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Create an
expression
for an
attribute
See Add an attribute from the attributes domain or Edit an attribute above.
Export the
attributes to a
CSV file
Select an entity from the Entities list on the left of the Manage Model window
and then select Export to CSV from the drop-down menu in the Attributes
toolbar. Depending on your browser settings, you will either be prompted to
download the <entityname>_Attributes.csv file or it will be downloaded to your
default Downloads location.
The CSV format differs slightly from the CSV format when Exporting
and importing projects using the CLI (page 77).
Setting up derived attributes
Derived attributes are attributes whose data is "derived" from other attributes. For example, lets
assume that the OrderDetails entity contains the attributes Quantity and UnitPrice but does not
contain the attribute TotalPrice. To gain better insight into the annual sales figures, the
organization would like to add the TotalPrice attribute to the model and derive its data from the
Quantity and UnitPrice attributes.
Assuming that the Northwind sample database is the model’s source, this could easily be done as
follows:
1. Add the TotalPrice attribute domain to the model as described in
Managing attributes (page
169)
.
2. After finalizing the model, create the data warehouse tables as described in
Creating the
data warehouse tables (page 194)
.
3. Click the OrderDetails mapping as described in
Editing column mappings (page 205)
.
Note that the TotalPrice attribute has no mapping as it was added after the Northwind
source was discovered:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
173

5 Data Warehouse projects
4. Open the Expression Builder by clicking the fx icon to the right of the TotalPrice column
name. Then, in the Expression Builder, add the Quantity and UnitPrice columns to create the
following expression:
Quantity*UnitPrice
For more information on creating expressions, see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
5. Click OK to close the Expression Builder and save the expression.
The Quantity and UnitPrice landing zone columns are now mapped to the TotalPrice data
warehouse column. Notice that the mapping lines are gray, indicating that the mapping is the
result of an expression.
Hovering the mouse cursor over the gray lines highlights the derived column (TotalPrice) and
the columns from which its data is derived (Quantity and UnitPrice).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
174

5 Data Warehouse projects
Managing the Attributes Domain
The Attributes Domain provides a list of all the attributes available in the Compose model, as well as
their data type. You can add, edit and delete attributes according to your data warehousing needs.
The Attributes Domain also allows you to see which entities each attribute belongs to, as a single
attribute may be present in several entities.
To manage the Attributes Domain
1. From the drop-down menu in the top right of the Model panel, select Attributes Domain.
2. Add, delete and edit attributes as describe in the table below.
To Do This
Add an
attributes
domain
1. Click the New Attributes Domain toolbar button.
The New Attribute Domain window opens.
2. In the Name field, specify a name for the attribute.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select one of the available data types.
4. If the selected data type requires further configuration, additional fields will
be displayed. For example, when Decimal is selected, the Length and Scale
fields will be displayed. Set the values as desired.
5. Optionally specify a Description.
6. Click OK to add the attribute and close the New Attribute Domain window.
Attribute domains names are case insensitive. For example, a project
cannot contain one attribute domain called date and another called
DATE.
Attribute Domain management options
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
175

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Edit an
attribute
domain
1. Select the desired attribute and then click the Edit toolbar button.
The Edit: Name window opens.
2. Edit the attribute as described in steps 2-6 of Add an attributes domain
above.
Note that the Edit: Name window also contains a Used in Entities list.
Knowing which entities the attribute is used in may affect the type of
changes you make, as the planned changes may not be appropriate for all
entities.
Remove an
attribute
1. Select the attribute you want to delete and then click the Delete toolbar
button.
2. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes.
Creating and managing relationships
Similar to a foreign key, a relationship "attribute" is a special type of attribute that points to another
entity in the same model. Typically, the relationship replaces the key attributes that connect an
entity to a related entity. You can add, edit and delete relationships as required.
Possible reason for creating relationships are as follows:
l
If your model is derived from the landing zone (as opposed to the source database(s)), the
model will be created without any relationships
l
Ensure data integrity between related entities
You can create relationship from the Manage Model window or from the Display Model window.
Both of these methods are described below.
When converting existing columns in a table with a relationship to another table,
historical values may be lost and need to be loaded again or reinserted manually.
Adding relationships via the Manage Model window
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Model panel.
The Manage Model window opens.
2. Select an Entity in the Entities list.
3. Click the Add Relationship button in the Attributes toolbar.
The Add Relationship From: Name window opens.
4. From the Add Relationship to Entity drop-down list, select the entity to which you want to
create a relationship.
5. If the originating entity contains attributes that were foreign keys in the source database, you
can replace these attributes with Business Key attributes of the associated entity.
To do this:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
176

5 Data Warehouse projects
a. Select the Replace Existing Attribute(s) check box.
The left column shows the Business Key Attributes of the Associated Entity.
b. From the Attributes of Originating Entity drop-down list on the right, select an
attribute from the originating entity that was meant to be a foreign key.
6. If you want the relationship attribute to be a Business Key, select the Business Key check
box. This option will only be displayed if the entity target can be designated as a Business
Key.
7. Set the History Type.
Since the history type for Business Keys must be type 1, the option to change the
history type is unavailable when the Business Key check box is selected.
8. Set a Satellite Number.
Since the satellite number for Business Keys must be "0", the option to change the
satellite number is unavailable when the Business Key check box is selected.
9. Optionally, specify a prefix.
10. Optionally, enter a description.
11. Click OK to save your settings.
Adding relationships via the Display Model window
1. Click the Display button in the bottom left of the Model panel. The Display Model window
opens.
2. Select one of the following methods:
l
Method 1: Right-click an entity and select Add Relationship.
The Add Relationship From: Name window opens.
l
Method 2: Right-click an entity and select Set as Relationship Source. This method is
useful if you need to search your model for the relationship target entity (since the
source entity remains selected while you search).
l
Method 3: Select two entities by clicking them while holding down the [Ctrl] key.
Then, right-click one of the entities and select the desired relationship from the
context menu (according to the entity that you want to be the relationship source), as
shown in the following example:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
177

5 Data Warehouse projects
3. If you selected Method 2, continue below. If you selected Method 1, continue from Step 4 in
Adding Relationships via the Manage Model window above. If you selected Method 3,
continue from Step 5 in Adding Relationships via the Manage Model window above.
4. Right-click the relationship target entity and select Relationship Target for Relationship
Source Name.
The Add Relationship: Name window opens with the relationship target entity already
selected.
5. If the originating entity contains attributes that were foreign keys in the source database, you
can replace these attributes with Business Key attributes of the associated entity.
To do this:
a. Select the Replace Existing Attribute(s) check box.
The left column shows the Business Key Attributes of the Associated Entity.
b. From the Attributes of Originating Entity drop-down list on the right, select an
attribute from the originating entity that was meant to be a foreign key.
6. If you want the relationship attribute to be a Business Key, select the Business Key check
box. This option will only be displayed if the entity target can be designated as a Business
Key.
7. Set the History Type.
Since the history type for Business Keys must be type 1, the option to change the
history type is unavailable when the Business Key check box is selected.
8. Set a Satellite Number.
Since the satellite number for Business Keys must be "0", the option to change the
satellite number is unavailable when the Business Key check box is selected.
9. Optionally, specify a prefix.
10. Optionally, enter a description.
11. Click OK to save your settings.
Preventing naming conflicts
When a relationship from entity A to entity B is created, Compose implicitly adds entity B’s primary
key columns to table A. This means that if there are two or more relationships from entity A to entity
B, a column naming conflict will arise (as entity B’s primary key columns will be added to table A
multiple times). Such conflicts can easily be avoided by adding a meaningful prefix to the
relationship attributes in entity A, which will result in the prefix being added to the physical columns
as well.
Example:
The Orders entity contains two attributes that are related to the People entity: the Customer and
Seller attributes. Therefore, Mike wants to create two relationships from the Orders entity to the
People entity. The primary key of the People table consists of the FirstName and LastName
attributes. As there are two relationships, the primary key columns of the People entity will be
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
178

5 Data Warehouse projects
added twice to the Orders entity. To prevent duplication errors, Mike adds the Customer_ and
Seller_ prefixes to the relationship attributes in the Orders entity, which results in the physical
columns Customer_FirstName, Seller_FirstName, Customer_LastName, and Seller_LastName.
Deleting relationships
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Model panel.
The Manage Model window opens.
2. Select the relationship attribute you want to delete.
3. Click the Delete button in the Attributes toolbar.
The Delete Relationship window opens.
4. To restore an attribute that was replaced when the relationship was created, select the
Restore original attribute(s) check box. For more information about replacing attributes,
see Step 5 in Adding relationships via the Manage Model window above.
5. Click Yes to delete the relationship attribute.
Bulk Editing History types and Satellite numbers
Use the Bulk Edit feature to edit the History type and Satellite number of multiple attributes.
To bulk edit history types and satellite numbers:
1. Select the attributes whose History type and/or Satellite number you want to change and
click the Bulk Edit toolbar button.
2. In the Bulk Edit window, change the History type and/or Satellite number as required.
3. Click OK close the Bulk Edit window and save your settings.
Lineage and impact analysis
Before editing an entity or attribute, you may want to see which other entities/attributes in the
entity’s/attribute’s lineage will be impacted by the change. For example, removing the "Discount"
attribute from a table will affect the "Total Price". Additionally, a single attribute may have different
names depending on its location.
Places where you can view lineage in Compose:
l
The Manage Model window described below.
l
The Display Model window described in
Displaying the model (page 164)
.
l
When editing a data mart. For more information, see
Managing data marts (page 237)
.
Top-level entities in the data mart fact will not be shown in the lineage. For example, if
both the Orders and Order Details entities are used in a Fact, the Model lineage for
Orders will show Order Details but not Orders.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
179
5 Data Warehouse projects
To view the lineage of an entity or attribute:
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Model panel.
The Manage Model window opens.
2. Display the lineage as described below:
To Do This
Show an entity’s
lineage
Select the entity and select Show Lineage from the drop-down menu in
the Entity toolbar.
Show an attribute’s
lineage
Select the attribute and click the Show Lineage button in the Attribute
toolbar.
Lineage procedures
Adding Date and Time entities to your model
Compose provides built-in Date and Time entities that you can add to your model. This facilitates
access to all attributes of date and time (such as day of the week, quarter, and so on) both in the BI
reports and when creating transformations in the data mart.
The Date entity contains a record for every day. Dates in the Date entity range from January 1st
1900 to December 31st 2099.
The Time entity contains all the hours and minutes in a 24 hour period. When you create the data
warehouse tables, the Date and Time entities are automatically populated with relevant data. You
can view this data as described in
Viewing the data warehouse tables (page 195)
.
Both the date and the time values are presented in multiple formats (e.g. 12 hour format or 24 hour
format), allowing you to choose which format will be displayed in your BI reports. Other format
include abbreviated forms of date and time, different month/year/day formats (e.g. 12/31/2017 as
opposed to 2017-12-31), and so on.
You can either add the entities to a new project (before you create the Data Warehouse tables) or
to an existing project. If you add them to an existing project’s model, you will also need to validate
and adjust the Data Warehouse as described in
Validating the data warehouse (page 226)
.
You can even add custom date and time attributes to the entities from the tables in your landing
zone. For example, if one of your source tables lists all the working days and non-working days, you
can add an "Is Working Day" attribute to the Date entity and then load it from the relevant source
table. Just like regular entities, Compose knows how to merge the incoming data of working and
non-working days into the existing Date entity.
For an explanation of how to add attributes to an entity, see
Managing attributes (page 169)
.
You cannot add relationships to the Date and Time entities. However, every date and time attribute
has an implicit relationship to the Date and Time dimensions, which allows you to select the relevant
dimension when creating your star schema in the data mart.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
180

5 Data Warehouse projects
For information on working with Date and Time dimensions in the data mart, see
Creating and
managing data marts (page 228)
.
For all of the supported data sources except Oracle, you can add both Date and Time
entities to your model. If you are using Oracle as your data source, you can only add the
Date entity to you model. This is because Oracle does not have a data type specifically
for Time.
To add Date and Time entities to your model:
1. Open the desired Compose project.
2. From the drop-down menu in the top right of the Model panel, select Add Date and Time
entities or Add Date Entity if you data source is Oracle (see Note above).
3. When prompted to confirm the action, click Yes.
4. The Date and Time entities will be added to your model. By default, the Date and Time
entities are hidden from the model display (as they are not related to other entities in your
model). If you want to show them anyway, select the Date and Time model check box in the
Data Warehouse Model window.
5. For information about displaying the model, see
Displaying the model (page 164)
.
You can also delete the Date and/or Time entities if you no longer require them
and add them again later.
Defining Table Creation Modifiers
You can set table modifiers for individual entities in the Physical Model tab, thereby overriding the
default settings in the project settings'
Table creation modifiers tab (page 42)
Table modifiers allow
you to append additional table properties to the default Compose CREATETABLE statement.
The available options are located below the Columns list on the right of the tab, and are as follows:
l
Project settings default - When this option is selected (the default), the settings from the
project settings'
Table creation modifiers tab (page 42)
will be used.
l
Custom - This option is useful for appending additional table properties to the default
Compose CREATETABLE statement. Leveraging this option requires SQLcoding knowledge.
l
Custom distribution keys - This option is useful if you only need to define custom
distribution keys for individual entities. Although this can also be done using the Custom
option (see below), the Custom distribution keys option is more convenient as it does not
require any prior SQL knowledge.
l
Supported with Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics and Amazon Redshift
only.
l
The default distribution key for all data warehouse tables is the ID column.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
181

5 Data Warehouse projects
Setting table creation modifiers
By default, Compose creates tables in the data warehouse using the standard CREATE TABLE
statement. However, organizations often need tables to be created with custom properties for
better performance, special permissions, custom collation, and so on. For example, in Microsoft
Azure Synapse Analytics, it’s possible to create a table as a HEAP, which is optimized for smaller
tables. By default, Compose creates tables in Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a CLUSTERED
COLUMNSTORE INDEX, which offers the best overall query performance for large tables.
The procedure for settings table modifiers is as follows:
1. In the Physical Model tab, select the desired entity.
2. Select the Custom option.
3. Click the Edit button to open the Table Creation Modifier editor.
4. Enter the SQL parts you wish to append to the CREATE TABLE statement.
5. Optionally, but strongly recommended, validate the SQL in an external validation tool that
supports your specific database and version. For instance, if you are validating
Compose does not provide any way of validating your SQL. Therefore, make sure
to validate the SQL before deploying in a production environment.
6. Click OK to close the editor and save your SQL parts.
Example of a Valid Table Creation Modifier
In the following example, the Compose CREATE TABLE statement (rows 1-5) is appended with an
SQL part instructing Compose to create the table as a HEAP (row 6).
CREATE TABLE MyTable
(
column1 integer,
column2 varchar(50),
)
WITH (HEAP)
Setting Custom Distribution Keys
This section describes how to set a custom distribution key for tables created in Amazon Redshift
and Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics. Note that depending on the selected Distribution Style
(Amazon Redshift) or Distribution Method (Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics), some of the
options may not be available.
Setting a distribution key for Amazon Redshift Data Warehouse
Select and entity and then set a distribution key for Amazon Redshift Data Warehouse according to
the table below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
182

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Set a distribution style From the Distribution Style drop-down, select Even, Key or All.
For more information on distribution styles, see:
Distribution styles - Amazon Redshift
Add a distribution key 1. Click the Add Distribution Key button.
A row is added to the table displaying a drop-down list.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Edit a distribution key 1. Double-click the row.
A drop-down list will be shown in the Column column.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Delete a distribution key Select the distribution key and then click the Delete button. The key
is deleted.
Change the position of a
distribution key
Select the distribution key and then click the "Up" or "Down" buttons
to move the key to the desired position.
Distribution key procedures
Setting a distribution key for Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics
Select and entity and then set a distribution key for Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics according to
the table below.
To Do This
Set a distribution
method
From the Distribution Method drop-down, select Hash, Round
Robin or Replicate.
For more information on the distributions options, see:
Guidance for designing distributed tables in Synapse SQL pool -
Microsoft Azure
Add a distribution key 1. Click the Add Distribution Key button.
A row is added to the table displaying a drop-down list.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Edit a distribution key 1. Double-click the row.
A drop-down list will be shown in the Column column.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Delete a distribution key Select the distribution key and then click the Delete button. The key
is deleted.
Change the position of a
distribution key
Select the distribution key and then click the "Up" or "Down" buttons
to move the key to the desired position.
Distribution key procedures
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
183

5 Data Warehouse projects
Creating expressions
Compose allows you to create data transformations in several different places according to your
needs. A transformation can either be a filter (i.e. excluding certain data) or an expression (i.e.
manipulating a single record). The table below lists the places where transformations can be
created and provides reasons for creating the transformation in each of the specified places.
Changes in a dimension expression or lookup of a column in a dimension are not updated
retroactively. In order to update historical data, you would need to reload the data which
could take a long time depending on the number of records and their history.
Where the
Transformation is
Created
Reasons to Create a Transformation There
When the Transformation
is Applied
Replicate
l
Filtering large amounts of data that is
not needed for the data warehouse (in
the present or the future)
l
Obfuscation due to regulatory reasons
or internal policies
l
Data type conversion (e.g. converting
a source data type that is not
supported on the data warehouse
platform)
Before the data reaches the
landing zone.
Model
l
The default location if you are not sure
where to put it
l
General business logic
l
Needed for several sources or several
data marts
Applied as an update to the
staging tables after creating
the mappings.
Data Warehouse
l
Specific source preparation
l
Needed for merging several sources
Between the landing zone
and the staging zone.
Data Mart
l
Specific to a data mart
l
Managed by a data mart data
specialist
Between the data
warehouse and the data
mart.
Data transformation location comparison
See also
Defining reusable transformations (page 191)
.
The following topics describe the Expression Builder:
l
Opening the expression builder (page 185)
l
Expression builder overview (page 185)
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
184

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Building expressions (page 186)
l
Testing expressions (page 188)
Opening the expression builder
The Expression Builder enables you to create a transformation without needing to type anything
manually.
The Expression Builder can be opened in several places, depending on your needs. For more
information about where to create a transformation, see the table in
Creating expressions (page
184)
.
Expression builder
Expression builder overview
The following section provides an overview of the Expression Builder functionality.
The Expression Builder consists of the following panels:
l
Tabs on the left of the Expression Builder: These tabs contains elements that you can add
to an expression. Select elements and add them to the Build Expression pane to create an
expression. For more information, see
Building expressions (page 186)
.
The following tabs are available:
l
Parameters - Only displayed when opening the Expression Builder from within the
Reusable Transformations > Edit Transformation window.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
185

5 Data Warehouse projects
For information on reusable transformations, see
Defining reusable transformations
(page 191)
below.
l
Input Columns/Input Attributes - Columns/attributes that can be used to build your
expression.
l
Transformations - Contains a list of reusable transformations. The tab is not
displayed if no reusable transformations have been defined.
For information on reusable transformations, see
Defining reusable transformations
(page 191)
below.
l
Operators - Operators that can be used to build your expression.
l
Functions - Functions that can be used to build your expression.
The Operators and Functions displayed in the Expression Builder use SQL
format. As SQL support and implementation is different for each data
warehouse (i.e. database) type and version, the data warehouse being
used in your Compose project will determine which Operators and
Functions will be available. For example, functions introduced with
Microsoft SQL Server 2017 will not work if the database being used for the
data warehouse is Microsoft SQL Server 2015.
Additionally, the list of Operators and Functions displayed in the Expression
Builder is not comprehensive. However, you can use any Operators and
Functions supported by the data warehouse, even if they are not included
in the list.
For an explanation of the available Operators and Functions, refer to the
Help for your data warehouse.
l
Build Expression Pane: The Build Expression pane is where you build your expression. You
can add elements, such as columns or operators to the panel as well as type all or part of the
expression. For more information, see
Building expressions (page 186)
.
l
Parse Expression Pane: This pane displays the parameters for the expression. After you
build the expression, click Parse Parameters to list the expression parameters. You can then
edit the parameters, enter a value for each of the parameters and associate attributes with
them. For more information, see
Parsing expressions (page 187)
.
l
Test Expression Pane: This panel displays the results of a test that you can run after you
provide values to each of the parameters in your expression. For more information, see
Testing expressions (page 188)
.
Building expressions
The first step in using the Expression Builder is to build an expression in the Build Expression pane.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
186

5 Data Warehouse projects
To add operators to your expression, you can use the Operator tab on the left or the
Operator buttons located above the Build Expression pane or any combination of
these.
To build an expression:
1. Hover the mouse cursor over the element that you want to add to your expression
(expressions usually start with an Input Column) and click the arrow that appears to its right.
2. Add Operators additional Input Columns and Functions as required.
To add operators to your expression, you can use the Operator tab on the left or the
Operator buttons located above the Build Expression pane or any combination of
these.
Example:
To create an expression that combines the FirstName name and LastName columns, do the following:
1. Add the FirstName Input Column to the Build Expression pane.
2. Assuming that Microsoft SQL Server is the data warehouse, in the Operator toolbar above
the Build Expression pane, click the concatenate (+) operator.
3. Then add a space between single quote characters and click the concatenate (+) operator
again.
4. Add the LastName Input Column to the Build Expression pane.
The expression would look like this:
Parsing expressions
When you add operators to the expression, the expression’s parameters are usually added
automatically to the Parse Expression pane. However, when you complete your expression or edit
it, you may need to parse the expression see all of the parameters.
To parse the expression parameters:
l
Click the Parse Expression button below the Build Expression pane.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
187

5 Data Warehouse projects
If the expression is not valid, a red error message will appear at the bottom of the Expression
Builder window.
If the expression is valid, the expression parameters and attributes (Input Columns) will be
displayed in the in the Parse Expression pane. See
Testing an expression (page 189)
.
Editing parameter names
By default, the parameter name is the same as the input column name. However, you can change
the parameter name as needed and then associate it with an input column. This is useful, for
instance, when you need to shorten attribute names. For example, EstimatedTimeOfArrival can be
abbreviated to ETA.
To edit a parameter and associate it with an input column:
1. In the Parse Expression pane, edit the parameter name as required.
2. From the Attribute drop-down list, select the desired input column.
Testing expressions
You test your expression to check that results are as expected. The following figure is an example
of an expression that has been evaluated and tested.
Certain expressions may fail during runtime, even though clicking Test Expression in the
Expression Builder indicated that they were valid.
This is because clicking Test Expression runs a query whereas during runtime, the
expression is run as a sub-query. This issue arises partly because the rules that govern
queries are slightly different from the rules that govern sub-queries.
For example, a semi-colon (;) is allowed in a query but not in a sub-query.
Testing an expression that contains an analytic function will validate the syntax without
actually executing the function. Additionally, the test will only be performed on a single
record.
Compose does not check the data types of columns used in an expression for
compatibility. For example, if a column of type integer is used in an expression for a
column of type varchar, the expression will not be executed successfully.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
188

5 Data Warehouse projects
Testing an expression
To test an expression:
1. In the Expression Builder window, build an expression as described in
Building expressions
(page 186)
.
2. Click Parse Expression as described in
Parsing expressions (page 187)
.
3. View the parameters that are displayed. If your expression is not valid, an error message is
displayed.
4. Optionally edit the parameters name(s) as described in
Editing parameter names (page 188)
.
5. Type values for each parameter and then click Test Expression to see the expression result.
For example, using the expression in
Testing an expression (page 189)
, type Mike for
FirstName and Smith for LastName. The result displayed is Mike Smith.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
189

5 Data Warehouse projects
6. This step is only available for transformations created in the Edit Mappings window. When
you create a transformation in the Edit Mappings window, an additional button called Show
Data appears to the left of the Test Expression button. You can click this button to see how
your expression translates into actual data.
For example, clicking the Show Data button for the expression UnitPrice*Quantity will open
the following window.
For more information on the Edit Mappings window, see
Editing column mappings (page
205)
in
Creating and managing the data warehouse (page 192)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
190

5 Data Warehouse projects
Defining reusable transformations
In a single Compose project there may be several processes that require similar data
transformations. For example a reusable transformation can be defined that concatenates first and
last names. This transformation could then be used both in the Customers mapping and in the
Employees mapping.
As opposed to stored functions or procedures which are environment dependent, reusable
transformations are environment agnostic, meaning that not only can they be used as required
within a Compose project, but they can also be used across different environments (using
Compose’s export/import function).
Centrally managed transformations increase efficiency by eliminating unnecessary duplication,
while at the same time, enabling the seamless propagation of changes to all transformation
instances.
To define a reusable transformation:
1. From the drop-down menu in the top right of the Model panel, select Reusable
Transformations.
The Reusable Transformations window opens.
The window is split into the following panes:
l
Upper pane - Lists the reusable transformations that have been defined.
l
Lower pane - Provides additional information about transformation instances such as
where they are in use (e.g. mappings, model, etc.) and the expression that was
created using the transformation.
Select a transformation to see the additional information.
2. Click the New Transformation toolbar button.
The New Transformation window opens.
1. In the Name field, specify a name for the transformation.
2. In the Category field, specify a category name. If the category name already exists it
will be displayed below the field when you start to type the name. To group the new
transformation in the same category, simply select the existing name (unless of course
you wish to create a new category with a similar name).
In the Expression Builder, transformations are grouped according to their category
name, making it easier to find the transformation you want to use. Therefore, when
specifying a category name, it is recommended to choose a name that reflects the
purpose of the transformation. For example, if you create several transformations that
concatenate data, it would make sense to group those transformations under a
category called "Join".
3. To add a parameter to the transformation, click the New button to the right of the
Parameters heading.
A new row is added to the Parameters list.
4. Specify a name for the parameter, select an appropriate data type, and optionally
provide a description.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
191

5 Data Warehouse projects
If you add multiple parameters, you can change a parameter’s position by
selecting the parameter and then using the Up/Down arrows (above the
Parameters list) to reposition it.
5. Click the Create Expression button below the Parameters list.
The Edit Transformation window opens.
6. In the Edit Transformation window, create an expression using the parameters you
defined earlier.
For information on creating expressions, see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
7. Click OK to save the transformation.
The transformation is added to the list in the upper pane.
Once a transformation has been defined, it will be available for selection as needed in the
Expression Builder’s Transformations tab.
For information on creating expressions, see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
Managing reusable transformations
You can manage reusable transformation as described in the table below.
To Do This
Delete a
transformation
Select the transformation and then click the Delete toolbar button. When
prompted to confirm the action, click OK.
If the transformation is in use, you first need to delete the
transformation instances.
Edit a
transformation
Double-click the transformation or select the transformation and then click
the Edit toolbar button. Continue as described in
Defining reusable
transformations (page 191)
.
Any changes you make to a transformation will be propagated to
all instances of that transformation.
Edit a parameter Open the Edit Transformation window as described in
Defining reusable
transformations (page 191)
. Then, select the parameter you want to delete
and click the Delete button above the Parameters list.
Reusable transformation management options
5.7 Creating and managing the data warehouse
Once your model is set up properly, the next step in the Compose workflow is to create the data
warehouse tables, generate the task(s) and run the data warehouse task.
In this section:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
192

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Data warehouse tasks (page 193)
l
Managing tasks (page 203)
l
Viewing and exporting task statements (page 219)
l
Modifying task settings (page 220)
l
Validating the data warehouse (page 226)
l
Clearing the data warehouse metadata cache (page 227)
Data warehouse tasks
This section, describes how to create the data warehouse tables, generate the task and run a data
warehouse task. It contains he following topics:
l
How Compose handles missing references in the data warehouse (page 193)
l
Creating the data warehouse tables (page 194)
l
Generating data warehouse tasks (page 196)
l
Controlling data warehouse tasks (page 198)
How Compose handles missing references in the data warehouse
Before running a data warehouse task, it is important to understand how Compose handles missing
references. Missing references may be involve records that are simply missing or records whose
arrival has been delayed. The latter might occur if data is ingested from two different systems (for
example, an ERP system and a CRM system), with each system having its own task.
Handling an early-arriving fact:
If a record references another record which does not exist yet, then Compose will do the following:
l
Insert a placeholder for the missing reference record. The placeholder record will only
include the business key and surrogate key. The rest of the columns will be set to NULL.
The fact being processed can already include a valid reference to the surrogate
key of the reference record.
l
Document the missing record in the TLOG_REF_ERRORS_VALUES table. The TLOG_REF_ERRORS_
VALUES table contains the following columns:
l
RUNNO - The task run number.
l
RELATIONNR - An internal number that can be used by Qlik Support to determine the
source entity.
l
NO_RELATIONS - The number of missing references. For example, if Customer A ordered
three different items (from the Orders table) and Customer A is missing, this number
will be three.
l
KEYVALUE1-20 - The missing record. Since the missing record is a Primary Key, which
may consist of several columns, there are 20 KEYVALUE columns.
Example:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
193

5 Data Warehouse projects
If the "Orders" table references "SuperGlue" in the "Products" table, but "SuperGlue" does not exist
in that table, Compose will mark "SuperGlue" as a missing reference, insert a record with the key
value "SuperGlue" (assuming that the product name is the business key) to the "Products" table,
and insert NULL values in the remaining "Products" table columns.
When the missing reference eventually arrives, it will be mapped to the record created for it and the
NULL values will be replaced by the actual values.
If the record is defined as history type 2, the record with the NULL values will remain as a
historical record.
See also:
Viewing missing references (page 267)
.
Creating the data warehouse tables
Compose create two types of data warehouse tables: staging tables (indicated by the TSTG prefix)
and the actual data warehouse tables (indicated by the TDWH prefix).
In addition, Compose automatically creates views for the TDWH tables in the following format:
<schema_name>.VDWH_<entity_name>[satellite_number_if_several]
Example:
dbo.VDWH_Customers02
For each entity, Compose creates a single view containing both the satellite data and the
associated hub data (or only the hub data if the entity has no satellites). If an entity has several
satellites, then Compose will create a view for each of the satellite tables. In such a case, the view
name will be suffixed with the user-defined satellite number as in the example above.
Compose for Data Warehouses adds RUNNO_INSERT and RUNNO_UPDATE columns to both the
Data Warehouse tables and the data mart tables. These columns contains the ETL task run number,
which can be used (in the Run Details window or in the Details tab) to find out more information
about the task (e.g. the number of rows updated or inserted per table). Note that in hub tables and
type 1 dimensions, the RUNNO_UPDATE number will usually be higher than the RUNNO_INSERT
number as these tables do not contain any history. In satellite tables or type 2 dimension tables
however, the RUNNO_INSERT number and the RUNNO_UPDATE number will always be the same as
a new row is inserted for each update (i.e. history is retained).
Data Warehouse views that contain both hub and satellite data will contain two RUNNO_
INSERT and two RUNNO_UPDATE columns. The hub table RUNNO columns are
appended with an "_H" (e.g. RUNNO_INSERT_H) while the satellite table table RUNNO
columns are appended with an "_S" e.g. RUNNO_UPDATE_S).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
194

5 Data Warehouse projects
To create the data warehouse tables:
1. Click the Create button in the bottom right of the Data Warehouse panel. The Creating Data
Warehouse window opens.
A progress bar indicates the current progress. For each stage of the Data Warehouse
generation process, a corresponding message appears in the Messages list.
When creating table in a Microsoft SQL Server data warehouse, you may
encounter the following error:
Data warehouse creation failed. Error: Cannot create a row of size 11272
which is greater than the allowable maximum row size of 8060.
The statement has been terminated.
This is a well-documented Microsoft SQL Server limitation. To work around this
limitation you need to split the offending table(s) into smaller tables.
2. When the "Data warehouse created successfully" message appears, click Close.
Viewing the data warehouse tables
After the data warehouse tables are created, you can view them by clicking the number to the left
of the Data Warehouse Tables Present text in the Data Warehouse panel.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
195

5 Data Warehouse projects
When you click the link, the Data Warehouse Tables window opens showing a list of all the tables
in your data warehouse.
Compose for Data Warehouses adds RUNNO_INSERT and RUNNO_UPDATE columns to both the
Data Warehouse tables and the data mart tables. These columns contains the ETL task run number,
which can be used (in the Run Details window or in the Details tab) to find out more information
about the task (e.g. the number of rows updated or inserted per table). Note that in hub tables and
type 1 dimensions, the RUNNO_UPDATE number will usually be higher than the RUNNO_INSERT
number as these tables do not contain any history. In satellite tables or type 2 dimension tables
however, the RUNNO_INSERT number and the RUNNO_UPDATE number will always be the same as
a new row is inserted for each update (i.e. history is retained).
Data Warehouse views that contain both hub and satellite data will contain two RUNNO_
INSERT and two RUNNO_UPDATE columns. The hub table RUNNO columns are
appended with an "_H" (e.g. RUNNO_INSERT_H) while the satellite table table RUNNO
columns are appended with an "_S" e.g. RUNNO_UPDATE_S).
In the data mart tables, the RUNNO_INSERT/RUNNO_UPDATE column names are
prefixed by the table name e.g. ORDERS_RUNNO_UPDATE.
To view a specific table, simply double-click the table.
Apart from the Date and Time tables which are automatically populated on creation, the
other tables will be empty until you run the data warehouse task.
See Controlling data warehouse tasks (page 198) below for information on running a
data warehouser task.
In the <Table Name> window, you can perform the following tasks:
l
Choose how many rows to display from the Rows drop-down list.
l
Click the Column Settings button to choose to choose which columns will be displayed and
the order in which they will be displayed.
Generating data warehouse tasks
After the data warehouse tables have been created, you then need to generate the task that will be
used in the data warehouse task. The task contains the Mappings ETL (which is automatically
created) and any custom ETLs that you have defined. If you need to make changes to the Mappings
or define custom ETLs, continue from
Managing tasks (page 203)
and
Creating and managing
custom ETLs (page 199)
respectively.
You can either generate individual tasks or you can generate multiple tasks concurrently.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
196

5 Data Warehouse projects
To generate a single data warehouse task:
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window opens.
2. If you have more than one task, in the left pane, select the task that you want to generate.
3. Do one of the following:
l
To generate the task with basic validations, click the Generate toolbar button.
By default, Compose generates the task with basic validations. Basic validations are
suitable for most tasks, but are especially useful for tasks with numerous expressions
and lookups, as generating such tasks with all validations could take a long time.
l
To generate the task with all validations, click the inverted triangle to the right of the
Generate button and select With all validations from the drop-down menu.
All validations includes validations that access the database to verify the existence of
columns used in expressions and lookups. As selecting With all validations will
significantly lengthen the time it takes to generate the task, you should only select it if
it's critical to verify that existence of such columns before the tasks starts.
The Generating task for <Name> progress window opens. When the "Generate task
finished successfully" message is displayed, close the window.
Only mappings selected in the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window will be
generated.
To generate multiple data warehouse tasks:
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window opens.
2. Click the inverted triangle to the right of the Generate toolbar button and select Bulk from
the drop-down menu.
The Bulk Generate dialog opens.
3. Select the tasks you want to generate.
4. Optionally, change the task validation level:
l
With basic validations: By default, Compose generates tasks with basic validations.
Basic validations are suitable for most tasks, but are especially useful for tasks with
numerous expressions and lookups, as generating such tasks with all validations could
take a long time.
l
With all validations: This includes validations that access the database to verify the
existence of columns used in expressions and lookups. As selecting All validations
will significantly lengthen the time it takes to generate the task, you should only select
it if it's critical to verify that existence of such columns before the tasks starts.
5. Click the OK to start the task generation.
Only mappings selected in the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window will be
generated.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
197

5 Data Warehouse projects
Controlling data warehouse tasks
Once the data warehouse tables have been created and the task has been generated, you can then
proceed to run the data warehouse task. The data warehouse task extracts data from the landing
tables, loads it into the staging tables, and finally loads the data into the data warehouse tables.
Ingesting a historical record deletes any history that is later than the ingested record.
For example, if a data warehouse contains the following historical records:
2012 - Boston
2014 - Chicago
2015 - New Jersey
Ingesting the record 2013 - New York will delete the 2014 and 2015 records.
Data warehouse tasks can be run manually, scheduled to run periodically or run as part of a
workflow. The section below describes how to run a data warehouse task manually. For information
on scheduling data warehouse tasks or including them in a workflow, see
Controlling and
monitoring tasks and workflows (page 265)
.
Data warehouse tasks cannot run in parallel with data mart tasks. Data warehouse tasks
that update the same tables cannot run in parallel.
To run a data warehouse task:
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom right of the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage
Data Warehouse Tasks window opens.
2. If you have more than one task, in the left pane, select the task that you want to generate.
3. Click the Run toolbar button. The window switches to Monitor view and a progress bar
shows the current progress in terms of percentage.
You can stop the task at any time by clicking the Abort toolbar button. This may be
necessary if you need to urgently edit the task settings due to some unforeseen
development. After editing the task settings, simply click the Run button again to restart the
task.
Aborting a task may leave the data warehouse tables in an inconsistent state.
Consistency will be restored the next time the task is run.
4. When the progress reaches 100% completed, close the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks
window.
Other monitoring information such as the task details (i.e. the number of rows inserted/updated)
and the task log files can be accessed by clicking the Run Details and Log buttons respectively.
Once the data warehouse has been successfully loaded into the data warehouse tables, you can
then proceed to the final part of the Compose workflow - defining and populating data marts. For
more information, see
Creating and managing data marts (page 228)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
198

5 Data Warehouse projects
Creating and managing custom ETLs
In addition to the Mappings ETL, you can define custom ETLs as required. User-defined ETLs can
perform a number of useful operations such as defining specific transformations, gathering
statistics, performing cleansing, and filtering data.
Common Table Expressions (CTEs) are not supported as well as some special clauses.
To create a custom ETL:
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window opens.
2. Select one of the following tabs according to your needs:
l
Pre Loading ETL - to define an ETL that will manipulate the data before it is loaded
from the landing tables to the data warehouse staging tables. When enabled, the Pre-
loading ETL will be run even if there are no mappings or Replicate-generated source
data associated with it, which is particularly useful for customer wanting to perform
transformations on data generated by third-party tools.
l
Multi Table ETL - to define an ETL for multiple tables.
l
Single Table ETL - to define an ETL for a single table.
l
Post Loading ETL - to define an ETL that will be executed after the data has been
loaded from the staging tables to the data warehouse.
3. If you selected Single Table ETL, select an entity in the Entity column and then click the New
button above the Entity list. For Multi Table and Post Loading ETLs, just click the New
button.
4. Specify a name for your ETL and then click OK.
If you selected Single Table ETL, the ETL is added as a link to the User Defined ETL column.
If you selected Multi Table ETL or Post Loading ETL, the ETL is added as a link in their
respective tabs.
5. Click the link to open the Edit ETL Instructions window.
6. If you selected Single Table ETL, select a column and click the arrow to the right of the
selected column to add it to the ETL.
If you selected Multi Table ETL or Post Loading ETL, select a table and a column and then
click the arrow to the right of the selected table/column to add it to the ETL. Repeat as
necessary.
7. Use the Select, Delete, Insert and Update toolbar buttons at the top of the window to add
SQL statements to your ETL.
8. To run the ETL as a stored procedure (that already exists in the data warehouse):
a. Select the Execute as Stored Procedure check box.
b. Click the Stored Procedure toolbar button.
c. Replace STORED_PROCEDURE with the name of your stored procedure and replace(PARAM1,
PARAM2) with any parameters that it needs. Note that parameters must be separated by
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
199

5 Data Warehouse projects
a comma. If no parameters are required, use empty parenthesis or drop them
altogether.
9. Use the Undo, Redo and Reset buttons at the bottom of the window if needed.
10. Optionally, specify a description in the Description box at the bottom of the window.
11. To save your ETL, click OK.
Single table example
The following example, based on the
Data warehouse project tutorial (page 106)
in
Getting started
with Data Warehouse projects (page 103)
, demonstrates how to concatenate two columns called
"First Name" and "Last Name" into a single column called "FullName".
1. Click the Manage button in the Model panel. The Manage Model window opens.
2. Select Employees from the Entities list on the left.
3. Click the + (plus) toolbar button to add a new Attribute. A new row is added to the Attributes
table.
4. Type any letter in the Column Name column to bring up the "Add New" option. Click the "Add
New" option when it appears.
The New Attribute Domain window opens.
5. In the Name field, type FullName. From the Type drop-down list, select Varchar. In the
Length field, enter 100.
6. In the History column, select Type 1 from the drop-down list.
7. Click OK to close the New Attribute Domain window and add the attribute to the Attributes
table.
8. Then click OK again (below the newly added attribute) to exit edit mode.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
200

5 Data Warehouse projects
9. Close the Edit Model window.
10. In the Data Warehouse panel, click the Create button.
11. After the Data Warehouse tables have been created, close the Creating Data Warehouse
window.
12. Click the Manage button in the bottom left corner of the Data Warehouse panel. The
Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window opens.
13. To view the current mappings between the source columns and data warehouse columns,
click the Map_Employees_1 link in the Mappings column. A "Processing" icon is displayed
while the mappings are generated. After the mappings are generated, the Edit Mappings -
Map_Employees_1 window opens automatically.
Note that the FullName column has been added to the data warehouse columns, but is
currently not mapped to the source columns.
14. The next stage is to define an ETL that will map the First Name and Last Name source
columns to the Full Name data warehouse column.
15. Close the Edit Mappings - Map_Employees_1 window and then select the Single Table ETL
tab on the left.
16. Select Employees in the Entity column and then click the New button above the column. The
Add New Single Table ETL window opens.
17. Specify a name or leave the default name and then click OK.
18. Click the Edit button (represented by a pencil icon) at the end of the Employees row. The
Edit Single Table ETL: <Name> window opens.
19. In the editing pane on the right, enter the following instruction:
UPDATE dbo.TSTG_EMPLOYEES set
FullName = LASTNAME + FIRSTNAME
20. Click OK to save the ETL and close the window.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
201

5 Data Warehouse projects
After Compose has finished populating the Data Warehouse, you can open the
table in Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and verify that the new column
has been added with the correct data.
Updating custom ETLs
Compose CLI requires Administrator permission. To grant Administrator permission,
select "Run as administrator" when opening the command prompt. All commands should
be run from the Compose
bin
directory (C:\Program Files\Qlik\Compose with a default
installation).
You can update custom ETLs using the Compose CLI. This functionality can be incorporated into a
script to easily update Custom ETLs.
Syntax:
composecli update_custom_etls --project name --infolder path
Where:
l
project is the name of the project with the custom ETLs you want to update
l
infolder is the full path to the folder containing the custom ETL files
Example:
composecli update_custom_etls --project my-project --infolder
c:\Compose\CustomETLs
The file names in the input folder must be identical to the custom ETL names in the
specified project. Otherwise, an error will occur. The file extension (for example, .txt) is
not important, but the file must be in SQL format.
ETLexecution sequence
The execution sequence of ETL scripts in Data Warehouse projects should be taken into
consideration when writing and ordering the scripts. A proper understanding of the ETL execution
order is important for preventing errors, such as those resulting from actions being performed on
objects that do not yet exist.
ETL scripts are usually executed in the following order:
Custom Pre-Loading (Source of data: landing tables)
↓
Mappings (Source of data: landing table)
↓
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
202

5 Data Warehouse projects
Multi Table ETL (Source of data: staging tables)
Whereas it's possible to define a single table ETL in the Multi Table ETL script, the
advantage of defining it as a single table ETL script is that it will be able to run in
parallel with other tables.
↓
Single Table ETL (Source of data: staging tables)
↓
Post Loading ETL (Source of data: data warehouse tables)
Within each of the above groups, the scripts are executed according to their numeric order (from
lowest to highest), which is set by the user-defined Sequence Number. The execution order of
several scripts in a group with the same sequence number will be random.
Managing tasks
a task contains the mappings between the columns in the landing zone tables and the columns in
the logical entities. The same mappings can be used by several tasks. You can create new tasks,
duplicate tasks and edit existing tasks as required.
The following options are available:
l
Adding, editing, and duplicating tasks (page 203)
l
Editing column mappings (page 205)
l
Creating and managing custom ETLs (page 199)
You must regenerate the task and then run a data warehouse task whenever the
mappings are modified or whenever custom ETLs are added or modified. Populating the
data warehouse can either be done manually as described in Controlling data warehouse
tasks (page 198) or automatically as described in Scheduling tasks (page 270).
If you have already run the data mart tasks, then you also need to regenerate the data
mart ETLs and run the tasks again as described in Creating and managing data marts
(page 228).
Adding, editing, and duplicating tasks
As the default tasks are generated automatically, there is usually no reason to manually create or
duplicate a task. An exception to this is if you import your model from ERwin without first defining
global mappings. In such a case, you will need to manually add the task and create the mappings.
For more information on global mappings, see
Managing global mappings (page 161)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
203

5 Data Warehouse projects
One possible reason to duplicate a task is if your model contains different types of tables and you
want to manage them in separate ETLs.
Adding tasks
To add a new task:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window opens.
2. Click the New Task toolbar button. The New Task dialog opens.
3. Specify a name for the task.
Task names cannot contain the following characters: /\,&#%$@=^*+"'`~?<>:;[]{}
as well as all non-printable characters (below 0x20). The task name can contain a
single dot, but it cannot be the first or last character.
4. Optionally, provide a description.
5. Select one of the following task types according to your needs:
l
Full Load: Loads the selected tables into the data warehouse.
l
Change Processing: Updates the data warehouse tables with the source table
changes.
Do not select a task type that conflicts with you Replicate task. For instance, do
not select Change Processing if your Replicate task is Full Load only.
6. Click OK to create the task. Select the task name in the left pane and continue from
Editing
column mappings (page 205)
.
Editing tasks
To edit an existing task:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window opens.
2. In the left pane, double-click the task you want to edit or hover your mouse cursor over the
task and click the button.
3. Edit the task as described in steps 3-5 of
Adding tasks (page 204)
above and then click OK.
4. Generate the task as described in
Generating data warehouse tasks (page 196)
.
Duplicating tasks
To duplicate an existing task:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window opens.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
204

5 Data Warehouse projects
2. Select the task you want to duplicate and then click the Duplicate toolbar button. The
Duplicate window opens.
3. Specify a Name for the new task.
4. Select a Landing Zone.
5. Optionally change the default Schema.
6. Select one of the available task types.
Do not select a task type that conflicts with you Replicate task. For instance, do
not select Change Tables Only if your Replicate task is Full Load only.
7. Click OK.
8. Select the task name in the left pane and continue from
Editing column mappings (page 205)
.
Editing column mappings
The mappings show the current mapping between the landing zone tables and the logical entities.
By default, the columns names and data in the source tables and the logical entities will be identical.
However, you can manually change the mappings according to your needs, either by simply
mapping a source column to a different data warehouse column and/or by using an expression.
To edit column mappings:
1. Click the Manage button in the Data Warehouse panel.
2. In the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window, select the Mappings tab. Each of the logical
entities has a corresponding mapping name.
3. In the Mappings column, click the mapping that you want to edit. The Edit Mapping: Name
window opens.
4. Edit the mapping as described below.
Mapping a landing zone table column to a staging area table column
The mapping procedure differs depending on whether you are in Standard View or
Compact View. For information on changing the view, see Changing the view (page
206).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
205

5 Data Warehouse projects
In Standard View:
1. Hover the mouse cursor over the source column name as shown in the image below. A gray
dot appears to the right of the column name.
2. Drag the mouse cursor from the gray dot to the desired column in the logical entity.
3. When the dotted line turns green (as shown below), release your mouse button.
Note that if the dotted line turns red (instead of a green), you will not be able to map the
source column with the desired data warehouse column. A red dotted line indicates that the
source and data warehouse column data types are incompatible with each other.
In Compact View:
1. Switch to Compact View as described in Change the view.
2. Drag the source column to the cell located to the left of the target data warehouse column.
Auto-generating mapping
Click the Auto-Map toolbar button.
Removing all mappings
Click the Reset toolbar button.
Changing the view
To change the view, click the Change View toolbar button.
Changing to a more compact view is recommended for sources tables that have numerous
columns. In compact view, the table columns are organized in rows (instead of a single list), making
it easier to locate source columns and map them to the desired data warehouse columns. You can
also use the search box to filter out all columns that
do not
match the search string.
For information on creating mappings in Compact view, see Map a column in a landing zone table to
a column in a staging area table.
Selecting a different source database
Select a database from the Landing Zone Database drop-down list on the left of the window.
Selecting a different source schema
Select a schema from the Schema drop-down list on the left of the window.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
206

5 Data Warehouse projects
Changing the entity type
Select Table, View or Query on the left of the window. If you choose the Query option, see also
Define a custom query.
Defining a custom query
When the entity type is set to Query, you can set a custom select query instead of using the
existing source tables/views.
To set a query:
1. Click the Set Query button. The Edit Mapping Select Query: <Mapping Name> window
opens.
2. Hover the mouse cursor over a table and/or a column and then click the arrow to the right of
the highlighted table/column to add it to the Query.
3. Use the Select button at the top of the window to add select statements to your query.
Optionally use the Undo, Redo and Clear buttons as required.
4. Click OK to save your settings and close the window.
The query results will be displayed on the left of the Edit Mappings: <Name> window.
Selecting a different table
Select a table from the Table Name drop-down list on the left of the window.
Seeing the data of a selected table
Select a source table and then click the Show Source Data button on the left of the window.
Creating a table-level transformation (Filter)
1. Click the Filter toolbar button in the Edit Mappings:Name window. The Expression Builder
opens.
2. Continue from
Opening the expression builder (page 185)
.
When creating a filter for a table, the expression should return 1 for data that you
want to include and 0 for data that you want to exclude.
The filter will be applied after any
Data Cleansing
rules that are defined.
Updates to records excluded by a filter (even for records previously included by
the filter) are not processed while the records are filtered out. Updating of filtered
out records will only resume if the record(s) once again meet the filter-in
condition, but any changes made while the records were filtered out would be
lost.
Example of a simple transformation
${Address} is not null
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
207

5 Data Warehouse projects
Each platform has its own variation of SQL syntax. Therefore, make sure the syntax you
use conforms to the SQL syntax supported by your data warehouse.
Creating a column-level transformation
1. Hover the mouse cursor over the data warehouse column for which you want to create a
transformation and then click the fx button that appears to its right. The Expression Builder
opens.
2. Continue from
Opening the expression builder (page 185)
.
Adding, deleting and renaming mappings
You can add, rename and delete mappings as required. For example, if you want one of the logical
entities to contain columns from several tables in the landing zone, then you need to add a new
mapping for each of the landing zone tables.
When mapping "From Date" columns in the Landing Zone to the "FD" Staging column,
make sure that the dates in the Landing Zone columns are not earlier than the "Lowest
Date" set in the
Project Settings
. Otherwise, any data with a "From Date" earlier than the
"Lowest Date" will be ignored.
If some of the dates in the Landing Zone column are earlier than the "Lowest Date" and
cannot be changed in the source, either change the "Lowest Date" set in the
Project
Settings
- or - use a transformation in Replicate to convert the source dates to dates that
are within"Lowest Date" to "Highest Date" range defined in your project.
To add, delete, and rename mappings:
1. Click the Manage button in the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage Data Warehouse Tasks
window opens.
2. In the left pane, select the task you want to add, delete, or rename.
3. Select the Mappings tab.
Adding a new mapping
To add a new mapping:
1. In the Logical Entities column, select the logical entity that you want to map.
2. Click the New button above the Logical Entities column. The New Mapping window opens.
3. Optionally change the default mapping name.
4. Click OK to save the mapping.
5. Enable the mapping.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
208

5 Data Warehouse projects
Deleting a mapping
To delete a mapping:
1. In the Mappings column, hover the mouse cursor over the mapping you want to delete.
2. Click the Delete (x) button that appears to its right.
3. Click OK when prompted to confirm the deletion.
Renaming a mapping
To rename a mapping:
1. In the Mappings column, hover the mouse cursor over the mapping you want to rename.
2. Click the Rename (A) button that appears to its right. The Rename window opens.
3. Specify a new name for the mapping and then click OK.
Handling duplicate business keys
When two or more records in the data source have the same business key, you can select the
Handle Duplicates check box to prevent an error from occurring when the data warehouse task is
run. When this check box is selected, Compose will only add one of the records to the data
warehouse.
Since Compose randomly chooses which record to add to the data warehouse, you may
want to run a data warehouse task first to see if there are any duplicate record errors. In
the event that there are, you can then modify the data source to remove records that
have the same business key.
You should also select the Handle Duplicates check box in the following situations:
l
The Data Warehouse task type is either Full Load and Change Tables or Change Tables
Only.
This is because the Change Tables may contain two records with the same business key:
The old record and the updated record. When the Handle Duplicates check box is selected,
the updated record will always be inserted/updated to/in the data warehouse.
l
When a single table in the data warehouse is derived from multiple landing zone tables, the
same business key will be set for each of the mappings. To prevent an error for occurring,
you need to select the Handle Duplicates check box.
Handling null updates
The default handling of null updates is set in the Advanced tab of the Settings - <ETL_Set_Name>
window. For each mapping, you can override the specified default.
To do this:
1. In the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window, select the desired mapping.
2. Click the Null Updates toolbar button.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
209

5 Data Warehouse projects
3. Select one of the available options. For a description of the options, see Handling Null
Updates.
Using lookup tables
Lookup tables are useful for replacing source data with the actual data that you want to appear in
the data warehouse. For example, a lookup table could be used to replace a zip code with a full
address or, conversely, to replace a full address with a zip code.
To link a lookup table column to a logical entity column:
1. Click the link to the desired task in the Data Warehouse panel. The Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window opens.
2. In the Mappings column, click the mapping for the logical entity containing the result column
(with the data that you want to replace). The Edit Mapping - Name window opens.
3. Hover the mouse cursor over the relevant data warehouse column and then click the Lookup
button that appears to the right of the column name. The Select Lookup Table window
opens.
a. From the Database drop-down list, select the database containing the lookup table.
The database must reside in your data warehouse.
b. From the Schema drop-down list, select the schema containing your source lookup
tables.
c. Select either Table or View according to the lookup table type.
d. From the Table drop-down list, select the lookup table.
The right side of the Select Lookup Table window displays the lookup table columns
and their data types. To view the data in the lookup table, click the Show Lookup Data
button.
e. After you have selected the lookup table, click OK.
4. After selecting the lookup table, the Lookup Transformations - Table Name.Column Name
window opens. The window is divided into the following panes:
l
Upper pane: The upper part of the right pane (Condition) displays the condition
expression, which stipulates the condition(s) for performing the lookup.
l
Lower pane: The lower part of the right pane (Result Column) displays the column
result expression, which stipulates what data to replace in the target column.
5. To change the lookup table, click the Change Lookup Table button above the lookup table
columns and then perform steps a. to d. above.
6. To view the lookup table or landing table data, click the Show Lookup Data or Show Landing
Data buttons respectively.
7. To specify condition(s) for performing the lookup, click the Create Expression button (which
changes to Edit Expression after an expression has been created) above the Condition
expression. The Condition Expression - Column Name window opens.
You can create an expression using the landing and lookup table columns on the left.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
210

5 Data Warehouse projects
For an example, see
Lookup example (page 211)
. For information on creating expressions,
see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
8. To specify what data to replace or add if the lookup conditions are met, click the Create
Expression button (which changes to Edit Expression after an expression has been created)
above the Result Column expression. The Result Expression - Column Name window
opens.
You can create an expression using the landing and lookup table columns on the left.
For an example, see
Lookup example (page 211)
. For information on creating expressions,
see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
9. To preview the results, click the Preview Results button.
10. Click OK to save your settings and close the Lookup Transformations - Table
Name.Column Name window.
Using lookup tables that do not have a task for CDC mapping
When the Store Changes option is enabled in the Replicate task, Replicate creates Change Tables
in the landing zone. These tables contain only the changes to the original data. The Compose task
CDC task reads the changes from Change Tables and applies them to the target tables. However, if
the landing zone contains dedicated lookup tables (i.e. tables that are not associated with any
Compose task), Compose will not be able to apply changes to these tables.
There are two ways of handling such a scenario, both of which are described below.
Method 1
Define another Replicate task with the Apply Changes replication option enabled.
Method 2
1. Discover the landing site and add all the lookup tables to the Compose model without any
relation to/from other entities.
2. Either, define lookups from the data warehouse hub tables to the newly added entities.
OR
Create relationships from the data warehouse hub tables to the newly added entities.
Creating relationships may not be a viable option when the lookup tables are
complex.
3. Define a new data warehouse Change Tables Only task that updates the lookup tables.
4. Ensure that the new task runs before the data warehouse task.
The advantage of this method is twofold: a.) All the tables used in the mappings are managed by
Compose, and b.) Only one Replicate task needs to be defined (which also means that the database
transaction logs are read only once). The disadvantage is that you need to ensure that the task that
updates the lookup entities always runs before any data warehouse task.
Lookup example
The following example shows how a lookup table is used to concatenate a Dutch translation of the
category name (located in the lookup table) to the original category name located in the landing
table.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
211

5 Data Warehouse projects
The lookup could be defined using the following expressions:
1. Condition expression: ${Lookup.CategoryID}=${Landing.CategoryID}
Meaning: Perform the lookup only if the Category ID in the landing table and the lookup table
are the same.
2. Result column expression: ${Lookup.CategoryName} + ’is’ + ${Landing.CategoryName}
Meaning: Add the data in the CategoryName column in the lookup table to the data in the
CategoryName column in the landing table (separated by the word "is").
Example:
Assuming the result column name is "Split Name", clicking the Preview Results button would
display the following table:
Split Name
Category Name
(Lookup)
Category Name
(Landing)
Category ID
(Lookup)
Category ID
(Landing)
dranken is Beverages dranken Beverages 1 1
Specerijen is
Condiments
Specerijen Condiments 2 2
Gebak is
Confectionary
Gebak Confectionary 3 3
Zuivelproducten is
Dairy Products
Zuivelproducten Dairy Products 4 4
Grains/Granen is
Grains/Cereal
Grains/Granen Grains/Cereal 5 5
Vlees/Gevolgete is
Meat/Poultry
Vlees/Gevolgete Meat/Poultry 6 6
Example table output
Dropping and recreating tables
You can drop and recreate tables in your data warehouse as required. If you change the model after
the data warehouse tables have already been created and loaded with data, you should adjust the
data warehouse to reflect the modified model (as described in
Validating the data warehouse (page
226)
). Some changes however cannot be resolved by adjusting the data warehouse. In such cases,
you can either revert the model to its pre-modified state or drop and (optionally) recreate the data
warehouse tables.
Note that dropping and recreating tables will delete
all
of the data in the tables and should only be
performed in lieu of a better option.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
212
5 Data Warehouse projects
In some scenarios, you need to edit the CREATE table statements before they are run.
This can be done using the
Generate DDL scripts but do not run them
in Project settings
(page 37). For example, if your data warehouse tables contain partitions, you will need to
edit the script to maintain the partitions.
To drop and recreate tables:
1. In the Data Warehouse panel, select the Drop and Recreate Tables item from the menu in
the top right corner. The Drop and Recreate Tables window opens.
2. You can select to drop and/or recreate one or more of the following tables:
l
Data Warehouse & Data Marts - The data warehouse tables are derived from the
model whereas the data mart tables are derived from the data warehouse tables.
l
Logging - These tables are generated when the task runs and contain logging
information. By default, these tables are prefixed with the string "TLOG".
l
Intermediate - These tables are temporary tables that are created when the task runs.
By default, these tables are prefixed with the string "TTMP".
Intermediate tables are created dynamically and therefore cannot be
recreated.
l
Error Mart - These are the data mart exception tables. Data that is rejected by data
quality rules will be copied to tables in the specified error mart schema. See also Error
Mart.
l
Archive Tables - These are the tables that are created when the option to archive
Change Tables after the changes have been applied (to the data warehouse tables) is
selected. For more information, see
Defining landing zones (page 140)
3. Click OK to perform the drop and/or recreate operation.
Data profiling
Data profiling is an analysis of the candidate data sources for a data warehouse to clarify the
structure, content, relationships and derivation rules of the data. In short, data profiling helps you
understand your data and model it correctly.
Qlik Compose enables you to profile the data in the landing zone tables before it is loaded into the
data warehouse. If you discover a problem with certain data, then you can either manually adjust
the source tables or create a rule for handling the data in question.
To profile the data:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom of the Data Warehouse panel.
2. In the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window, click the link in the Mapping column for the
table you want to profile.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
213

5 Data Warehouse projects
3. In the Edit Mappings - <Name> window, click the Data Profiler toolbar button. The Profile
<Table Name> (Landing Zone) window opens. The following columns are displayed:
l
Column Name - The name of the table column
l
Nulls - The number of null values in the column
l
Count - The number of rows in the column.
l
Count Distinct - The number of unique rows in the column.
l
Duplicates - The number of duplicate values in the column.
Note that although Compose calculates the number of duplicate values by subtracting
Count Distinct from Count, the actual number of records displayed when you click
the Duplicates number will be higher. This is because Compose has no way of
knowing which of the records that share the same column value are legitimate
duplicates (if any). It therefore displays all records that share the same value so you
can decide which of them to delete (if any).
For example, in the Employees table, there may be several employees that live in
London (the City column). Therefore duplicates of "London" are perfectly acceptable.
However, two employees with the same phone number and a different address, for
example, may indicate that the phone number in one of the records was entered
incorrectly.
Duplicate values are quite common and usually do not indicate a problem. Where this
feature is particularly useful however, is for detecting duplicate Primary Key candidate
columns.
l
Data Type - The column data type
l
Max - The highest data value
l
Max Length - The longest data value
l
Min - The lowest data value
l
Min Length - The shortest data value
4. For more information about a value, click the link in the column. A window opens showing the
record(s) containing the value. To add a Data Quality rule, click the Data Quality button and
continue as described in
Defining and managing data quality rules (page 215)
.
5. To only show columns that are mapped to a logical entity column, select the Only show
mapped columns check box.
6. To change the number or rows sampled, select a different value from the Rows to sample
drop-down list. Note that the table may contain less rows than the selected value. The
Sampled records value is the actual number of rows sampled.
7. To see all the table data, click the Show Data button.
The table's Full Load data will always be shown, even for a mapping in a Change
Processing (CDC) task.
8. To recalculate the data, click the Recalculate button. This is useful if the data in the landing
zone tables is being constantly updated (for example, due to a Replicate Change Processing
task).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
214

5 Data Warehouse projects
9. To search for a particular value, start typing the value in the Search box. Only values that
match the search term will be shown.
Defining and managing data quality rules
There are many definitions of data quality but data is generally considered high quality if, "they are
fit for their intended uses in operations, decision making and planning." (Tom Redman<Redman,
T.C. (2008). With Compose, the data must be "fit" for use in a data mart.
Compose provides two ways of ensuring data quality: Data validation and data cleansing. As
opposed to data validation which usually results in data being rejected, data cleansing provides a
means of replacing, modifying, or deleting incomplete, incorrect or inaccurate data.
Data that is rejected by a rule will be copied to Error Mart tables in the Error Mart schema defined in
the Landing Zone database settings.
Details about rejected data can be viewed in the monitor's Error Mart tab. For more information,
see
Viewing information in the monitor (page 265)
.
Defining data cleansing rules
Qlik Compose enables you to define data cleansing rules for each of a table’s columns. Each rule
consists of a data validation condition and a cleansing process that is performed as required (i.e. if
the data is not valid).
Data Cleansing rules will be applied before any
filters that are defined
.
To add a rule:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom of the Data Warehouse panel.
2. In the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window, click the link in the Mapping column for the
relevant table.
3. In the Edit Mappings - <Name> window, click the Data Quality toolbar button. The Data
Quality Rules - <Table Name> window opens.
4. To add a new rule, click the New toolbar button. A row is added to the rules table.
5. In the Name column, specify a name for the rule.
6. From the drop-down list in the Column column, select the column to which the rule will be
applied.
7. Hover the mouse-cursor over the Condition column and then click the fx button that appears
on the right.
8. In the Edit Condition Rule window, create a condition (using an expression) that the data in
the column must meet in order to be considered valid. For more information on creating
expressions, see
Opening the expression builder (page 185)
.
See also
Simple Example Rule (page 216)
below.
9. From the drop-down list in the If Condition is False column, select Cleanse Silently.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
215

5 Data Warehouse projects
10. Hover the mouse-cursor over the Correction column and then click the fx button that
appears on the right.
11. In the Edit Correction Rule window, create an expression to cleanse the data. For more
information on creating expressions, see
Opening the expression builder (page 185)
.
See also
Simple Example Rule (page 216)
below.
12. In the Description column, enter a description for the rule.
13. In the Enabled column, select or clear the check box to enable (the default) or disable the
rule respectively.
Simple Example Rule
The condition expression on the left stipulates that the product ID number must be less than 100. If
it is greater than or equal to 100, the data will be corrected using the expression on the right.
${ProductID} < 100 ${ProductID} - 100
Defining data validation rules
Qlik Compose enables you to define data validation rules that are applied to the data before it is
loaded into the data warehouse. In addition to defining rules, you can also define what action
should be taken when data is rejected/accepted by Compose.
To add a rule:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom of the Data Warehouse panel.
2. In the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window, click the link in the Mapping column for the
table you want to profile.
3. In the Edit Mappings - <Name> window, click the Data Quality toolbar button. The Data
Quality Rules - <Table Name> window opens.
The default rule rejects primary keys that have a null value and reports the rows.
4. To add a new rule, click the New toolbar button. A row is added to the rules table.
5. In the Name column, specify a name for the rule.
6. Hover the mouse-cursor over the Rule column and then click the fx button that appears on
the right.
7. In the Edit Data Quality Rule window create a rule using an expression. For more information
on creating expressions, see
Opening the expression builder (page 185)
.
See also
Simple Example Rule (page 216)
below.
8. From the drop-down list in the Error Action column, select one of the following actions
(performed when the data does not meet the rule conditions):
l
Reject and report - Reject the data and send a report
l
Reject silently - Reject the data without sending a report
l
Reject and abort - Reject the data and abort the data warehouse task
l
Accept and report - Accept the data and send a report
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
216

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
When the "report" option is selected, the row is reported to the <landing_
table_name>__ex table in the data warehouse error mart.
l
When there are multiple data validation rules, Compose will stop evaluating
the data after the first error (and report only that error). Once the error is
fixed, additional data evaluation errors may be reported for the remaining
rules, each time the data is loaded.
9. In the Description column, enter a description for the rule.
10. In the Enabled column, select or clear the check box to enable (the default) or disable the
rule respectively.
A rule that is defined to reject or accept a non-null value (e.g. 2) in a given column
will also reject/accept NULL values that appear in the same column, but in
different records. To prevent this from happening, add the following condition to
the rule: "and column value is not null"
Example:
LEN(${CName})<2 and (${CName} is not null)
Simple Example Rule
The following rule stipulates that the number of units in stock must be greater than 1.
${UnitsInStock}>1
Managing Data Quality rules
The following options are available for managing Data Quality rules.
Enabling/disabling a Data Quality rule
Select or clear the check box in the rule’s Enabled column.
Editing a Data Quality rule
Select the rule and edit it as described in
Defining data cleansing rules (page 215)
and
Defining data
validation rules (page 216)
respectively.
Deleting a Data Quality rule
Select the rule and then click the Delete button above the rules list. When prompted to confirm the
deletion, click Yes.
Searching for a Data Quality rule
Enter a search term in the Search box above the rules list.
Changing the order of Data Quality rules
The order of the rules is important since rules are applied in the order that they appear. For
example, placing Reject and abort rules first will prevent other rules from being applied if the data
is rejected by the Reject and abort rule.
To change the order of Data Quality rules, select the rule that you want to move and then use the
arrows above the rules list to change the position of the rule.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
217

5 Data Warehouse projects
Viewing missing references
In some cases, incoming data is dependent on or refers to other data. If the referenced data cannot
be loaded for some reason, you can either decide to add the data manually or continue on the
assumption that the data will arrive before it is needed.
There are two ways you can view missing references in Compose. Either via the Monitor tab in the
Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window or by switching the console to Monitor view and selecting
the Missing References tab. The instructions below cover both of these methods.
To check for missing references in the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window:
1. Click the Manage button in the lower left corner of the Data Warehouse panel.
2. Select the desired task in the left side of the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window.
3. Switch to Monitor view by clicking the Monitor tab in the top right of the Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window.
4. Click the View Missing References toolbar button. The Missing References - <
task
Name
> window opens.
The following information is displayed:
l
General information: The run number of the task, when it started and ended, the total
number of inserts and updates, and the number of reported rows (if any).
l
Missing references information:
l
Missing Records from Entity - The name of the entity with missing reference
and the number of missing references.
To see the missing record keys for the entity, click the number in parentheses
to the right of the entity name.
The Missing Record Keys for Entity - <Entity Name> window opens showing
the list of missing keys and the number of times each key is referenced per
entity.
l
Referenced from Entity - The entities that are referencing the entity with
missing references.
l
Via Relationship - The name of the relationship in the Model.
5. To close the window, click Close.
To check for missing references in the Compose Monitor:
1. Switch the console to Monitor View.
2. Select the desired task.
3. Click the Missing References tab below the task list.
The following information is displayed:
l
General information: The run number of the task, when it started and ended, the total
number of inserts and updates, and the number of reported rows (if any).
l
Missing references information:
l
Missing Records from Entity - The name of the entity with missing reference
and the number of missing references.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
218

5 Data Warehouse projects
To see the missing record keys for the entity, click the number in parentheses
to the right of the entity name.
The Missing Record Keys for Entity - <Entity Name> window opens showing
the list of missing keys and the number of times each key is referenced per
entity.
l
Referenced from Entity - The entities that are referencing the entity with
missing references.
l
Via Relationship - The name of the relationship in the Model.
4. To close the window, click Close.
Missing references example
In the following example, Orders and Disputes both reference Customers.
Orders contains seven records pointing to Mr. Brown and one record pointing to Mr. Smith.
Disputes contains four records referencing Mr. Brown. Mr. Brown and Mr. Smith are "missing" from
Customers.
The would be reflected as follows:
Missing Records from Entity Referenced from Entity Via Relationship
Customers (2) Orders (8) Customers
- Disputes (4) CustomerDisputes
Example table content
Clicking the number to the right of Customers (in the Missing Records from Entity column) would
open the following window:
Key Referenced from Entity Via Relationship
Mr. Brown Orders (7) Customers
- Disputes (4) CustomerDisputes
Mr. Smith Orders (1) Customers
Example table content
See also:
How Compose handles missing references in the data warehouse (page 193)
.
Viewing and exporting task statements
You can view the task statements that were run during the data warehouse task. You can also
export the task statements to a CSV file for reviewing and sharing.
To view the task statements:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the DATA WAREHOUSE panel.
The Manage Tasks window open.
2. Click the Task Statements toolbar button.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
219

5 Data Warehouse projects
3. The Task Statements - <Name> window opens in List View. Navigate through the
commands using the scroll bar or find specific commands using the Search box.
OR
Click the Item View button and navigate through the commands using the navigation
buttons at the bottom of the Task Statements - <Name> window.
To jump to a specific command, type the command number in the Go To field at the
bottom of the window and then press [Enter].
To export the task statements to a CSV file:
1. In List View, click the Export to CSV File button located to the left of the search field.
2. A file named "
<name>_ETL_Instructions.csv
" will be saved to your default Downloads
location or you will be prompted to save it (according to your browser settings).
Modifying task settings
For each task, you can modify the settings according to your needs.
To open the Settings window:
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the DATA WAREHOUSE panel.
2. Select a task in the left panel.
3. Click the Settings toolbar button.
A window opens displaying the following tabs: General, Advanced, and Consolidation.
General Tab
In the General tab, the following settings are available:
l
Log level: Select the log level granularity, which can be any of the following:
l
INFO (default) - Logs informational messages that highlight the progress of the ETL
process at a coarse-grained level.
l
VERBOSE - Logs fine-grained informational events that are most useful to debug the
ETL process.
l
TRACE - Logs finer-grained informational events than the VERBOSE level.
The log levels VERBOSE and TRACE impact performance. Therefore, you should only select
them for troubleshooting if advised by Qlik Support.
l
Default History Resolution: Choose the granularity of the "From Date" column value when a
new history record is inserted:
l
Minutes to update with the date and time. This is the default. When this option is
selected, a new record will be inserted each time the data is updated.
l
Days to update with the date only. When this option is selected, only one record (the
most recently updated) will be inserted at the end of the day.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
220

5 Data Warehouse projects
These settings will be applied, regardless of the original source column (when
mapped) or Change Table [header__] timestamp column (when not mapped)
granularity. So, for instance, if a source column with date and time granularity is
mapped to the "From Date" column and Days is selected, then only one record
(the most recently updated) will be inserted at the end of the day.
l
When updating a non-null data warehouse column with a null value:
l
Do not change the target value: Select this to keep values unchanged between two
mappings for the same record. For instance, if the same record exists in two different
source tables (A and B), but the record in Table A has a null value for data that is
present in Table B (e.g. ZIP Code). In this case, if the record in Table A arrives
after
the
record in Table B, the target value will be set to null. Selecting this option will prevent
such an occurrence.
When creating a new project, the default behavior is to write NULL instead
of keeping the values unchanged between the two mappings.
l
Set the target value to null: Select this if you want the source and target values to
correspond. This can be useful, for example, when a person moves address and one of
the column values (e.g. "State") changes to null.
When ingesting changes from an Oracle source, this option requires full
supplemental logging for all source table columns that exist on the target
and any source columns referenced in filters, data quality rules, lookups,
and expressions.
l
When a data warehouse column is unassigned
A data warehouse column is assigned a value using the following means:
l
Mapping
l
Mapping expression
l
Lookup
If none of the above apply, the column will be unassigned. There are two ways to handle
unassigned columns:
l
Use the previous column value: When a column is unassigned, Compose will try and
replace it with the most recently used (previous) value from the data warehouse. This
might degrade performance.
l
Assign null to this column: Choosing the Assign null to this column option will set
the unassigned column to NULL, resulting in faster ETL operations.
Advanced Tab
In the Advanced tab, the following settings are available:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
221

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Sequential Processing: Select this option if you want all the data warehouse tasks to run
sequentially, even if they can be run in parallel. This may be useful for debugging or profiling,
but it may also affect performance.
l
Maximum number of database connections: Enter the maximum number of connections
allowed. The default size is 10.
For more information, see
Determining the required number of database connections (page
21)
.
l
JVM memory settings: Edit the memory for the java virtual machine (JVM) if you experience
performance issues. Xms is the minimum memory; Xmx is the maximum memory. The JVM
starts running with the Xms value and can use up to the Xmx value.
Only the following characters are supported (shown as a regular expression):
/^[-a-zA-Z0-9:]*$/
l
Position in default workflow: Select where you want the data warehouse tasks to appear in
the default workflow. For more information on workflows, see
Workflows (page 274)
.
l
Optimize for initial load: Optimizes initial load in certain cases. Only select this option if the
source tables do not reference missing records, use lookups, map different source records
to the same record, do not contain Type 1 self-references, or contain historical records. Note
also that when this option is selected, the following features are not supported:
l
Data quality rules
l
Derived attributes
l
Consolidation of uniform sources (see Consolidation below)
l
The Handle duplicates option
In the event that the task is used for incremental loading (using query-based change
processing), clear the check box after the initial load task completes and regenerate the task.
l
Write task statement duration to the TLOG_PROCLOG table in the data warehouse: This
option is useful for troubleshooting performance issues with ETL processes as it records the
duration of each task statement in a special table (named TLOG_PROCLOG) in the data
warehouse. You can then use this information to locate task statements with abnormal
duration times and modify them accordingly.
l
Do not create indexes for data warehouse tables: During the task, Compose creates an
internal index for each of the Data Warehouse tables (for query optimization). When running
several consecutive tasks (e.g. via a workflow) with a large volume of tables, this process
can be extremely time-consuming. In such a scenario, best practice is to select the check
box for each of the tasks, except the last one.
l
Do not truncate staging tables: Select this option if you want the ETL process to preserve
the staging tables. Only use for debugging.
l
Stop processing after populating the staging tables: Select if you do not want to proceed
to populating the warehouse. Only use for debugging.
l
Do not drop temporary tables: Select this option if you want to keep the temporary tables
created during the ETL process. Only use for debugging.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
222

5 Data Warehouse projects
Consolidation Tab
When the Consolidate uniform sources option is enabled, Compose will read from the selected
data sources and write the data to one consolidated entity. This is especially useful if your source
data is managed across several databases with the same structure, as instead of having to define
multiple data warehouse tasks (one for each source), you only need to define a single task that
consolidates the data from the selected data sources.
Consolidation tab showing selected data sources
Editing the list of data sources requires you to regenerate the task.
The list of selectable data sources reflects the list of Source Databases that appears in
the Databases panel in Designer view.
To facilitate downstream processing, you might want to add a record identifier column
(for example, SourceID) to the primary key of all your entities. However, if one entity
references another (for example, Orders → Customers), a naming conflict will arise as
the new column (SourceID) will then appear in the referencing entity (Orders) twice. To
prevent such conflicts from occurring, you should add the column to each entity with a
unique prefix derived from the entity name. So, continuing with the Orders →
Customers relationship example, the column name in the Orders entity should be
orders_SourceID while the column name in the Customers entity should be customers_
SourceID.
Prerequisites
l
The structure of the tables in the selected sources must be identical.
l
Source type can be Table or View, but not Query.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
223

5 Data Warehouse projects
The source data does not have to reside in tables only or in views only; it can be
ingested from a combination of views and tables. For example, the source data
might be ingested from tables A, B, and C in Landing 1, and views A, B, and C in
Landing 2.
See also:
Editing column mappings (page 205)
.
Limitations and considerations
l
The Optimize for initial load option is not supported with consolidation.
l
A selected data source cannot contain an asterisk (*) in its specified schema name (asterisks
in schema names are supported with Microsoft SQL Server only).
See also:
Using Microsoft SQL Server as a source (page 149)
l
If you have existing Full Load and Change Tables (CDC) tasks, setting the consolidation
settings for the Full Load task will not automatically set the consolidation settings for the
Change Tables task as well. You need to do this manually.
See also:
Adding, editing, and duplicating tasks (page 203)
l
Uniform consolidation settings will not be included in task settings that are exported to a CSV
file.
See also:
Migrating objects as CSV files (page 46)
l
Lineage andproject documentation will not reflect all of the selected sources.
See also:
Exporting project documentation (page 98)
and
Lineage and impact analysis (page
179)
.
l
Custom ETLs (Pre Loading ETL, Multi Table ETL, Single Table ETL, and Post Loading ETL) will
run only once, regardless of how many sources are selected.
See also:
Creating and managing custom ETLs (page 199)
.
l
Generating the ETLs will only validate the Landing Zone database(s) defined in the
mappings, and not all of the data sources selected in the Consolidation tab.
l
Error marts will be created for each Landing Zone database.
To see the number of reported rows in each error mart:
1. Open the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window, and select the consolidation task
in the left pane.
2. Select the Monitor tab, and click the Total Reported Rows number.
Alternatively:
1. Switch to the main Monitor view and select the consolidation task.
2. In the Progress Status tab (below the tasks list), click the Total Reported Rows
number.
The Error Mart - <task-name> window opens.
Error Mart window showing the number of rows reported for each error mart
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
224

5 Data Warehouse projects
For more information on error marts, see
Viewing information in the monitor (page 265)
.
Monitoring tasks with consolidates sources
The monitor shows the sum total of all the records (for example, the total number of INSERTs) from
all of the selected sources.
Monitor showing a consolidation task with the total number of rows inserted from all data sources
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
225

5 Data Warehouse projects
Validating the data warehouse
Data warehouse validation should be performed each time the model is edited (after the data
warehouse has already been created). Validating the data warehouse allows you automatically
resolve any differences between the model and the data warehouse.
For a data warehouse to be considered valid, the tables defined in the data warehouse need to be
identical to the physical tables in terms of metadata. Depending on the change, this may require
adjusting the physical tables or dropping and recreating them (via Compose).
If the data warehouse is not valid, any tasks that you attempt to run will fail.
Changes to Distribution Keys cannot be validated (or adjusted). Such changes need to
be applied manually to the Data Warehouse tables.
Sometimes, however, the differences between the model and the data warehouse cannot be
resolved automatically. In such cases, you need to drop and recreate the tables as described in
Dropping and recreating tables (page 212)
.
To validate the data warehouse:
1. Click the Validate button at the bottom right of the Data Warehouse panel. The Validating
the Data Warehouse progress window opens.
If any differences are detected, the following message will be displayed:
The data
warehouse is different from the model.
2. Click Close. The Model and Data Warehouse Comparison Report window opens.
3. Review the report and then click Adjust Automatically to resolve the differences
automatically or Generate Adjust Script to generate a script with the adjust commands.
l
The Adjust Automatically button will be disabled either if the
Generate
DDL scripts but do not run them
option is selected or if Compose is unable
to automatically adjust the data warehouse. In such cases, you should click
Generate Adjust Script as described below.
l
Due to Google Cloud BigQuery limitations, if Compose is unable to
automatically adjust the data warehouse, then the generated script may be
not valid either. Consequently, users should review the script carefully and
adjust it manually (if required) before running.
l
If you clicked Adjust Automatically, the Adjust Data Warehouse progress window
opens.
When the "The data warehouse was adjusted successfully." message is displayed, you
can close the window. Note that adjusting the data warehouse may require you to
update the data mart. In such a case, an appropriate message will be displayed for
each of the data marts that require updating.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
226

5 Data Warehouse projects
Cases where Compose is unable to automatically adjust the data
warehouse are as follows:
l
A data type change that is not supported by the database or a data
type change that may result in data loss.
l
A change in an entity’s business key or distribution key.
l
An attribute’s history type is Type 2 and the satellite table number in
the attribute’s settings has changed.
l
If you clicked Generate Adjust Script, the Generate DDL Scripts window opens
showing the progress of the script generation.
The generated scripts will be saved to:
<product_dir>\data\projects\<project_name>\ddl-scripts
Once the script(s) have been generated, you can close the Generate DDL Scripts
window.
After you close the Generate DDL Scripts window, the DDL Script Files window
opens automatically displaying the generated scripts. The DDL Script Files provides a
read-only view that allows you to review the scripts and download them.
The scripts need to be executed directly in your data warehouse. Make sure that any
modifications that you make to the scripts are done prior to executing them.
When you run the adjust scripts, backup tables are created from the
existing tables. The backup table names are appended with an "_old" suffix
and must be deleted manually after the script completes.
Search for "TODO" in the script to locate the part of the script that needs
modifying.
Clearing the data warehouse metadata cache
To improve performance when reading from the Landing Zone or from the Data Warehouse tables,
Compose caches the metadata from both the Landing Zone and the Data Warehouse tables.
However, synchronization issues may sometimes occur if the metadata structure of the Landing
Zone or the Data Warehouse tables is altered outside of the Compose project.
If you aware of external changes to the metadata or if you notice any data synchronization
anomalies, Compose enables you to clear the metadata cache, either using the UI or using the CLI.
Clearing the data warehouse metadata cache with the web console
To clear the metadata cache with the web console:
1. In the Data Warehouse panel, select Clear Metadata Cache from the menu in the top right
corner.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
227

5 Data Warehouse projects
A progress window opens.
2. After the metadata cache has been cleared, click Close to exit the progress window.
For information on clearing the Landing Zone metadata cache, see
Clearing the Landing Zone
metadata cache (page 158)
.
Clearing the metadata cache with the CLI
The
storage
value for the
--type
parameter described below refers to the data
warehouse metadata cache.
You can also clear the metadata cache using the CLI.
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe clear_cache --project
project_name
[--type landing|storage] [--landing_zone
source_name]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--type Which type of metadata cache to clear. Possible values are:
l
landing
l
storage
If --type
landing
and you want to clear a specific landing
zone, you must set the --landing_zone parameter as well. To
clear the metadata cache in all landing zones, specify --type
landing
and omit the --landing_zone parameter.
--landing_zone the name of the landing zone when --type landing_zone
Example
ComposeCli.exe clear_cache --project MyProject --type landing --landing_zone MySource1
5.8 Creating and managing data marts
This section explains how to create data marts from your data warehouse tables.
In this section:
l
Adding star schemas and dimensions (page 238)
l
Displaying data in a pivot table (page 235)
l
Managing data marts (page 237)
l
Creating and managing custom ETLs (page 254)
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
228

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Viewing and exporting task statements (page 256)
l
Validating and adjusting the data mart (page 256)
l
Modifying data mart settings (page 260)
l
The "Obsolete" indicator (page 262)
Adding data marts and star schemas
This topic explains how to create and manage data marts and star schemas in Qlik Compose. Since
a data mart is essentially a subset of the data warehouse, you can create any number of data marts
according to your BI needs. You can also create multiple star schemas for a single data mart. Star
schemas allow you to reuse existing dimension tables within the same data mart, thereby saving
space in the data warehouse while at the same time improving query performance. For example,
you could create one star schema with an Order Details fact table and Customers and Products
dimensions and another star schema with the same dimensions but a different fact type (or the
same fact type, but different dimensions). This also allows you to generate BI reports using
different facts that share the same dimensions. Additionally, in a star schema, dimensions are
linked with each other through one join path intersecting the fact table, facilitating accurate and
consistent query results.
l
If you edit an expression or a column lookup in a dimension, the changes will not
be applied to existing data. To apply such changes, you need to reload the data
(which could take some time, depending on the number of records and whether
there are a lot of historical records).
l
Data warehouse tasks cannot run in parallel with data mart tasks.
A new data mart should be created in the following situations:
l
Setting up a Compose project for the first time.
l
To serve the needs of each individual business unit (different data marts can be used to
obtain specific information for various enterprise departments, such as accounting,
marketing, sales, and so on).
To create a data mart with a star schema:
1. Click the New button located at the bottom of the Data Mart panel.
OR
Click the Manage button and then click the New button located at the top of the Manage
Data Marts window. The New Data Mart window opens.
2. Optionally change the default name and provide a description.
Data mart names cannot contain the following characters: /\,&#%$@=^*+"'`~?<>:;
[]{} as well as all non-printable characters (below 0x20). The data mart name can
contain a single dot, but it cannot be the first or last character.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
229

5 Data Warehouse projects
3. Make sure that the Start New Star Schema Wizard check box is selected (the default) and
then click OK. The New Star Schema wizard opens.
4. Provide a name and description (optional) for the star schema.
5. Select one of the available fact types:
l
Transactional - A star schema with a transactional fact table allows you to retrieve
the desired data, even if a dimension table contains multiple versions of the same
record. To use an example from the automotive industry, selecting "OrderDate" as the
Transaction Date would allow you to generate a report for the number of customers
who bought cars in New York between 2013 and 2016, even if a customer moved to a
different city (which would also result in a new record being added to the Customers
dimension).
l
Aggregated - A star schema with an aggregated fact table allows you to make
aggregate calculations based on the fact table attributes. For instance, you could
create an aggregated fact that shows the total freight costs per shipping region and
product category. Additionally, the presence of a transaction date in the fact table
makes it possible to retrieve the desired data, even if a dimension contains multiple
versions of the same record. To use an example from the shipping industry, a shipper
could use an aggregated fact to generate a report for the total cost of shipping rice to
Australia from 2015-2016.
l
State Oriented - A star schema with a state oriented fact supports Type 2 columns in
the fact table. This is useful in cases where the fact is not a singular event in time, but
rather, consists of multiple "states" or events that occur over time. Typical example of
facts with multiple states are insurance claims or flight reservations. There are also
cases when the same entity is treated as both a fact and a dimension - for example,
Customers. In such cases, a report could be generated that relates to the state of the
fact, such as the time a claim was submitted to the time it was approved.
6. Click Next.
7. In the Facts screen, choose one fact for the star schema and then click Next. The
Dimensions screen is displayed. The left pane lists the dimensions that can be selected
while the right pane displays a diagram of the star schema with the selected dimensions. You
can view a dimension’s lineage by selecting the desired dimension and then clicking the
Lineage button. For more information on lineage, see
Lineage and impact analysis (page
179)
.
The left pane of the Dimensions screen contains the following areas:
l
Existing Dimensions - Lists the dimensions that already exist in your data mart. Note
that only dimensions that are relevant to the selected fact table will be displayed.
l
Create New Dimensions - Lists all of the dimensions that can be added to the star
schema.
l
Date Dimensions - Lists all of the Date dimensions that can be added to the star
schema. Note that these dimensions will only be available for selection if you added
the Date and Time entities to your model. For an explanation of how to do this, see
Adding Date and Time entities to your model (page 180)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
230

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Time Dimensions - Lists all of the Time dimensions that can be added to the star
schema. Note that these dimensions will only be available for selection if you added
the Date and Time entities to your model. For an explanation of how to do this, see
Adding Date and Time entities to your model (page 180)
.
When adding dimensions using the wizard, if a root dimension already exists in
the data mart, any dimensions selected under the root dimension will be ignored.
Workaround: Edit the dimension and delete or add columns as required.
8. Choose which dimensions to include in the star schema and then click Next.
9. If you chose Star Schema with State Orientation as your star schema type, click Finish.
Otherwise, continue from Step 10 below.
10. In the Transaction Date screen, choose which Transaction Date to include in the data mart
fact table. Selecting a Transaction Date enables you to retrieve the required data, even if the
Dimension table contains multiple versions of the same record.
For example, a car salesman wants to know how many customers bought cars in New York
between 2013 and 2015. Selecting OrderDate as the Transaction Date for the Customers
Dimension would make it possible to retrieve this information, even if a customer moved to a
different city (which would also result in a new record being added to the data mart).
11. If you chose Transactional as your star schema fact type, click Finish. If you chose
Aggregated as your star schema fact type, continue from Step 12 below.
12. In the Aggregated Fact screen:
a. Select one or more columns from the Fact table on the left of the screen.
You can select multiple columns by holding down the [Shift] (sequential
selection) or [Ctrl] (non-sequential selection) buttons while selecting the
columns.
b. To add the column(s) to the Group By list on the right, either drag the columns to the
list or click the arrowhead button to the left of the Group By list. Note that each
dimension has a default "Group By" column that cannot be deleted.
c. To add the column(s) to the Aggregations list on the right, either drag the columns to
the list or click the arrowhead button to the left of the Aggregations list.
d. To add new columns to the Group By or Aggregations list, click the New button
above the list. In the New column window, specify a Name, Type, Description and
Aggregation (when adding a new aggregation column) and then click OK. The column
is added to the list.
e. To add an expression, hover the mouse cursor over the table cell in the Expression
column and then click the fx button that appears on the right. The Edit Expression:
<Name> window opens.
For more information on creating expressions, see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
f. To delete a column, select the column in the list and then click the Delete button
above the list.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
231

5 Data Warehouse projects
You can select multiple columns for deletion by holding down the [Shift]
(sequential selection) or [Ctrl] (non-sequential selection) buttons while
selecting the columns.
See also
Aggregation example (page 234)
.
13. Click Finish. The newly created star schema is displayed below the Star Schemas heading,
as shown below.
14. Click the Create Tables toolbar button. The Creating Data Mart: Data Mart Name in Target
progress window opens. Wait for the "Create Data Mart tables finished successfully."
message to be displayed and then click Close.
After the data mart tables are created, the Create Tables button changes to Drop
and Recreate tables.
15. Do one of the following:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
232

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
To generate the task with basic validations, click the Generate toolbar button.
By default, Compose generates the task with basic validations. Basic validations are
suitable for most tasks, but are especially useful for tasks with numerous expressions
and lookups, as generating such tasks with all validations could take a long time.
l
To generate the task with all validations, click the inverted triangle to the right of the
Generate button and select With all validations from the drop-down menu.
All validations includes validations that access the database to verify the existence of
columns used in expressions and lookups. As selecting With all validations will
significantly lengthen the time it takes to generate the task, you should only select it if
it's critical to verify that existence of such columns before the tasks starts.
The Generating Statements for Task: Data Mart Name window opens. Wait for the
"Generating Statement for Data Mart No. <
number
> finished successfully." message to be
displayed and then click Close.
16. Click the Run toolbar button. The window switches to Monitor view and a progress bar
shows the current progress in terms of percentage.
When the Total ETL reaches 100 percent, data mart population is complete.
You can stop the task at any time by clicking the Abort toolbar button. This may be
necessary if you need to urgently edit the task settings due to some unforeseen
development. After editing the task settings, simply click the Run button again to restart the
task.
l
Aborting a task may leave the data warehouse tables in an inconsistent
state. Consistency will be restored the next time the task is run.
l
In rare situations, the Monitor view in the Manage Data Marts window may
not show any tasks initially. To remedy this, refresh the browser window.
Other monitoring information such as the run details (i.e. the number of rows
inserted/updated) and the task log files can be accessed by clicking the Run Details and Log
buttons respectively.
Should any errors occur, you can click the link at the end of the Failed bar for additional
information that may help you troubleshoot the problem.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
233

5 Data Warehouse projects
Once your data mart has been loaded with data, you can check that the required data is
available for your BI tools. For more information, see
Displaying data in a pivot table (page
235)
.
Understanding star schema icons
Compose displays various icons to indicate both the status and characteristics of the star schema
tables. These icons are displayed in the table below.
Icon Description
Indicates that although the structure for the star schema has been
defined, all or part of the dimension(s) and/or fact table do not
physically exist in the data warehouse. Click Create Tables to create
the tables and/or click Validate to see what needs to be adjusted.
Displayed when the dimension(s) and/or fact table physically exist in
the data warehouse.
Indicates a conformed (shared) dimension.
Small squares indicate that there are denormalized tables under the
root dimension table. Each square represents a denormalized table, so
in the image on the left, the Orders root dimension has four
denormalized tables. To view the denormalized table names, hover the
mouse cursor over each of the squares.
Displayed when a dimension has a reference to itself.
Star schema icons
Aggregation example
In the following example, Mike the organization’s data scientist, wants to create an aggregation
table that shows the total freight costs per shipping region and product category; for example, the
total cost of shipping rice to Australia in 2015.
To achieve this objective, he adds the CategoryName and ShipRegion attributes to the Group By list
and then adds the Freight attribute to the Aggregations list. As Mike is interested in the total
freight cost, he selects SUM as the Aggregation Type.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
234

5 Data Warehouse projects
Displaying data in a pivot table
This section explains how you can use Compose to view the data in your star schema.
To view the data in a star schema:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom of the Data Marts panel.
2. In the Manage Data Marts window, either:
Switch to Monitor view (by clicking the monitor icon) in the top right corner.
OR
Remain in Design view and select a star schema.
3. Click the Pivot toolbar button. If you clicked the Pivot toolbar button in Monitor view and
your data mart contains several star schemas, you will be prompted to selected a star
schema. The Select columns for Pivot table window opens. The drop-down list at the top of
the window contains the Fact table and the Dimensions tables that were used to create the
star schema.
The Fact table name is prefixed with "Fct_" while dimension table names are prefixed with
"Dim_".
4. Make sure that "Fct_<FactName>" is selected in the drop-down list and then select which
fact column to add to the pivot table.
5. From the drop-down list, select a dimension and then select which dimension columns to add
to the pivot table.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
235

5 Data Warehouse projects
If you added the Date and Time dimension tables to your data mart, you will be
able to select.
6. Optionally, repeat Step 5 to add columns from different dimensions to the pivot table.
When the same column is included in two different dimensions, the pivot table
may show incorrect data.
7. Click OK. The pivot table window opens.
The names of columns that you can use to generate the data will be displayed at the top of
the window.
8. To form the actual table, drag columns to the gray area below the column names (the X-axis)
and to the gray area on the left of the window (the Y-axis). In the following example, the
ShippedDate column has been dragged to the X-axis while the OrderID column has been
dragged to the Y-axis.
In this example, the QTR column was selected from the Date dimension, allowing orders to
be grouped by quarter.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
236

5 Data Warehouse projects
9. Change the table format, set aggregation, or perform additional actions as described in the
table below.
To Do this
Set the table
format
From the upper drop-down list in the left of the pivot table window,
choose one of the following:
l
Table
l
Table bar chart
l
Heatmap
l
Row heatmap
l
Col heatmap
l
Treemap
Aggregation
options
From the lower drop-down list in the left of the pivot table window,
choose one of the available options.
Note that additional drop-down lists may be displayed depending on the
selected aggregation option. For example, when Sum over Sum is
selected, two additional drop-down lists (containing column names) will
appear below the aggregation options. The Sum over Sum aggregate is
calculated by selecting one column from each of the drop-down lists.
Change the
columns
Click the Customize Columns button and continue from Step 3 above.
Additional actions
10. Click OK to close the window.
Managing data marts
This section describes the following management options:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
237

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Adding star schemas and dimensions (page 238)
l
Editing star schemas (page 241)
l
Editing dimensions (page 247)
l
Deleting data marts, schemas and dimensions (page 254)
Data marts pointing to different databases cannot contain tables with the same name.
Adding star schemas and dimensions
A data mart can contain any number of star schemas and dimensions. You can either add
dimensions when you create a new star schema or you can add them later and attach them to star
schemas as needed. Regardless of how they are added, dimensions can be reused across several
star schemas as necessary.
To add a star schema:
1. Either click the New Star Schema toolbar button.
OR
Right-click the Star Schemas or Dimensions items and select New Star Schema.
The New Star Schema wizard opens.
2. Perform steps4 to 13 in
Adding data marts and star schemas (page 229)
. The star schema is
added to the Star Schemas list.
3. If you already created the data mart tables (as described in
Adding data marts and star
schemas (page 229)
), you need to create the new star schema tables in the data mart. To do
this, perform the validation process described in
Validating and adjusting the data mart
(page 256)
.
Otherwise, perform steps 4 to 13 in
Adding data marts and star schemas (page 229)
. If you
also want to run a data mart task, perform step 16 as well.
To add a dimension:
1. Select the dimension(s) you want to add to the data mart. Then click OK. The dimension(s)
are added to the Dimensions list.
2. If you already created the data mart tables (as described in
Adding data marts and star
schemas (page 229)
), you need to create the new dimension table(s) in the data mart. To do
this, perform the validation process described in
Validating and adjusting the data mart
(page 256)
.
Otherwise, perform steps 14 and 15 in
Adding data marts and star schemas (page 229)
. If you
also want to run a data mart task, perform step 16 as well.
3. Select the dimension(s) you want to add to the data mart. Then click OK. The dimension(s)
are added to the Dimensions list.
4. If you already created the data mart tables (as described in
Adding data marts and star
schemas (page 229)
), you need to create the new dimension table(s) in the data mart. To do
this, perform the validation process described in
Validating and adjusting the data mart
(page 256)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
238

5 Data Warehouse projects
Otherwise, perform steps 14 and 15 in
Adding data marts and star schemas (page 229)
. If you
also want to run a data mart task, perform step 16 as well.
To attach a newly added dimension to a star schema:
1. Perform Steps 1-2 described in
To add a dimension: (page 238)
above.
2. Select the dimension(s) you want to add to the star schema and then click the Add
Dimension to Star Schema toolbar button. The Add Dimension <Name> to Star Schema
window opens.
3. Select which star schema(s) you want to add the dimension to and then click OK. The
dimension is attached to the selected star schema(s).
4. If you already created the data mart tables (as described in
Adding data marts and star
schemas (page 229)
), you need to create the new dimension table(s) in the data mart. To do
this, perform the validation process described in
Validating and adjusting the data mart
(page 256)
.
Otherwise, perform steps 14 and 15 in
Adding data marts and star schemas (page 229)
. If you
also want to run a data mart task, perform step 16 as well.
Importing and referencing dimensions
You can import dimensions or reference existing dimensions as needed.
Importing dimensions
You can import dimensions from other data marts in the same project. This is especially useful if:
l
Several developers are working on the same data mart, developing different complex
dimensions
l
You need to use a dimension from another data mart and modify it slightly
To import dimensions
1. Open the Manage Data Marts window and click the Import or Reference Dimensions
toolbar button.
2. From the Source data mart drop-down list, select the data mart containing the dimensions
to import.
3. Select Import the selected dimensions.
4. Select which dimensions to import and then click OK.
Only dimensions that do not already exist in the current data mart (with same
name) are available for selection.
The dimensions are imported to your data mart.
Referencing dimensions
The ability to reference dimensions improves data mart design efficiency and execution flexibility
by facilitating the reuse of data sets. Reuse of dimension tables across data marts allows you to
break up fact tables into smaller units of work for both design and data loading, while ensuring
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
239

5 Data Warehouse projects
consistency of data for analytics.
Throughout this section, a dimension that references another dimension will be referred
to as a "referencing dimension" where a dimension that is referenced by another
dimension will be referred to as a "referenced dimension".
To add a referencing dimension:
1. Open the Manage Data Marts window and click the Import or Reference Dimensions
toolbar button.
2. In the Import or Reference Dimensions window, select the Source data mart and then
select Reference the selected dimension.
3. Select which dimensions you want to reference, then click OK.
The dimensions are added to the data mart.
Referencing Dimension names have the following format:
<dimension name>_
<data mart name>
Data mart with referencing dimension
Referencing dimensions are read-only.
4. To add the newly added dimension to the star schema, right-click the dimension and then
select Add to Star Schema.
The Add Dimension <name> to Star Schema window opens.
5. Select which star schema(s) you want to add the dimension to and then click OK.
After adding the referencing dimension to the star schema, you might see a
icon next to the star schema name. This means that you need to validate and
adjust the data mart containing the referenced dimension.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
240

5 Data Warehouse projects
Working with referenced dimensions
It's important to be aware of the limitations and considerations when referencing other dimensions
as well as the best practice guidelines.
Limitations and considerations
l
Referenced dimensions cannot be deleted from the source data mart.
l
Date and time dimensions cannot be referenced.
l
Data lineage will not show all of the referenced dimensions.
l
Deleting a dimension that references another referenced dimension should be done with
caution. For example, If dimension X is referencing dimension Y which in turn is referencing
dimension Z, deleting dimension Y will affect dimension X as well.
l
Referenced dimensions must be created in the same database as the star schema or fact
using them. They can be in a different schema however.
Best practices
l
To prevent data inconsistencies, make sure that the source data marts ( i.e. the data marts
containing the original dimensions) are processed before any data marts referencing those
dimensions.
l
To ensure correct processing of referenced dimensions, it is preferable to avoid circular
references. An example of a circular reference is if Data Mart B references Dimension A in
Data Mart A and Data Mart A references Dimension B in Data Mart B.
In some cases, it is okay to use circular references. If, for example, both Data Mart
A and Data Mart B are incrementally updated, then any updates to Data Mart A
will use the current version of Data Mart B, and vice versa.
l
Conformed referenced dimensions that are used by one or more data marts should be
grouped into a single data mart, without fact tables.
l
Transactional fact tables should be grouped into data marts, based on processing
requirements.
l
Aggregate and State-oriented star schemas (fact tables) are typically processed during
batch windows as they require complete rebuilds. It is therefore recommended practice to
separate Aggregate and State-oriented fact tables from Transactional fact tables. Doing so,
allows Transactional fact tables to be processed incrementally throughout the day as
required, while allowing Aggregate and State-oriented fact tables to be processed during
batch windows.
Editing star schemas
You can edit a star schema according to your needs. Editing options include adding columns,
adding attributes and defining filters.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
241

5 Data Warehouse projects
To edit a star schema (fact table):
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Data Mart panel. The Manage Data Marts
window opens.
2. In the left pane, select the data mart containing the star schema you want to edit.
3. Expand the list of start schemas and select the star schema you want to edit. Then either
click the Edit button in the lower toolbar or right-click the star schema and select Edit.
The Edit Star Schema - Name window opens. The following tabs are displayed:
l
General tab: In the General tab, you can edit the star schema name, the fact table
name, the fact view name and the description.
The following option is also available for transactional and aggregated facts:
l
Update fact with changes to Type 2 data warehouse entities - Select this
option (the default) if you want the fact table to always be updated with the last
record version of any Type 2 data warehouse entities the star schema contains.
Example:
Assuming the data warehouse has the following Type 2 entities:
l
Orders
l
Order Details
l
Address
And the data mart consists of the following:
l
Fact = Orders and Order Details
l
Transaction date = Order Date in Orders
l
Dimension = Address (Type 2)
Then the last version of Orders and Order Details will always used and
Address will be updated according to the Oder Date.
See also:
Data mart views (page 253)
.
l
Logical Attributes tab: In the Logical Attributes tab, you can add and delete columns,
edit a column’s properties, view a column’s lineage, change the column order, and
define filters.
Edit the Logical Attributes tab according to the table below.
l
Physical Table tab: The Physical Table tab provides a preview of the actual
"physical" columns that will be created in the database. All editing tasks are performed
in the Logical Attributes tab, except for defining table creation modifiers which is
performed in the Physical Table tab.
For an explanation of how to define table creation modifiers, see
Example of a Valid
Table Creation Modifier (page 245)
.
l
Transaction Date tab: The Transaction Date tab enables you to change the
transaction date that you selected when you created the star schema.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
242

5 Data Warehouse projects
For more information on transaction dates, see the Transaction Date screen.
This tab will not be displayed if your Star Schema Type is "State Oriented".
Editing Logical Attributes
To Do this
Add a new
column
1. Click the New toolbar button.
The New Column window opens.
2. In the Name field, specify a name for the column.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select one of the available data types.
4. If the selected data type requires further configuration, additional fields
will be displayed. For example, when Decimal is selected, the Length and
Scale fields will be displayed. Set the values as required.
5. Optionally specify a Description.
6. Click OK to add the column and close the New Column window.
Edit a
column’s
properties
1. Double-click the row containing the column.
The Edit: Column Name window opens.
2. Edit the properties as described in steps 2-6 of Add a new column above.
Delete a
column
Select the column(s) you want to delete (multi-selection is supported) and click
the Delete toolbar button.
The column(s) are deleted.
View a
Column’s
Lineage
1. Select the desired column.
2. Click the Lineage toolbar button.
A windows displaying the column’s lineage is displayed.
For more information about lineages, see
Lineage and impact analysis
(page 179)
.
Logical attributes editing options
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
243

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do this
Create a
filter
Click the Filter toolbar button. The Expression Builder opens with the heading:
Edit Filter - TableName.
For information on creating filters, see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
Using From Date (FD) and To Date (TD) columns in a filtering
expression is not supported.
The assumption is that columns that are used in the filters do not
change between different versions of the record. If this is not the
case, the
Full rebuild
option should be selected in the Data Mart
settings. This assumption is also true for relationships; for example, if
a Sales record relates to Product which relates to Country, and the
filter is applied to the product's country, then the assumption is that
the sale cannot change its product so that it is filtered in or out based
on a new country.
Create or
edit an
expression
Hover the mouse cursor over the desired table column and then click the fx
button that appears to the right of the Expression column. The Expression
Builder opens with the heading: Edit Expression - Column Name.
For information on creating an expression, see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
Change the
column order
Select the column(s) you want to move and then click the Move Down/Move to
Bottom or Move Up/Move to Top buttons as desired.
Defining Fact Table Creation Modifiers
You can set table creation modifiers for individual star schema (fact) tables, thereby overriding the
default settings in the project settings'
Table creation modifiers tab (page 42)
. Table modifiers
allow you to append additional table properties to the default Compose CREATETABLE statement.
The available options are located below the Columns list in the Physical Table tab, and are as
follows:
l
Project settings default - When this option is selected (the default), the settings from the
project settings'
Table creation modifiers tab (page 42)
will be used.
l
Custom - This option is useful for if you need to append table creation modifiers to the
default CREATETABLE statement Compose uses for fact tables. Leveraging this option
requires SQLcoding knowledge.
l
Custom distribution and sort keys - This option is useful if you only need to define custom
distribution keys or sort keys for the fact table. Although this can also be done using the
Custom option (see below), the Custom distribution and sort keys option is more
convenient as it does not require any prior SQL coding knowledge.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
244

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Supported with Amazon Redshift only.
l
The default distribution key for all data warehouse tables is the ID column.
Setting table creation modifiers
By default, Compose creates tables in the data warehouse using the standard CREATE TABLE
statement. However, organizations often need tables to be created with custom properties for
better performance, special permissions, custom collation, and so on. For example, in Microsoft
Azure Synapse Analytics, it’s possible to create a table as a HEAP, which is optimized for smaller
tables. By default, Compose creates tables in Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a CLUSTERED
COLUMNSTORE INDEX, which offers the best overall query performance for large tables.
The procedure for settings table modifiers is as follows:
1. Open the star schema and select the Physical Table tab.
2. Select the Custom option.
3. Click the Edit button to open the Table Creation Modifier editor.
4. Enter the SQL parts you wish to append to the CREATE TABLE statement.
5. Optionally, but strongly recommended, validate the SQL in an external validation tool that
supports your specific database and version.
Compose does not provide any way of validating your SQL. Therefore, make sure
to validate the SQL before deploying in a production environment.
6. Click OK to close the editor and save your SQL parts.
Example of a Valid Table Creation Modifier
In the following example, the Compose CREATE TABLE statement (rows 1-5) is appended with an
SQL part instructing Compose to create the table as a HEAP (row 6).
CREATE TABLE MyTable
(
column1 integer,
column2 varchar(50),
)
WITH (HEAP)
Setting and managing custom distribution keys for Amazon Redshift tables
Set and manage distribution keys for Amazon Redshift Data Warehouse according to the table
below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
245

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Add a distribution key 1. Click the Add Distribution Key button.
A row is added to the table displaying a drop-down list.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Set a distribution style From the Distribution Style drop-down, select Even, Key or All.
For more information on distribution styles, see:
Distribution styles - Amazon Redshift
Edit a distribution key 1. Double-click the row.
A drop-down list will be shown in the Column column.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Delete a distribution key Select the distribution key and then click the Delete button. The key
is deleted.
Change the position of a
distribution key
Select the distribution key and then click the "Up" or "Down" buttons
to move the key to the desired position.
Distribution key procedures
Setting and managing custom sort keys for Amazon Redshift tables
You can define one or more of the physical table columns as sort keys. Amazon Redshift stores your
data on disk in sorted order according to the sort key. The Amazon Redshift query optimizer uses
sort order when it determines optimal query plans. For guidelines on choosing sort keys, visit
Choose the best sort key - Amazon Redshift.
Set and manage sort keys for Amazon Redshift Data Warehouse according to the table below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
246

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Add a sort key 1. Select the Sort Keys tab below the Columns list.
2. From the Sort key style drop-down list, choose one of the
following styles:
l
None to disable the sort keys
l
Compound to use all of the columns listed in the sort key
definition, in the order they are listed
l
Interleaved to give equal weight to each column in the sort
key
3. Click the Add Sort Key button.
A new row is added to the Sort Keys list. The Position column
indicates the order of the column.
4. From the drop-down list in the Column column, select the desired
column.
The column is add to the list.
5. Click OK to save your settings and close the Edit Dimension/Edit
Star Schema window.
Edit a sort key 1. Double-click the row.
A drop-down list will be shown in the Column column.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Change the position
of a sort key
Select the sort key you want to move and then click the up or down
arrows to promote or demote the key.
Delete a sort key Select the sort key you want to delete and then click the Delete button.
Sort key procedures
For more information about sort keys, visit: Choosing sort keys - Amazon Redshift.
Editing dimensions
You can edit a dimension according to your needs. Editing options include adding columns, adding
attributes and defining filters.
Changes in a dimension expression or lookup of a column in a dimension are not updated
retroactively. In order to update historical data, you would need to reload the data which
could take a long time depending on the number of records and their history.
To edit a dimension:
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Data Mart panel.The Manage Data Marts
window opens.
2. In the left pane, select the data mart containing the star schema you want to edit.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
247

5 Data Warehouse projects
3. Expand the list of dimensions and select the dimension you want to edit. Then either click the
Edit button in the lower toolbar or right-click the star schema and select Edit.
The Edit Conformed Dimension - Name (or Edit Dimension - Name if the dimension has not
yet been added to the data mart) window opens. The following tabs are displayed:
l
General tab: In the General tab, you can edit the dimension name, the dimension table
name, the dimension view name and the description. You can also change the
dimension’s history type by selecting Type 1 or Type 2 from the History Type drop-
down list. For more information on changing the history type, see
Understanding
dimension history types (page 252)
.
See also
Data mart views (page 253)
.
l
Logical Attributes tab: In the Logical Attributes tab, you can add and delete columns,
edit a column’s properties, view a column’s lineage, change the column order, and
define filters.
Edit the Logical Attributes tab according to the table below.
l
Physical Table tab: The Physical Table tab provides a preview of the actual
"physical" columns that will be created in the database. All editing tasks are performed
in the Logical Attributes tab, except for defining table creation modifiers which is
performed in the Physical Table tab.
For an explanation of how to define table creation modifiers, see
Example of a Valid
Table Creation Modifier (page 245)
.
4. Edit the Logical Attributes tab according to
Editing star schemas (page 241)
.
You can apply or revert your changes at any time, simply by clicking the Apply or
Cancel buttons respectively.
5. Click OK to close the window and save your settings or Cancel to close the window without
saving your settings.
Editing Logical Attributes
To Do this
Add a new
column
1. Click the New toolbar button.
The New Column window opens.
2. In the Name field, specify a name for the column.
3. From the Type drop-down list, select one of the available data types.
4. If the selected data type requires further configuration, additional fields
will be displayed. For example, when Decimal is selected, the Length and
Scale fields will be displayed. Set the values as required.
5. Optionally specify a Description.
6. Click OK to add the column and close the New Column window.
Logical attributes editing options
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
248

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do this
Edit a
column’s
properties
1. Double-click the row containing the column.
The Edit: Column Name window opens.
2. Edit the properties as described in steps 2-6 of Add a new column above.
Delete a
column
Select the column(s) you want to delete (multi-selection is supported) and click
the Delete toolbar button.
The column(s) are deleted.
View a
Column’s
Lineage
1. Select the desired column.
2. Click the Lineage toolbar button.
A windows displaying the column’s lineage is displayed.
For more information about lineages, see
Lineage and impact analysis
(page 179)
.
Create a
filter
Click the Filter toolbar button. The Expression Builder opens with the heading:
Edit Filter - TableName.
For information on creating filters, see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
Using From Date (FD) and To Date (TD) columns in a filtering
expression is not supported.
The assumption is that columns that are used in the filters do not
change between different versions of the record. If this is not the
case, the
Full rebuild
option should be selected in the Data Mart
settings. This assumption is also true for relationships; for example, if
a Sales record relates to Product which relates to Country, and the
filter is applied to the product's country, then the assumption is that
the sale cannot change its product so that it is filtered in or out based
on a new country.
Create or
edit an
expression
Hover the mouse cursor over the desired table column and then click the fx
button that appears to the right of the Expression column. The Expression
Builder opens with the heading: Edit Expression - Column Name.
For information on creating an expression, see
Creating expressions (page 184)
.
Change the
column order
Select the column(s) you want to move and then click the Move Down/Move to
Bottom or Move Up/Move to Top buttons as desired.
Defining Dimension Table Creation Modifiers
You can set table creation modifiers for individual dimension tables, thereby overriding the default
settings in the project settings'
Table creation modifiers tab (page 42)
. Table modifiers allow you to
append additional table properties to the default Compose CREATETABLE statement.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
249

5 Data Warehouse projects
The available options are located below the Columns list in the Physical Table tab, and are as
follows:
l
Project settings default - When this option is selected (the default), the settings from the
project settings'
Table creation modifiers tab (page 42)
will be used.
l
Custom - This option is useful for if you need to append table creation modifiers to the
default CREATETABLE statement Compose uses for dimension tables. Leveraging this
option requires SQLcoding knowledge.
l
Custom distribution and sort keys - This option is useful if you only need to define custom
distribution keys or sort keys for the dimension table. Although this can also be done using
the Custom option (see below), the Custom distribution and sort keys option is more
convenient as it does not require any prior SQL coding knowledge.
l
Supported with Amazon Redshift only.
l
The default distribution key for all data warehouse tables is the ID column.
Setting table creation modifiers
By default, Compose creates tables in the data warehouse using the standard CREATE TABLE
statement. However, organizations often need tables to be created with custom properties for
better performance, special permissions, custom collation, and so on. For example, in Microsoft
Azure Synapse Analytics, it’s possible to create a table as a HEAP, which is optimized for smaller
tables. By default, Compose creates tables in Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics as a CLUSTERED
COLUMNSTORE INDEX, which offers the best overall query performance for large tables.
The procedure for settings table modifiers is as follows:
1. Open the dimension and select the Physical Table tab.
2. Select the Custom option.
3. Click the Edit button to open the Table Creation Modifier editor.
4. Enter the SQL parts you wish to append to the CREATE TABLE statement.
5. Optionally, but strongly recommended, validate the SQL in an external validation tool that
supports your specific database and version.
Compose does not provide any way of validating your SQL. Therefore, make sure
to validate the SQL before deploying in a production environment.
6. Click OK to close the editor and save your SQL parts.
Example of a Valid Table Creation Modifier
In the following example, the Compose CREATE TABLE statement (rows 1-5) is appended with an
SQL part instructing Compose to create the table as a HEAP (row 6).
CREATE TABLE MyTable
(
column1 integer,
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
250

5 Data Warehouse projects
column2 varchar(50),
)
WITH (HEAP)
Setting and managing custom distribution keys for Amazon Redshift tables
Set and manage distribution keys for Amazon Redshift Data Warehouse according to the table
below.
To Do This
Add a distribution key 1. Click the Add Distribution Key button.
A row is added to the table displaying a drop-down list.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Set a distribution style From the Distribution Style drop-down, select Even, Key or All.
For more information on distribution styles, see:
Distribution styles - Amazon Redshift
Edit a distribution key 1. Double-click the row.
A drop-down list will be shown in the Column column.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Delete a distribution key Select the distribution key and then click the Delete button. The key
is deleted.
Change the position of a
distribution key
Select the distribution key and then click the "Up" or "Down" buttons
to move the key to the desired position.
Distribution key procedures
Setting and managing custom sort keys for Amazon Redshift tables
You can define one or more of the physical table columns as sort keys. Amazon Redshift stores your
data on disk in sorted order according to the sort key. The Amazon Redshift query optimizer uses
sort order when it determines optimal query plans. For guidelines on choosing sort keys, visit
Choose the best sort key - Amazon Redshift.
Set and manage sort keys for Amazon Redshift Data Warehouse according to the table below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
251

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Add a sort key 1. Select the Sort Keys tab below the Columns list.
2. From the Sort key style drop-down list, choose one of the
following styles:
l
None to disable the sort keys
l
Compound to use all of the columns listed in the sort key
definition, in the order they are listed
l
Interleaved to give equal weight to each column in the sort
key
3. Click the Add Sort Key button.
A new row is added to the Sort Keys list. The Position column
indicates the order of the column.
4. From the drop-down list in the Column column, select the desired
column.
The column is add to the list.
5. Click OK to save your settings and close the Edit Dimension/Edit
Star Schema window.
Edit a sort key 1. Double-click the row.
A drop-down list will be shown in the Column column.
2. Select one of the available columns.
Change the position
of a sort key
Select the sort key you want to move and then click the up or down
arrows to promote or demote the key.
Delete a sort key Select the sort key you want to delete and then click the Delete button.
Sort key procedures
For more information about sort keys, visit: Choosing sort keys - Amazon Redshift.
Understanding dimension history types
By default, dimension tables are defined as history type 2, meaning that a new record is added each
time a record is updated (as opposed to updating the same record). In the data warehouse,
dimension tables always contain an object identifier column which is the table name appended with
"_OID". However, when a dimension table’s history type is 2, an additional "version" column is
added as the dimension table’s Primary Key. This column, which is used to identify the version, has
the same name as the table, but is appended with "VID".
The flowing figure shows the Customer_VID and Customer_OID (object identifier) columns in the
Customers dimension table:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
252

5 Data Warehouse projects
If a dimension table is defined as history type 1 and one or more of the columns in the
corresponding data warehouse are defined as type 2, records in the dimension table will
simply be replaced with the most up-to-date record in the corresponding data
warehouse table.
Bulk operations
You can perform the following bulk operations on one or more data marts:
l
Drop and recreate tables
l
Enable/Disable the Optimize for initial load option
l
Generate the data mart task
To perform bulk operations
1. Click the Bulk Operations toolbar button in the Manage Data Marts widow. The Bulk
Operations window opens.
2. Select which operations to perform and on which data marts to perform them.
3. Click OK. The Preparing All Data Marts window opens, displaying the progress of the
selected operations.
4. When the <n> data marts were prepared successfully message is displayed, click Close.
Data mart views
By default, data mart tables are created without corresponding views. Views may be useful
however because they:
l
Allow authorized employees to utilize the data mart for analytics while preventing changes to
the actual data.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
253

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Can be queried without needing to worry about "locking" the data.
When you create a view for a fact or dimension table, you also need to set the schema in which the
view will be created.
Additionally, the schema permissions should only allow authorized employees to access the view
(s).
For instructions on setting the view schema, see
Modifying data mart settings (page 260)
.
See also
Editing star schemas (page 241)
and
Editing dimensions (page 247)
.
Deleting data marts, schemas and dimensions
You can delete data marts, star schemas and dimensions that you no longer require.
Deleting a data mart
1. Select the data mart and then click the upper Delete Data Mart toolbar button.
2. Click OK when prompted to confirm the deletion.
Deleting a star schema
1. Select the star schema and then click the lower Delete toolbar button.
OR
Right-click the star schema and select Delete.
2. Optionally select the Drop unused dimensions check box.
3. Click OK when prompted to confirm the deletion.
Deleting a dimension
1. Select the dimension and then click the lower Delete toolbar button.
OR
Right-click the dimension and select Delete.
2. Click OK when prompted to confirm the deletion.
Creating and managing custom ETLs
You can create and manage Pre and Post Loading ETLs as described in the table below.
Common Table Expressions (CTEs) are not supported as well as some special clauses.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
254

5 Data Warehouse projects
To Do This
Define a Pre Loading or
Post Loading ETL
1. Select either the Pre Loading or Post Loading tab as
appropriate.
2. Click the New button above the User Defined ETL column.
The Add New Pre/Post Loading window opens.
3. Specify a name for the ETL and then click OK.
The name is added as a link to the User-Defined ETL column.
4. Click the link.
The Edit ETL Instruction: Name window opens.
5. To define an ETL:
a. Select a table and/or column and click the arrow to the
right of the selected table/column to add it to the ETL.
b. Use the Select, Delete, Insert and Update quick access
buttons at the top of the window to add SQL statements
to your ETL.
c. To save your ETL, click OK.
d. To enable/disable the ETL, select or clear the check box
to the left of it as required.
Rename a Pre Loading
or Post Loading ETL
1. Select either the Pre Loading or Post Loading tab as
appropriate.
2. At the end of the row containing the ETL name click the Rename
button (A).
3. Rename the ETL and then click OK to save the new name.
Edit a Pre Loading or
Post Loading ETL
1. Select either the Pre Loading or Post Loading tab as
appropriate.
2. At the end of the row containing the ETL name click the Edit
button.
3. Edit the ETL as described in Step 5 of Define a Pre Loading or
Post Loading ETL.
ETLactions
Updating custom ETLs
Compose CLI requires Administrator permission. To grant Administrator permission,
select "Run as administrator" when opening the command prompt. All commands should
be run from the Compose
bin
directory (C:\Program Files\Qlik\Compose with a default
installation).
You can update custom ETLs using the Compose CLI. This functionality can be incorporated into a
script to easily update Custom ETLs.
Syntax:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
255

5 Data Warehouse projects
composecli update_custom_etls --project name --infolder path
Where:
l
project is the name of the project with the custom ETLs you want to update
l
infolder is the full path to the folder containing the custom ETL files
Example:
composecli update_custom_etls --project my-project --infolder
c:\Compose\CustomETLs
The file names in the input folder must be identical to the custom ETL names in the
specified project. Otherwise, an error will occur. The file extension (for example, .txt) is
not important, but the file must be in SQL format.
Viewing and exporting task statements
You can view the task statements that are run during the data mart task. You can also export the
task statements to a CSV file for reviewing and sharing.
To view the task statements:
l
Click the Task statements toolbar button. The ETL - Name window opens in List View.
Navigate through the statements using the scroll bar or find specific statements using the
Search box.
OR
l
Click the Item View button and navigate through the statements using the navigation
buttons at the bottom of the ETL - Name window
To jump to a specific statement, type the statement number in the Go To field at the
bottom of the window and then press [Enter].
To export the task statements to a CSV file:
1. In List View, click the Export to CSV File button located to the left of the search field.
2. A file named "<name>_ETL_Instructions.csv" will be saved to your default Downloads
location or you will be prompted to save it (according to your browser settings).
Validating and adjusting the data mart
Whenever you edit a data mart, certain actions need to be performed to ensure that the data mart is
valid. For a data mart to be considered valid, the tables defined in the data mart need to be identical
to the physical tables in terms of metadata. Depending on the change, this may require adjusting
the physical tables or dropping and recreating them (via Compose).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
256

5 Data Warehouse projects
Additionally, the generated task statements must reflect the current state of the data mart. So, for
example, if a filter or expression was added/edited, you will need to regenerate the task statements
before running the data mart task.
If the data mart is not valid, any tasks that you attempt to run will fail.
Situations in which you need to validate the data mart and/or regenerate the task statements
include:
l
Each time the data warehouse is adjusted
l
Each time a new dimension is added to a star schema
l
Each time a new star schema is added to a data mart
l
Adding or removing columns
l
Changes to a dimension’s history type
l
Changes to transformations (expressions/filters)
l
Changes to a star schema’s transaction date
l
Changes to a star schema’s aggregation type (max, min, etc.)
Note that clicking the Validate button only verifies that the table metadata is valid. In certain cases,
even if the metadata is valid, Compose will prompt you to regenerate the task statements (by
clicking the Generate button).
When you validate a data mart, Compose presents you with a list of operations that it needs to
perform for the data mart to be valid. Examples of such operations include adding dimension and
fact tables, deleting the fact table when the transaction date column has been deleted from the
model, and so on. You can either click Adjust Automatically or Drop and Recreate Tables to
approve the operations or click Cancel to continue working with the data mart in its present state.
To validate the data mart:
1. Click the Validate toolbar button in the Manage Data Marts window. The Validating the
Data Mart progress window opens.
If any differences are detected, the following message will be displayed:
Data mart validation failed. The data mart is different from the model.
2. Click Close. The Model and Data Mart Comparison Report window opens.
3. Review the report and then click Adjust Automatically or Drop and Recreate Tables to
resolve the differences.
Either the Adjust Data Mart progress window opens or, if you clicked Drop and Recreate
Tables, confirm the drop and recreate operation. When you confirm the drop and recreate
operation, the Creating Data Mart: Name window is displayed.
4. When the "The data mart was adjusted successfully." or "The data mart has been created
successfully." (in the case of drop and recreate) message is displayed, close the window.
5. Click the Generate toolbar button to regenerate the task statements.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
257

5 Data Warehouse projects
When a dimension’s history type has been changed directly in the data mart, the data
mart validation will be successful, but you also need to drop and recreate the tables by
clicking the Create Tables toolbar button. For information on changing history types,
see the
General tab
tab in the Edit Dimensions window.
You can also adjust the data mart automatically using the generate_project CLI. For more
information, see
Generating projects using the CLI (page 97)
.
Auto-adjust limitations and considerations
The Adjust Automatically option has the following limitations, which also apply when the data mart
is adjusted using the generate_project CLI.
l
If a new data warehouse attribute was added to a dimension or to a fact by directly editing
them in Compose:
l
All columns are supported except Transaction Date columns, which cannot be added
automatically.
l
For existing records, the newly added column will be set to the database default value,
usually NULL. If you want to load historical data for this column, you need to drop and
create the data mart and then reload it. For information on reloading the data mart, see
Reloading the data mart (page 258)
.
l
If a logical attribute was dropped from a dimension or from a fact in the data mart, the data
mart adjust will:
l
Drop it in the relevant tables, except Transaction Date columns which cannot be
dropped automatically.
l
When there is an external dependent object that prevents deletion of the column (for
example, a View is defined on top of the data mart table), Compose will report the
error in the adjust execution messages. You then need to drop that object and run the
adjust again.
l
For referenced dimensions:
l
Adjusting a data mart does not adjust any dimensions that are referencing that data
mart. The data mart containing the referencing dimensions needs to be adjusted
separately.
l
Adjusting a dimension might also affect the referencing data mart facts.
The limitations and considerations are also applicable when the data mart is
automatically adjusted using the
generate_project CLI
.
Reloading the data mart
After columns have been added to dimension or fact tables as part of an adjust operation, you
might want to load those columns with historical data. You can do this using the
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
258

5 Data Warehouse projects
markReloadDatamartOnNextRun CLI. You mark the entire data mart to be reloaded on the next
run, which might be useful if many columns have been added, or you can mark only specific facts or
dimensions to be reloaded on the next run.
You can also mark dimensions and facts from several data marts to be reloaded on the next run or
mark multiple data marts to be reloaded in their entirety (on the next run) using a CSV file.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe mark_reload_datamart_on_next_run --project
project_name
--datamart
datamart_
name
[--fact
fact_name
|--dimension
dimension_name
|--csv
csvfile_name
] [--obsoleteallrecords]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--datamart The name of the data mart containing the fact(s) or dimension(s) to
be reloaded.
--fact The name of a specific fact you want to be reloaded.
--dimension The name of a specific dimension you want to be reloaded. Any
facts related to these dimensions will also be reloaded to ensure
that the data mart VIDs stay valid.
--obsoleteallrecords Use this parameter to mark all of the existing dimension records as
obsolete. You might need to do this if, for example, a new column
was added to the dimension and you want to reload existing
records with the new column. In such a case, you might want to
preserve the old records as they were before the new column was
added and populated.
See also:
The "Obsolete" indicator (page 262)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
259

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameter Description
--csv A CSV file containing a list of facts or dimensions from one or more
data marts, or a list of data marts. Each row in the CSV file should
also contain "yes" or "no", indicating whether or not to mark the
records as obsolete.
CSV file format:
data mart,fact|dimension,yes|no
Example 1 - Reloading dimensions from two different data
marts:
MyDataMart1,orders,no
MyDataMart2,customers,yes
Example 2 - Reloading two complete data marts:
MyDataMart1,,no
MyDataMart2,,no
Example
ComposeCli.exe mark_reload_datamart_on_next_run --project inventory --datamart MyDataMart
--
fact orders
Modifying data mart settings
You can modify the data mart settings according to your needs.
To modify data mart settings:
1. In the Manage Data Marts window, select a data mart and click Settings.
The Setting - Data Mart Name window opens. In the General tab, the following settings are
available:
l
Log level: Select the log level granularity, which can be any of the following:
l
INFO (default) - Logs informational messages that highlight the progress of the
ETL process at a coarse-grained level.
l
VERBOSE - Logs fine-grained informational events that are most useful to
debug the ETL process.
l
TRACE - Logs finer-grained informational events than the VERBOSE level.
The log levels VERBOSE and TRACE impact performance. Therefore, you should only
select them for troubleshooting if advised by Qlik Support.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
260

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Load Type: Select Full rebuild to build the data mart from scratch each time or
Incremental loading (default) to only load changes.
Incremental loading is not available for Aggregated or State Oriented fact
tables.
l
Create tables in database - By default, data mart tables are created in the database
specified in the data warehouse connection settings. Optionally, click the browse
button and select a different database.
This option is only available for Microsoft SQL Server.
l
Create tables in schema - By default, data mart tables are created in the schema
specified in the data warehouse connection settings. Optionally, specify a different
schema, either by typing the schema name or by clicking the browse button and
selecting one of the existing schemas. If you specify the name of a non-existing
schema, Compose will create the schema automatically.
This option is only available for Microsoft SQL Server, Amazon Redshift,
Snowflake, and Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics.
l
Create views in schema - By default, data mart views are created in the schema
specified in the data warehouse connection settings. Optionally, specify a different
schema, either by typing the schema name or by clicking the browse button and
selecting one of the existing schemas. If you specify the name of a non-existing
schema, Compose will create the schema automatically, unless the database is
Oracle.
If the view schema is different from the data mart schema, you need to
grant the following permission:
Grant SELECT on DM_SCHEMA to DM_VIEW_SCHEMA WITH GRANT OPTION
See also
Data mart views (page 253)
.
2. In the Advanced tab, the following settings are available:
l
Sequential Processing: Select this option if you want to run all the data mart tasks
sequentially, even if they can be run in parallel. This can be good for debugging or
profiling.
l
Maximum number of database connections: Enter the maximum number of
connections allowed. The default size is 10.
For more information, see
Determining the required number of database connections
(page 21)
.
l
JVM memory settings: Edit the memory for the java virtual machine (JVM) if you
experience performance issues. Xms is the minimum memory; Xmx is the maximum
memory. The JVM starts running with the Xms value and can use up to the Xmx value.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
261

5 Data Warehouse projects
Only the following characters are supported (shown as a regular
expression):
/^[-a-zA-Z0-9:]*$/
l
Position in Default Workflow: Set the position you want the data mart to appear in
the default workflow. For more information on workflows, see
Workflows (page 274)
.
l
Optimize for initial load: This option is not applicable to the State Oriented and
Aggregated fact types. If the "Incremental Loading" option is enabled (the default),
clear the "Optimize for initial load" option after the initial load task completes and
regenerate the Data Mart task. If the "Full Rebuild" option is enabled, selecting
"Optimize for initial load" may accelerate the loading process.
l
Write task statement duration to the TLOG_PROCLOG table in the data
warehouse: This option is useful for troubleshooting performance issues with task
statements as it records the duration of each task statement in a special table (named
TLOG_PROCLOG) in the data warehouse. You can then use this information to locate
task statements with abnormal duration times and modify them accordingly.
l
Do not drop temporary tables: Select this option if you want to keep the temporary
tables created during the task. Only use for debugging.
l
Enable table logging: This option is available for Oracle only. When enabled, the data
mart tables will be created with the Oracle LOGGING option enabled. Leaving this
option unselected (the default) should improve performance, but in some cases DML
operations will not be recorded in the redo log file. For more information on this option,
refer to the Oracle online documentation.
3. Click OK.
The "Obsolete" indicator
The Obsolete indicator is used in data marts with Type 2 dimensions and State Oriented Fact tables
only. These type of tables store history, so the attribute OBSOLETE__INDICATION will
always
be
present in data mart tables that contain the From Date and To Date attributes.
The Obsolete indicator is used in data marts when retroactive changes are applied. When a row is
added to a table for an object in which the From Date is earlier than the date of the existing row, the
existing row will be earmarked as obsolete by setting the value for OBSOLETE__INDICATION to the
current run number of the data mark task.
If no retroactive changes are used in the data marts, the value for the OBSOLETE__INDICATION will
be 0.
Rows in a dimension that become obsolete will also enforce changes to the Fact table. The
references of the Fact table to the obsolete rows is updated automatically so that the current,
correct rows are referenced. This means that obsolete rows are isolated, in the sense that they can
be deleted without subverting the referential integrity of the data mart.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
262

5 Data Warehouse projects
The reason Compose does not delete these rows is for auditing purposes. For instance, consider a
report that was generated in the past (using the data mart) and now contains incorrect information.
Inspecting the obsolete rows may account for the discrepancy (i.e. incorrect data in the database
as opposed to a deliberate attempt to manipulate the data).
5.9 Creating and managing command tasks
Command tasks enable you to incorporate custom processes into your Compose workflow. This is
especially useful if you need to leverage external tools to transfer files, validate data, and so on. A
Command task can run any script or executable supported by the operating system including batch
files, Python scripts, PowerShell scripts, executables and so on.
For security reasons, command tasks are blocked by default. To enable command tasks,
a Compose administrator needs to run the following commands in the Compose CLI:
ComposeCli.exe connect [--url connection-url]
Where --url connection-url is only required if the Compose Server is on a different
machine.
To enable task commands:
ComposeCli.exe allow_user_scripts --enable
To disable task commands:
ComposeCli.exe allow_user_scripts --disable
In this section:
l
Defining command tasks (page 263)
l
Managing command tasks (page 264)
l
Controlling and monitoring command tasks (page 264)
Defining command tasks
This section explains how to define a command task. You can define as many command tasks as
you need and execute them at different stages of a Compose workflow.
Before you define a command task, make sure that the executable or script file that you
want to run resides in the following directory on the Compose server machine:
PRODUCT_DIR\data\projects\YOUR_PROJECT\scripts
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
263

5 Data Warehouse projects
To define a command task:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Manage Command Tasks.
The Manage Command Tasks window opens.
2. Provide a name for the task.
Task names cannot contain the following characters: /\,&#%$@=^*+"'`~?<>:;[]{}
as well as all non-printable characters (below 0x20). The task name can contain a
single dot, but it cannot be the first or last character.
3. Optionally, enter a description.
4. In the Script/Executable File field, specify the name of the files that you want to run.
5. In the Parameters field, specify any parameters required by the command. Parameters
should be separated by a space.
6. The user context is the user account under which the Task will run. To change the current
user context, provide the User, Password and Domain of the account under which you want
the Task to run.
7. Click Save to save your changes or Discard to discard any unsaved changes.
The task will be added to the list of tasks in the left of the window.
Managing command tasks
The table below describes the task management options.
Editing a task
Select the task in the tasks list in the left of the Manage Command Tasks window and edit it as
described in
Defining command tasks (page 263)
.
Deleting a task
Select the task in the tasks list in the left of the Manage Command Tasks window and then click
the Delete toolbar button. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click OK.
Searching for a task
Enter part of the task name in the search box above the task list. The list of tasks will be filtered to
show only tasks that include the search term in their name.
Controlling and monitoring command tasks
Command Tasks can be run from the Manage Command Tasks window or from the main Compose
Monitor view. Although they can be run individually, command tasks are usually run as part of a
workflow.
For information on defining workflows, controlling and monitoring tasks, and controlling and
monitoring workflows, see
Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows (page 265)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
264

5 Data Warehouse projects
To run a command task from the Manage Command Tasks window:
1. Open the Manage Command Tasks window and select the task you want to run.
2. Click the Run toolbar button.
3. The Manage Command Tasks window switches to Monitor view.
In Monitor view the following information is available:
l
The task ID
l
The current status
l
When the task started and ended
l
The overall task progress
5.10 Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows
The Compose monitor shows the current status of all your tasks and enables you to drill-down for
additional information about each task. Task instances can be run immediately or scheduled to run
in the future (either once or at set intervals).
In this section:
l
Viewing information in the monitor (page 265)
l
Viewing missing references (page 267)
l
Controlling tasks (page 269)
l
Notifications (page 272)
l
Workflows (page 274)
l
Monitoring and controlling Qlik Replicate tasks (page 279)
Viewing information in the monitor
As well as providing a high-level summary of all your tasks, the monitor also lets you view more
detailed information about specific tasks.
To switch to monitor view:
1. Open a data warehouse project and click the Monitor icon in the top right of the console.
A list of tasks is displayed for the current project. The left pane of the monitor allows you to
filter the task list by status as well as indicating the current number of running, failed and
completed tasks.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
265

5 Data Warehouse projects
For each task, the monitor displays the following information:
l
Status - Running, Completed or Failed
l
Name - The task name.
l
Type - Data Warehouse, Data Mart, Workflow, Command Task or Replicate Task.
l
Started and Ended - The date and time the task started and completed (according to
the server time). If the task is running, the Ended column will display the current
progress. In the case of a Replicate task performing Change Processing, Running CDC
will be displayed.
l
Next Instance - The next time the task is due to run (if the task is scheduled).
l
Elapsed Time - The time it took for the task to complete or - if the task is still running -
how long the task has been running.
l
Inserted Rows - The number of rows inserted into the data warehouse or data mart.
l
Updated Rows - The number of rows updated in the data warehouse or data mart.
l
Reported Rows - The number of rows reported to the error mart table(s). - The
number of rows reported to the error mart table(s).
For more information on error marts, see
Defining and managing data quality rules
(page 215)
.
l
Disabled - Whether the scheduled job has been disabled.
2. To view additional information about a task, select the task. The information is displayed in
the following tabs in the lower pane of the monitor:
l
Details - Use the navigation arrows to browse through task instances. For each entity,
the total number of inserted, updated and deleted rows is shown. Click the number to
see more information about the record.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
266

5 Data Warehouse projects
For fact tables, it is possible to view details about inserted rows, but not of
updated rows.
l
History - The History tab provides a list of previous task instances.
To view a task instance’s log file, select the task and click the View Log button.
To view more details about a task instance, either double-click the instance or select
the instance and then click the View Instance Details button. The Details tab is
shown.
l
Progress Status - The Progress Status tab shows the task’s current progress as well
as the sub-status of task statements within the task (Waiting/Standby, Running,
Failed, etc.). To see details about a specific task statements, click the number to the
right of the command status.
For example, to view more information about an task statement with an error status,
click the number to the right of Error.
l
Error Mart - The Error Mart tab displays information when one or more Data Quality
rules are enforced during the task (and the rules have been configured to report non-
compliant data).
The following information is available:
l
Entity Name - The name of the entity for which rule was created.
l
Mappings - The mapping for which the rule was created.
l
Error Mart Table - The name of the error mart table crated as a result of the
rule being enforced.
l
Schema - The name of the schema containing the error mart table.
l
Reported Rows - The number of rows reported to the error mart. Clicking the
number opens the actual error mart table as it appears in the data warehouse.
l
Missing References - For a description of this tab, see
Viewing missing references
(page 267)
.
See also:
Defining and managing data quality rules (page 215)
.
3. To run a job immediately, select the task and then click the Run toolbar button.
4. To view a task’s settings, select the task and then click the Open toolbar button. For more
information about the settings, see
Creating and managing the data warehouse (page 192)
and
Creating and managing data marts (page 228)
.
Viewing missing references
In some cases, incoming data is dependent on or refers to other data. If the referenced data cannot
be loaded for some reason, you can either decide to add the data manually or continue on the
assumption that the data will arrive before it is needed.
There are two ways you can view missing references in Compose. Either via the Monitor tab in the
Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window or by switching the console to Monitor view and selecting
the Missing References tab. The instructions below cover both of these methods.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
267

5 Data Warehouse projects
To check for missing references in the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window:
1. Click the Manage button in the lower left corner of the Data Warehouse panel.
2. Select the desired task in the left side of the Manage Data Warehouse Tasks window.
3. Switch to Monitor view by clicking the Monitor tab in the top right of the Manage Data
Warehouse Tasks window.
4. Click the View Missing References toolbar button. The Missing References - <
task
Name
> window opens.
The following information is displayed:
l
General information: The run number of the task, when it started and ended, the total
number of inserts and updates, and the number of reported rows (if any).
l
Missing references information:
l
Missing Records from Entity - The name of the entity with missing reference
and the number of missing references.
To see the missing record keys for the entity, click the number in parentheses
to the right of the entity name.
The Missing Record Keys for Entity - <Entity Name> window opens showing
the list of missing keys and the number of times each key is referenced per
entity.
l
Referenced from Entity - The entities that are referencing the entity with
missing references.
l
Via Relationship - The name of the relationship in the Model.
5. To close the window, click Close.
To check for missing references in the Compose Monitor:
1. Switch the console to Monitor View.
2. Select the desired task.
3. Click the Missing References tab below the task list.
The following information is displayed:
l
General information: The run number of the task, when it started and ended, the total
number of inserts and updates, and the number of reported rows (if any).
l
Missing references information:
l
Missing Records from Entity - The name of the entity with missing reference
and the number of missing references.
To see the missing record keys for the entity, click the number in parentheses
to the right of the entity name.
The Missing Record Keys for Entity - <Entity Name> window opens showing
the list of missing keys and the number of times each key is referenced per
entity.
l
Referenced from Entity - The entities that are referencing the entity with
missing references.
l
Via Relationship - The name of the relationship in the Model.
4. To close the window, click Close.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
268

5 Data Warehouse projects
Missing references example
In the following example, Orders and Disputes both reference Customers.
Orders contains seven records pointing to Mr. Brown and one record pointing to Mr. Smith.
Disputes contains four records referencing Mr. Brown. Mr. Brown and Mr. Smith are "missing" from
Customers.
The would be reflected as follows:
Missing Records from Entity Referenced from Entity Via Relationship
Customers (2) Orders (8) Customers
- Disputes (4) CustomerDisputes
Example table content
Clicking the number to the right of Customers (in the Missing Records from Entity column) would
open the following window:
Key Referenced from Entity Via Relationship
Mr. Brown Orders (7) Customers
- Disputes (4) CustomerDisputes
Mr. Smith Orders (1) Customers
Example table content
See also:
How Compose handles missing references in the data warehouse (page 193)
.
Controlling tasks
You can run and stop tasks/workflow manually or you can schedule them to run periodically.
In this section:
l
Running and aborting tasks manually (page 269)
l
Scheduling tasks (page 270)
l
Generating tasks using the CLI (page 270)
l
Running tasks using the CLI (page 271)
Running and aborting tasks manually
You can run tasks manually and abort them if required.
To run a task manually:
l
Select the task and click the Run toolbar button.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
269

5 Data Warehouse projects
To abort a task:
l
Select the task and click the Abort toolbar button.
The task process is aborted. Note that aborting a task may leave the data warehouse or data
mart tables in an inconsistent state. Consistency will be restored the next time the task is
run.
Scheduling tasks
Scheduling tasks is a convenient way of continually updating the data warehouse and associated
data mart(s). For instance, you could schedule a data warehouse task to run at 4:00 pm and then
schedule a data mart task to run at 5:00 pm.
Note that as Compose does not provide a task-chaining option (i.e. run another task as soon as the
current task completes), it may be better to schedule tasks using an external tool that supports this
capability.
You can also use the command line interface (CLI) to run an task. For details, see
Running tasks
using the CLI (page 271)
.
To schedule a task:
1. Click the Schedule toolbar button.
2. In the <Name> Scheduler window, choose one of the following options from the Run Job
drop-down list.
l
Once - to run the job once on a specific date and time.
l
Every - to run the job at set intervals.
l
Daily - to run the job every day at a specific time.
l
Weekly - to run the job on selected days at a specific time
l
Monthly - to run the job on the nth of every month at a specific time
l
Advanced - to use a Cron expression. For a description of allowed cron formats
together with usage examples, see
Cron format and examples (page 405)
.
3. Set the scheduling parameters according to the selected scheduling option.
4. Click OK to save your settings.
The date and time the next instance is scheduled to run will appear in the Next Instance
column.
5. To disable a scheduled job, select the task and click the Edit Scheduling toolbar button.
Then, select the Disable check box in the <Name> Scheduler window.
6. To cancel a scheduled job for a task, select the task and click the Edit Scheduling toolbar
button. Then, in the <Name> Scheduler window, click Delete.
Generating tasks using the CLI
Before you can generate a task, you must first run the Connect command as described in
Connecting
to Qlik Compose server (page 77)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
270

5 Data Warehouse projects
As Compose CLI requires Administrator permission, make sure to select "Run as
administrator" when opening the command prompt.
Use the generate_tasks command to generate tasks at project, task, data warehouse, and data mart
level.
When this command succeeds, it returns 0.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe generate_tasks --project [project-name] --type [DW|DM] --task [task-name] --
timeout --skip_external_checks
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--type The type of tasks to generate. Specify DW to generate data
warehouse tasks or DM to generate data mart tasks. If omitted, all
tasks will be generated, unless the "task" and/or "project"
parameters are included in the command.
--task The name of the task to generate. If omitted, all tasks will be
generated, unless the "project" and/or "type" parameters are
included in the command.
Example
ComposeCli.exe generate_tasks --project myproject --type DW --task mytask --timeout --skip_
external_checks
Running tasks using the CLI
Before you can run a task, you must first run the Connect command as described in
Connecting to
Qlik Compose server (page 77)
.
As Compose CLI requires Administrator permission, make sure to select "Run as
administrator" when opening the command prompt.
The run_task command populates the data warehouse or data mart with data. The "ETL" operation
can also be performed using the Run toolbar button located in Monitor view as well as in the
Manage Data Warehouse Tasks and Manage Data Marts windows.
When this command succeeds, it returns 0.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe run_task --project
project_name
--type DW|DM|WF --task
task_name
--wait
timeout_in_sec
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
271

5 Data Warehouse projects
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--type The type of tables that you want to populate. Specify DW to
populate a data warehouse, DM to populate a data mart, or WF to run
a workflow.
--task When:
l
--type DW, this should be specified as the name of the task
that you want to run.
l
--type DM, this should be specified as the name of the data
mart that you want to populate.
l
--type WF, this should be specified as the name of the
workflow that you want to run.
--wait The wait time specified in seconds.
The command line can run in sync or async mode. A value of 0
(seconds) indicates sync mode. This means that as soon as the
task finishes, the command line returns to prompt. The default
mode is async, with a value of -1. This is also applied if you leave
this parameter empty. Other negative values are not permitted.
Note that if wait is excluded from the command, the task may
appear to complete successfully even if it encountered an error.
Example
ComposeCli.exe run_task --project MyProject --type DW --task DWH1 --wait 1
Notifications
You can select events, on the occurrence of which, a notification will be sent to the specified
recipients.
Adding a notification rule
To set a notification rule:
1. Switch to Monitor view.
2. Click the downward arrow at the top left of the console and select Notification Rules from
the drop-down menu.
The Notification Rules window opens.
3. Click the New toolbar button.
The New Notification wizard opens.
4. In the Events screen:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
272

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Specify a name for the notification
l
Choose for which type of events you want the notification to be sent, both at the task
level and at the workflow level.
5. Click Next. In the Recipients screen:
l
Select Windows Event to send the notification to Windows Event Log and/or
Recipients to send the notification to a list of email recipients.
l
If you selected Recipients, enter the recipient email addresse(s) in the To, Cc
(optional) and Bcc (optional) boxes. Multiple addresses must be separated by a semi-
colon.
6. Click Next. In the Message screen, optionally, edit the default notification message. You can
add variables to the message by selecting the variable on the right and then clicking the
arrow to the left of the variables list.
The following variables are available:
Variable Description
${PROJECT} The name of the Compose project in which the event
occurred.
${TASK_NAME} The name of the task in which the event occurred.
${INSERTED} The number of rows inserted in the Data Warehouse/Data
Mart.
${UPDATED} The number of rows updated in the Data Warehouse/Data
Mart.
${DELETED} The number of rows deleted from the Data
Warehouse/Data Mart.
${ERROR_CODE} The error code if an error was encountered during the task.
${ERROR_DETAILS} The error message if an error was encountered during the
task.
${EVENT_TYPE} The event type (Started, Error or Completed).
${EVENT_TYPE_
DESCRIPTION}
-
${EVENT_TIME} The date and time the event occurred.
${LINK} A link to the relevant Compose project.
Notification message variables
7. Click Next. In the Associate with screen, select whether to apply the rule to all tasks of to
selected tasks. If you chose Selected Tasks, select which tasks to apply the rule to.
8. Click Next to see a summary of the notification settings or Finish to save your settings and
exit the wizard.
9. If you clicked Next, review your settings and then click Finish to save the notification rule
and exit the wizard or Prev to edit your settings. You can also click the headings on the right
of the wizard to go directly to a specific window.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
273

5 Data Warehouse projects
The notification will be added to the list of notifications in the Notification Rules window.
Managing notification rules
In the Notification Rules window, you can edit, delete and enable/disable notification rules as
described in the table below.
To Do This
Delete a
Rule
Select the rule and then click the Delete toolbar button. When prompted to confirm
the deletion, click Yes.
Edit a
Rule
Either double-click the rule you want to edit or select the rule and click the Edit
toolbar button. Continue from
Notifications (page 272)
.
Disable a
Rule
Select the rule you want to disable and then either click the Disable toolbar button or
clear the check box in the Enabled column.
Enable a
Rule
Select the rule you want to enable and then click the Enable toolbar button or select
the check box in the Enabled column.
Notification rule actions
Event IDs in Windows Event Log
The table below lists the Event IDs for Compose events in Windows Event Log.
If a notification is set for several events, the event ID will be 0 for each of the events.
Event IDs for task states within Workflows are not supported.
Event ID Description
261 The task ended with error
400 The task has started.
406 The task completed successfully.
Windows Event Log IDs
Workflows
Workflows enable you to run tasks both sequentially and in parallel. You can either schedule
workflows as described in
Scheduling tasks (page 270)
or run them manually using the Run toolbar
button.
You can create your own workflow and/or use the built-in workflow. The built-in workflow enables
you to run all of your data warehouse and data mart tasks as a single, end-to-end process. In a
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
274

5 Data Warehouse projects
project with a single data mart, all tasks run sequentially in the default workflow, starting with the
data warehouse tasks and ending with the data mart task. However, in projects with multiple data
marts, the data mart tasks run in parallel, following the completion of the data warehouse tasks.
When you create your own workflow, you decide which tasks to include in the workflow and the
order in which they will be run.
In this topic:
l
Adding and designing workflows (page 275)
l
Validating workflows (page 277)
l
Managing workflows (page 279)
l
Running and monitoring workflows (page 278)
Adding and designing workflows
This section provides instructions for adding and creating workflows.
Adding a workflow
To add a workflow:
1. Switch to Monitor view by clicking the Monitor button in the top right of the Compose
console.
2. Click the New Workflow toolbar button.
The New Workflow window opens.
3. To create a workflow with all current tasks, select Create default workflow and then click
OK. Otherwise, continue from Step 4 below. Separate workflows will be created for Full Load
and Change Processing tasks. The default workflow cannot be edited and will appear as
Default Workflow in the list of monitored tasks.
To update the default workflow with newly added tasks, repeat steps 2-3 above.
4. Specify a name for your workflow.
5. To create a workflow based on an existing workflow, select the Duplicate from check box
and then select an existing workflow from the drop-down list.
6. Click OK to save your settings.
The <workflow_name> window opens.
7. Continue from Designing a workflow below.
Designing a workflow
The workflow window is divided into two panes. The pane on the left (hereafter referred to as the
Elements pane) is where you design your workflow and contains two default elements: Start and
End.
The Elements pane contains gateways and tasks that you can use in your workflow. The following
elements are available:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
275

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
Tasks - All existing Data Warehouse tasks, Data Mart tasks, and Command tasks.
l
Gateways - There are two types of gateway: Parallel Split and Synchronize. Use the
Parallel Split gateway to create parallel paths. This is useful, for example, if you want two or
more tasks to run in parallel.
Use the Synchronize gateway to merge parallel paths. The workflow waits for all the Tasks
that precede the gateway to complete before continuing the flow.
To design a workflow:
1. Drag the desired workflow elements from the Elements pane to the pane on the left.
2. Arrange the elements in the order that you want them to run.
3. Connect the elements to each other by dragging the connector from the gray dot (that
appears on the right of an element when you hover the mouse cursor over it) to the target
element. When a blue outline appear around the target element, release the mouse button.
4. Optionally add error paths to the workflow. The workflow will follow the error path if a task
encounters an error. For example, if an error occurs with a Data Mart task, you may want to
run another Data Mart task in its place.
To add an error path, hover your mouse cursor over the task element. A red dot will appears
below the element. Drag the connector from the red dot to the target element, as shown
below.
Connecting two error paths to the same task should be avoided as the workflow will fail
if the task tries to run twice.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
276
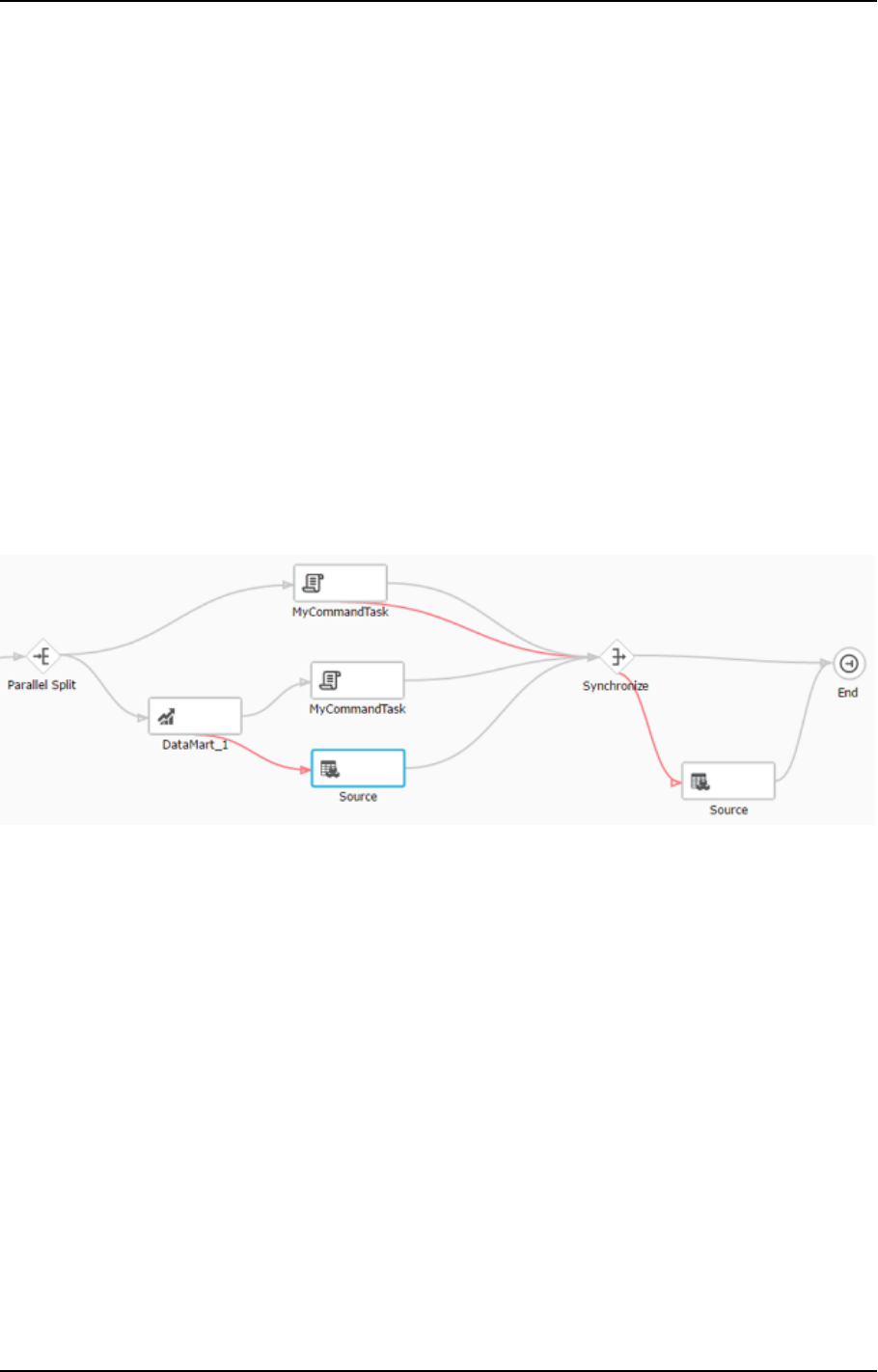
5 Data Warehouse projects
Continuing a workflow in the event of parallel task failure
In a workflow, all task elements have an error port. This allows you to change the course of the
workflow in the event of a task failure, as described in Step
Adding and designing workflows (page
275)
above. Similar to Task elements, the Synchronize gateway also has an error port which can be
used to reroute the workflow if any of the tasks between the Parallel Split and Synchronize
gateways should fail.
By default, a workflow will end with an error if one or more parallel tasks do not complete
successfully. However, in certain cases you may want the workflow to continue, even if one or more
of the parallel tasks failed.
To do this, you need to connect the error port of the relevant task(s) directly to the Synchronize
gateway. You can also design the workflow so that it follows the path leading from the Synchronize
error port, instead of continuing its normal flow.
In the example below, the error port of the MyCommandTask is connected to the Synchronize
gateway, meaning that even if MyCommandTask task fails, the workflow will continue. However, if
the MyCommandTask task fails, the workflow will not proceed directly to the End element. Instead,
it will follow the Synchronize gateway’s error path to the Source task.
Validating workflows
It is strongly recommended to validate your workflow before running it. This will prevent errors from
occurring during runtime due to an invalid workflow.
Workflow rules include:
l
All elements must be connected to each other
l
A workflow must contain Start and End elements and at least one task.
l
A workflow cannot contain a Parallel Split gateway without a Synchronize gateway and vice
versa.
l
Data warehouse tasks cannot run in parallel with data mart tasks.
l
Data warehouse tasks that update the same tables cannot run in parallel.
l
A workflow cannot contain a Parallel Split gateway without a Synchronize gateway and vice
versa.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
277

5 Data Warehouse projects
l
The execution order of elements must be sequential and not cyclic. For example an element
cannot loop back to an element that precedes it in the execution order.
To validate your workflow:
l
Click the Validate Flow toolbar button.
If the workflow is valid, a "<workflow_name> is valid." message will be appear at the top of the
window. If the workflow is not valid, a message describing the problems will appear instead.
Generating workflow tasks
If you made changes to workflow tasks that require the tasks to be regenerated, you can generate
To generate workflow tasks:
1. In the workflow editor, click the Generate button.
The Bulk Generate dialog opens.
2. Select the tasks you want to generate.
3. Optionally, change the task validation level:
l
With basic validations: By default, Compose generates tasks with basic validations.
Basic validations are suitable for most tasks, but are especially useful for tasks with
numerous expressions and lookups, as generating such tasks with all validations could
take a long time.
l
With all validations: This includes validations that access the database to verify the
existence of columns used in expressions and lookups. As selecting All validations
will significantly lengthen the time it takes to generate the task, you should only select
it if it's critical to verify that existence of such columns before the tasks starts.
4. Click the OK to close the dialog and start the task generation.
Running and monitoring workflows
You can either schedule workflows as described in
Scheduling tasks (page 270)
or run them
manually using the Run toolbar button. The Run toolbar button appears both in the main Monitor
view and in the workflow design window. Note that when you run a workflow from the workflow
design window, a new Monitor tab is added to the window and the view automatically switches to
the Monitor tab.
You can monitor the workflow either in the Monitor tab or in the Progress Status tab. During
runtime, the workflow elements fill with blue providing a graphic indication of progress. If a task
encounters an error, the task element will appear with red fill instead of blue.
The example below shows a workflow containing three data warehouse tasks and one data mart
task. In the workflow, the data mart task will be run only after the completion of the parallel data
warehouse tasks.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
278

5 Data Warehouse projects
Managing workflows
The table below describes the options available for managing workflows.
To Do This
Delete a
Workflow
In Monitor view, select the workflow in the Task column and then click the
Delete Workflow toolbar button.
Edit a
Workflow
In Monitor view, either double-click the workflow you want to edit or select the
workflow and click the Open toolbar button. Continue from
Adding and
designing workflows (page 275)
.
Delete an
element in
workflow
Either right-click the element and select Delete or select the element and then
click the Delete toolbar button.
Reset the
workflow view
Click the reset button to the right of the slider at the top of the window.
Zoom in
to/zoom out of
the workflow
Move the slider at the top of the window to the left or right as required.
Workflow management actions
Monitoring and controlling Qlik Replicate tasks
Before you can create a Compose project, you need to define a Replicate task that replicates the
relevant source tables from the source database to the landing zone. You can define a different
task for each project or the same task can serve several projects.
Monitoring and controlling Replicate tasks from within Compose involves the following steps:
l
Step 1: Configure Compose to connect to the Replicate machine (page 280)
l
Step 2: Add the Replicate task to the data source settings (page 280)
l
Step 3: Monitor and control the Replicate task (page 281)
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
279

5 Data Warehouse projects
Step 1: Configure Compose to connect to the Replicate machine
1. Open the Manage Replicate Servers window using any of the following methods:
l
From the Management drop-down menu in the main toolbar, select Manage
Replicate Servers.
l
In the New Data Source window, click the Replicate Server Settings link below the
Associate with Replicate task field.
The Manage Replicate Servers window opens.
2. Click Add Replicate Server.
The Add Server window opens.
3. Enter the following information:
l
Name: A display name for the server.
l
Description: (Optional) A description for the server.
l
Host: The IP address or host name of the Qlik Replicate machine.
When Replicate Server is installed on Linux, enter the IP address of the
Windows machine on which the Replicate UI Server is running.
l
Port: Optionally, change the default port (443). You should only change the default
port if you are certain that a different SSL port is being used.
l
User Name and Password: Your credentials for logging in to the Qlik Replicate
machine.
When Replicate Server is installed on Linux, enter the user name and
password for the Windows machine on which the Replicate UI Server is
running.
l
Get metadata timeout - The time to wait when discovering a task’s source database
or refreshing the metadata cache before returning a timeout error.
l
Get task timeout - The time to wait when starting a Replicate task before returning a
timeout error.
In environments with complex networks, operations related to Replicate
may exceed the default timeout limit. If you experience frequent timeouts
starting tasks, discovering a task’s source database, or refreshing the
metadata cache, increasing these values may help.
4. Click Test Connection and then click OK if the connection is successfully verified.
The server is added to the Manage Replicate Servers window. Click Close to close the
window.
Step 2: Add the Replicate task to the data source settings
1. Open the New Data Source or Edit Data Source: <Name> window as described in
Defining
landing zones (page 140)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
280

5 Data Warehouse projects
2. Click the browse button to the right of the Associate with Replicate task field.
The Select Replicate Task window opens.
3. Select a Replicate Server from the Server drop-down list.
The Replicate Tasks list is populated with all tasks defined on the selected server.
4. Select the task that is replicating the source tables to the landing zone and then click OK.
5. If you want to discover source database for model generation, select Source database
connection and then configure the settings as described in
Defining Replicate data source
connections (page 147)
.
6. When you're done, click OK again to save the data source settings.
The Replicate task is immediately added to the Compose monitor.
Step 3: Monitor and control the Replicate task
The example below shows how the Replicate task appears in the Compose Monitor. You can start
and stop the Replicate task using the Abort and Run toolbar buttons. To view and edit the task on
Replicate Server, click Open.
If a task is stopped from within Replicate, the task status in Compose will be
"Completed" instead of "Aborted".
You can also define notifications for the task and add the task to a workflow. For more information,
see
Notifications (page 272)
and
Workflows (page 274)
respectively.
The monitor provides various information about the task. For details, see
Viewing information in the
monitor (page 265)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
281

6 Data Lake projects
6 Data Lake projects
This section explains how to set up Data Lake projects.
In this section:
l
Defining a Qlik Replicate task (page 282)
l
Adding and managing Data Lake projects (page 284)
l
Getting started with Data Lake projects (page 311)
l
Setting up landing and storage connections (page 314)
l
Selecting source tables and managing metadata (page 325)
l
Creating and Managing Storage Zone Tasks (page 347)
l
Creating and managing command tasks (page 363)
l
Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows (page 365)
6.1 Defining a Qlik Replicate task
In order to work with Compose, you first need to define a Qlik Replicate task that replicates the
source tables from the source endpoint to a landing zone in the storage (defined as the target
endpoint in the Replicate task). The landing zone should then be defined as the data source for the
Compose project.
For information on which endpoints can be used in a Replicate task that lands data for Compose,
see
Supported hive distributions for Data Lake projects (page 404)
.
Configuring multiple Replicate tasks with the same landing zone is not supported.
The steps below highlight the settings that are required when using Qlik Replicate with Compose.
For a full description of setting up tasks in Qlik Replicate, please refer
to the
Qlik Replicate Help
.
Prerequisites
When defining the Replicate task, make sure the following prerequisites have been met.
l
If the Landing Zone database supports append, it is recommended to select Sequence as
the file format in the Replicate target endpoint settings and to set the Control Tables format
(if available) to Text. This will improve performance by allowing Replicate to append to the
file instead of creating a new file for every Change Data Partition.
If the above is not possible, then it is recommended to periodically delete files that are no
longer required from the target directory. This will prevent files from amassing and degrading
performance. This can be done automatically using Replicate's partition retention feature.
For more information, see the Qlik Replicate Help
.
l
When Microsoft Azure HDInsight is defined as the Replicate target endpoint, you must set
the endpoint's Target storage format to Sequence.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
282

6 Data Lake projects
l
When Oracle is defined as the source endpoint in the Replicate task, full supplemental
logging should be defined for all source table columns that exist on the target and any source
columns referenced in expressions.
When using
live views
, to ensure transactional consistency, it is recommended to turn
off Speed partition mode in the Replicate task settings. When set to off, Replicate will
close the partition only at the end of each transaction. This might require you to shorten
the partition interval in order for the changes to be propagated to Compose in a timely
manner. Shortening the partition interval might also require you to increase the partition
cleanup frequency to prevent too many files from accumulating on the target and
degrading performance.
For information about turning off Speed partition mode, setting partitioning intervals,
and partition cleanup, see the
Replicate Help
.
Limitations and Considerations
l
Replicate allows you to define global transformations that are applied to source/Change
tables during task runtime. The following global transformations, however, should not be
defined (as they are not compatible with Compose tasks):
l
Rename Change Table
l
Rename Change Table schema
l
The Create target control tables in schema option in the Replicate task settings' Control
Table tab is not supported.
l
As Compose does not use the before-image for UPDATEoperations, it is recommended to
set On UPDATE in the Store Changes Settings tab of the Replicate task settings to Store
after image only. Note that this should only be done if the Replicate task is dedicated for use
with Compose.
l
As Compose requires a full after-image to be able to perform Change Processing, the
following Replicate source endpoints are not directly supported (as they do not provide a full
after-image):
l
SAP HANA (log based)
l
Salesforce
l
Compose does not support the JSON and XML data types. Therefore, columns that are
usually created with these data types (by the Replicate target endpoint) should be created as
STRINGs instead. This can be done automatically within Replicate using a data type
transformation. For information on which target endpoints support JSON and XML data types
as well as instructions on how to create a data type transformation, refer to the Replicate
Help.
l
If you use Replicate November 2022 to land data in Databricks, only the Databricks (Cloud
Storage) target endpoint can be used. If you are using an earlier supported version of
Replicate, you can continue using the existing Databricks target endpoints.
Setting up the task
To define the task:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
283

6 Data Lake projects
1. Open Qlik Replicate and in the New Task dialog, do one of the following:
l
To enable Full Load and CDC replication, enable the Full Load and Store Changes
options only (the Apply Changes option should not be enabled).
l
To enable Full Load only replication (without CDC), enable the Full Load replication
option only.
2. Open the Manage Endpoint Connections window and define a source and target endpoint.
The target endpoint must be the Hive database where you want Compose to create the
Storage Zone tables. For more information on supported endpoints, see
Supported hive
distributions for Data Lake projects (page 404)
.
3. Add the endpoints to the Replicate task and then select which source tables to replicate.
4. This step is not relevant for Full Load only tasks. To facilitate
Schema evolution (page 337)
in
Compose, select the DDL History Control Table in the Task Settings’ Metadata|Control
Tables tab. If you intend to scan all data sources (when performing schema evolution), then
you must do this for ALL Replicate tasks that move data to the Landing Zone, even those with
source endpoints that do not support schema evolution (e.g. Salesforce).
If you want the DDL History Control Table to be updated with any new source
tables that are added during the Replicate task, you must define Table Selection
Patterns in Replicate's Select Tables window.
5. This step is not relevant for Full Load only tasks. In the Task Settings' Store Change Setting
tab, make sure that Store Changes in is set to Change tables.
6. This step is not relevant for Full Load only tasks. In the Task Settings’ Change
Processing|Store Changes Settings tab, enable Change Data Partitioning.
7. This step is not relevant for Full Load only tasks. In the Task Settings’ Metadata|Control
Tables tab, select the Change Data Partitioning Control Table.
8. This step is not relevant for Full Load only tasks. If a Primary Key in a source table can be
updated, it is recommended to turn on the DELETE and INSERT when updating a primary
key column option in Replicate's task settings' Change Processing Tuning tab. When this
option is turned on, history of the old record will not be preserved in the new record. Note
that this option is supported from Replicate November 2022 only.
9. Run the task.
Wait for the Full Load replication to complete and then continue the workflow in Compose as
described in
Adding and managing data warehouse projects (page 35)
.
6.2 Adding and managing Data Lake projects
This section describes how to add and manage Data Lake projects.
Prerequisites
Before defining your Data Lake project, make sure the following prerequisites have been met.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
284

6 Data Lake projects
Required clients
Depending on the Compute platform you select when you set up your project, you will need to
install one of the following drivers.
l
As the driver name is the same for Cloudera Data Platform, Google Dataproc, and
Azure HDInsight, in order to prevent driver conflicts, only one project with any of
the aforementioned compute platforms can be created per Compose installation.
l
As the driver name is the same for Cloudera Data Platform and Amazon EMR, in
order to prevent driver conflicts, only one project with any of the aforementioned
compute platforms can be created per Compose installation.
Cloudera Data Platform, Google Dataproc, and Azure HDInsight
1. Download the Hive JDBC Driver from the Cloudera website:
https://www.cloudera.com/downloads/
Then, extract the HiveJDBC41.jar file from the zip file that contains the Hive JDBC
Connector.
You need to register on the Simba and Cloudera websites before you can
download the Hortonworks or Hive JDBC Driver.
2. Copy the HiveJDBC41.jar file to <Compose_Installation_Dir>\java\jdbc.
3. Restart the Qlik Compose service.
Databricks
1. Download the SimbaSparkJDBC42-<version>.zip or DatabricksJDBC42-<version>.zip
file from the Databricks website.
Unity Catalog support requires DatabricksJDBC42-2.6.32.1054.zip or later.
2. Copy the SparkJDBC42.jar file or the DatabricksJDBC42.jar file (according to the file you
downloaded) to
<compose_product_dir>\java\jdbc
.
3. Restart the Qlik Compose service.
Amazon EMR
1. Download the Amazon Hive JDBC Driver (HiveJDBC41.jar) from the Amazon website.
2. Copy the HiveJDBC41.jar file to <compose_product_dir>\java\jdbc.
3. Restart the Qlik Compose service.
Required databases and privileges
Compose Data Lake projects require four separate databases. You can create the required
databases manually (which will also allow you to override the default storage location for the files)
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
285

6 Data Lake projects
or let Compose create them for you. If you want Compose to create the databases, you need to
grant the user defined in the Storage Zone settings, the CREATE DATABASE privilege for the
following databases:
l
Storage Zone database - The database specified in the Storage Zone settings. This
database can have any name.
l
Landing Zone database - The database specified in the Landing Zone settings. This
database can have any name.
l
Exposed views database - This database must have the same name as the Storage Zone
database and be appended with the suffix defined in the project settings’ Naming tab (_v by
default).
l
Internal views database - Both ODS Live Views and the HDS Live Views reference this
database for updates. This database must have the same name as the Storage Zone
database and be appended with the suffix defined in the project settings’ Naming tab (_v_
internal by default).
For more information about Compose views, see
Working with views (page 322)
.
Required table and view privileges
The user specified in the Storage Connection Settings must be granted the following privileges on
the required databases:
l
SELECT
l
CREATE
l
MODIFY
l
READ_METADATA
Data Lake project guidelines
The following topic provides guidelines for setting up your Hive cluster and determining the
scheduling frequency of Change Processing storage tasks.
Working with views
Compose creates the Storage Zone with both storage tables and storage views. The storage tables
are created in the database that you defined in your storage settings while two separate database
are created for the views:The exposed views database and the internal views database. The
exposed views database is the primary views database and contains all view types. The internal
views database is used to store updates to ODS Live Views and HDS Live Views. The exposed
views database and the internal views database share the same name as the Storage Zone
database, but are appended with a unique suffix (by default, _v and _v_internal respectively),
which is set in the project settings’ Naming tab. Consuming applications should be set up to read
from the exposed views database, which provide several benefits over tables including better
security (requiring read-only access only), data concurrency, and minimizing duplicate records in
projects defined with non-ACID storage.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
286

6 Data Lake projects
Optimizing your Hive cluster setup
While the convenience of having the metadata, storage system, and compute platform on a single
machine may have certain benefits (Option 1 below), it may also increase costs. Having the
metadata and the storage on separate clusters to the compute platform (Option 2 below) will allow
you to power down the compute machine when it's not in use, thereby saving costs.
Compose can work with either Option 1 or Option 2 without requiring any special configuration.
Simply specify the Hive server and database name in the storage connection settings.
Note that certain platforms such as Databricks automatically power the compute platform on and
off as needed. With these platforms, Option 2 may not offer any benefits over Option 1.
As the “Federated” architecture may be better suited to certain environments, it’s recommended to
compare the performance of both options in a test environment before deciding which one to go
with.
Determining scheduling frequency
To prevent data inconsistency issues, you should schedule the Change Processing storage task
frequency to be greater than or equal to the Partition every interval defined for the Replicate task
(in the Task Settings’ Store Changes Settings tab).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
287
6 Data Lake projects
As a general rule, the shorter the Change Processing task interval, the greater the impact on
performance and the higher the computing costs. Therefore, it is recommended to limit the
frequency of Change Processing tasks only to what is absolutely necessary.
The scheduling frequency should be determined by the rate at which data updates are required by
downstream consuming applications.
Adding data lake projects
Adding a new project is the first task you need to undertake in order to work with Qlik Compose.
There are two types of project:
l
Data Lake - for ingesting data from multiple sources and moving it to a storage system for
analytics.
l
Data Warehouse - for ingesting data from multiple sources and creating analytics-ready data
marts.
This topic guides you through the steps required to set up a Data Lake project. For instructions on
setting up a Data Warehouse project, see
Adding data warehouse projects (page 35)
.
You can set up as many projects as you need, although the ability to actually run tasks is
determined by your Compose license.
To prevent unpredictable behavior, each project must be defined with a dedicated
Storage Zone
.
To add a new Data Lake project:
1. Click the New Project toolbar button.
The New Project wizard opens.
2. In the Project Name tab, specify the following and then click Next:
l
Name: The project name.
Project names cannot contain the following characters:
/\,&#%$@=^*+"'`~?<>:;[]{} as well as all non-printable characters (below
0x20). The project name can contain a single dot, but it cannot be the first
or last character.
l
Environment Type: Optionally, change the default environment type.
l
Environment Title: Optionally, specify an environment title.
For information about the environment settings, see
Environment tab (page 294)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
288

6 Data Lake projects
The following names are reserved system names and cannot be used as project
names: >CON, PRN, AUX, CLOCK$, NUL, COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, COM5, COM6, COM7,
COM8, COM9, LPT1, LPT2, LPT3, LPT4, LPT5, LPT6, LPT7, LPT8 and >LPT9.
3. Select Data Lake as your project type.
4. Choose whether to create your Storage as an Operational Data Store (ODS)or as an
Operational and Historical Data Store (ODS + HDS). Choose Operational Data Store to
create an ODS from the source data or Operational and Historical Data Store to create an
ODS from the source data while maintaining previous versions of updated records. Once you
have made your choice, click Next.
5. In the Deployment tab, select where you want your Data Lake to be deployed. Then click
Next.
Your choice will determine which storage system options are available in the
Storage screen.
6. In the Storage tab, select a storage system. If you select File System, choose a file format.
Then click Next.
l
Renaming a column in Parquet or Avro format will cause the loss of all data
in that column.
l
Parquet and Avro formats do not allow spaces in Primary Key column
names. If your project is set up to ingest tables from Replicate, you can
define a global transformation in Replicate to remove spaces from Primary
Key column names.
7. In the Compute tab, select a compute platform and then click Finish to exit the wizard.
Before
configuring connectivity
, make sure to install the relevant driver for your
compute platform. See Prerequisites (page 284) for more information.
8. The project panels will be displayed.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
289

6 Data Lake projects
9. Add a Storage Zone (Data Lake) and at least one source database as described in
Defining a
Storage Zone (page 314)
and
Defining Landing Zones (page 323)
respectively.
10. Select the source tables as described in
Selecting source tables and managing metadata
(page 325)
.
11. Create the storage tables as described in
Creating and Managing Storage Zone Tasks (page
347)
.
Managing and monitoring projects
The table below describes the available project management options.
Project management actions are performed in the main Compose window. To switch
from a specific project to the main window, click the downward arrow to the right of the
project name and then select All Projects from the drop-down menu.
To Do this
Edit a project Any of the following:
l
Double-click the project.
l
Right-click the project and select Designer.
l
Select the project and then click the Open toolbar button.
Monitor a project Any of the following:
l
Right-click the project and select Monitor.
l
Double-click the project and select the Monitor tab on the right of
the console.
Project management procedures
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
290

6 Data Lake projects
To Do this
Create a
deployment
package
Any of the following:
l
Right-click the project and select Create Deployment Package.
l
Select the project and then select Create Deployment Package
from the Deployment toolbar menu.
See also:
Project deployment (page 44)
(Data Warehouse projects) and
Project deployment (page 297)
(Data Lake projects).
Delete a project Any of the following:
l
Right-click the project and select Delete.
l
Select the project and then click the Delete toolbar button.
View or change
user permissions
Right-click the project and select User Permissions.
Relevant for Data Warehouse projects only.
See also:
User permissions (page 384)
.
Project settings
You can modify the project settings according to your needs.
To open the project settings window
1. Open your project as described in
Managing and monitoring projects (page 290)
.
2. Click the downward arrow to the right of the project name and select Settings from the drop-
down menu.
The Settings window opens.
The project settings window is divided into the following tabs:
l
General tab (page 291)
l
Naming tab (page 293)
l
Environment tab (page 294)
General tab
In this tab, the following settings are available:
Project details
Read-only information about the project deployment type, storage type, and compute type (which
were all set in the project setup wizard).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
291

6 Data Lake projects
Miscellaneous
l
Generate DDL scripts but do not run them: By default, Compose executes the CREATE,
ADJUST and DROP statements immediately upon user request. When you select this option,
Compose will only generate the scripts but not execute them. This allows you to review and
edit the scripts before they are executed.
For example, if you want to apply custom sorting or special formatting, you will need to edit
the CREATE statement accordingly.
Note that if you select this option, you will need to copy the scripts to your Storage Zone and
run them manually. You can view, copy and download the DDL scripts as described in
Viewing and downloading DDL scripts (page 307)
.
When this option is selected, you need to do the following to see the results:
l
After running the scripts, clear the metadata cache as described in Clearing
the metadata cache (page 361).
l
When this option is selected, you need to press [F5] (i.e. refresh the page)
in order for the web console to display the updated list of tables. This can
be done either before running the scripts (recommended) or after running
the scripts. Note that until you refresh the browser, the information in the
web console will only be partially updated.
l
Ignore Mapping Data Type Validation: By default, Compose issues a validation error when a
landing table is mapped to a staging table with a different data type. You can select this
option to allow the mapping of different data types. Note that you should only select this
option if you need to map landing table data types to compatible (though not identical)
staging table data types.
l
Do not display the default workflows in the monitor: Select this option if you want to
prevent the default workflows from being executed.
Default data store type for new entities
Choose one of the following:
l
Operational Data Store - This will create an ODS from the source data.
l
Operational and Historical Data Store - This will create an ODS from the source data while
maintaining previous versions of updated records.
Deleted records in ODS (Operational Data Store) views
You can choose to exclude/include records marked as deleted from/in the ODS views.
l
Exclude the corresponding record from the ODS views - This is the default option as
records marked as deleted should not usually be included in ODS views.
l
Include the corresponding record in the ODS views - Although not common, in some
cases, you might want include records marked as deleted in the ODS views in order to
analyze the number of deleted records and investigate the reason for their deletion. Also,
regulatory compliance might require you to be able to retrieve the past record status (which
requires change history as well).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
292

6 Data Lake projects
Dates
l
Lowest Date - The value of the "From Date" column when no other value is available.
l
Highest Date - The value of the "To Date" column when no other value is available.
For a description of the "From Date" and "To Date" columns, see Naming tab below.
Naming tab
In this tab, you can change the default column, prefix, and suffix names.
If you change the prefix or suffix of existing tables (e.g. data warehouse tables), you
need to drop and create the data warehouse and data mart tables.
Name Description
Suffix for
exposed
views
database
The suffix used to identify the database used for exposed views.
Suffix for
internal
views
database
The suffix used to identify the database used for internal views.
Suffix for
Replicate
Change
Tables
The suffix used to identify Replicate Change Tables in the landing zone of the
Storage Zone.
Prefix for
storage
tables
The prefix to add to table names in the Storage Zone. Changing this after the
Storage Zone tables have already been created requires you drop and recreate
your Storage Zone tables.
Prefix for all
storage view
types
The prefix to add to view names in the Storage Zone. Changing this after the
Storage Zone tables have already been created requires you drop and recreate
your Storage Zone tables.
For more information on storage view types, see
Working with views (page 322)
.
Suffix for
ODS
standard
views
The suffix used to identify ODS standard views.
For more information on storage view types, see
Working with views (page 322)
.
Suffix for
ODS Live
Views
The suffix used to identify ODS live views.
For more information on storage view types, see
Working with views (page 322)
.
Name management options
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
293

6 Data Lake projects
Name Description
Suffix for
HDS
standard
views
The suffix used to identify HDS standard views.
For more information on storage view types, see
Working with views (page 322)
.
Suffix for
HDS Live
Views
The suffix used to identify HDS live views.
For more information on storage view types, see
Working with views (page 322)
.
"From Date"
column name
The name of the "From Date" column. This column is added to tables that contain
attributes (columns) with history. The column is used to delimit the range of
dates for a given record version.
l
This name cannot be used in other columns.
l
NULL values are not allowed in this column. If the source "From
Date" column contains NULLs, an expression should be created
to convert them to non-null values.
"To Date"
column name
The name of the "To Date" column. This column is added to tables that contain
attributes (columns) with history. The column is used to delimit the range of
dates for a given record version.
This name cannot be used in other columns.
Environment tab
In this tab, you can specify information about your environment that will be displayed as a banner at
the top of the window when you open the project.
Provide the following information and then click OK to save your settings.
l
Environment type:Select one of the following types according to your environment type:
Development, Test, Acceptance, Production, Other. This information will not be displayed
in the banner.
l
Environment title: Specify a title for your environment. The title will be displayed in the
banner at the top of the console.
l
Project title: Specify a title for your project. The project title will be shown in the console
banner. If both an Environment Title and a Project Title are defined, the project title will be
displayed to the right of the environment title.
l
The Project title option requires Compose August 2021 Patch Release 12 or
later.
l
When a project is deployed to a new environment, the environment title and
environment type in the new environment will not be overridden.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
294

6 Data Lake projects
The following image shows the banner with both an Environment title and a Project title:
The banner text is shown without the Environment title and Project title labels.
This provides greater flexibility as it allows you add any banner text you like,
regardless of the actual label name. For example, specifying
Project
owner: Mike Smith
in the Project title field, will display that text in the banner.
Creating or Dropping Storage Tables
Limit the number of database connections to: The higher the number of database connections,
the more storage tables Compose will be able to create or drop in parallel. While increasing the
default should improve performance, it may also impact other database applications. It is therefore
not recommended to increase the default unless you encounter performance issues.
As environments are project-specific, the environment information can be
imported
to a
new project, but cannot be imported to an existing project.
Task recovery
You can set SQL state classes and error codes, on the occurrence of which, a task will be retried.
You can set the following parameters:
l
Maximum retry count: The number of times to retry a task before exiting with failure.
Increasing the number of retries will impact system resources. Therefore, only increase the
default value if you expect tasks to recover after the default number of retries.
l
Interval between retry attempts (sec): The time to wait between retry attempts. Increasing
the interval will consume more system resources. Therefore, only increase the default value
if it is critical that the task recover as soon as possible.
l
Retry on these SQL state classes: The default is 08 (connection exceptions). You can add
additional classes as desired. Classes should be separated with a comma.
Example: 08,22,2F
l
Retry also on these error codes: The default is 1205 (which occurs when a table is locked
by another process). You can add additional error codes as desired. Error codes should be
separated with a comma.
Example: 1205,2020,233
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
295

6 Data Lake projects
Limitations and considerations:
l
Schema evolution retries are not supported.
l
ODBC statements comprise a small part of the task execution sequence. However, as the
task retry mechanism is JDBC-based, ODBC statements will not be retried even if the
specified SQL state/error code is encountered.
Task and Workflow Information Retention
You can set the maximum number of runs to keep task and workflow logs and messages. The
default is 100. Task information includes logs, the number of inserted/updated rows per table,
errors, and various other runtime messages. If you find that the number of accumulated logs and
messages is degrading performance, reducing this value might help.
Resetting projects
You can reset projects as required. This can be useful during the project development stage as it
allows you to easily delete unwanted project elements.
Be careful not to reset a project and delete data in a production environment.
To reset a project:
1. Open your project as described in
Managing and monitoring projects (page 290)
.
2. Click the downward arrow to the right of the project name and select Reset Project from the
drop-down menu.
The Reset Project window opens.
3. Select which elements to reset according to your project type.
l
Metadata and mapping definitions
For information on mappings, data storage tasks and metadata, see
Selecting source
tables and managing metadata (page 325)
.
l
Reusable transformations
For information on the reusable transformations, see
Reusable transformations (page
345)
.
l
Storage tables and files
For information on the Storage Zone, see
Creating and Managing Storage Zone Tasks
(page 347)
.
l
Command tasks
For more information, see
Creating and managing command tasks (page 363)
.
l
DDL scripts
For more information on DDL scripts, see
Project settings (page 291)
and
Viewing and
downloading DDL scripts (page 307)
.
4. Click Reset Project and then click Yes when prompted to confirm your request.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
296

6 Data Lake projects
Project deployment
Project deployment packages can be used to back up projects or migrate projects between
different environments (e.g. testing to production). As a deployment package is intended to be
deployed in a new environment, it contains the Storage Zone and data source definitions, but
without any passwords. The deployment package also does not contain any data from the Storage
Zone, only the metadata. The deployment package also contains the project metadata and mapping
information, which should be consistent with the Landing Zone tables in the new environment.
For a complete list of objects contained in the deployment package, see
Exporting a project (page
299)
.
Project deployment should always be unidirectional (for example, from test to
production), and not the other way around.
Creating deployment packages
This section explains how to create a project deployment package.
To create a deployment package:
1. Choose one of the following methods:
l
In the main Compose window, right-click the desired project and select Create
Deployment Package from the context menu.
l
In the main Compose window, select the desired project. Then, click the Deployment
toolbar button and select Create Deployment Package from the drop-down menu.
l
In the project window, select Deployment > Create Deployment Package from the
project drop-down menu.
The Create Deployment Package - <Project_Name> window opens.
2. Provide a Version number and a Description in the designated fields and then click OK.
A ZIP file containing a JSON file (i.e. the project settings) and a readme.txt file will be saved
to your browser's default download location.
The ZIP file name is in the following format:
<Project_Name>_deployment_<Date>__<Time>.zip
The readme.txt file contains the following information about the deployment package:
project name, export date, exporter user name, deployment version, and description.
Deploying packages
This section explains how to deploy a project deployment package. You can only deploy packages
to an existing project. Therefore, before deploying a project, create a new project with the user
name and password required for connecting to the Storage Zone database and the Landing Zone
database (if defined) in the new environment. In addition, the Landing Zone databases in the target
project must have the same display name (defined in the Compose console) as the corresponding
databases in the source project. Note that as database settings are usually environment specific,
the database settings in the target project will not be overwritten by those of the source project.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
297

6 Data Lake projects
When deploying, Compose does not override existing connection parameters, assuming they are
environment-local. This enables you to easily migrate projects from test to production, for example,
without the need to change user names, passwords or IP addresses.
If preferred, you can create an empty project and provide the required credentials after
the deployment completes. In this case, an error message prompting you for the missing
credentials will be displayed after the deployment completes.
To deploy a project:
1. Copy the ZIP file created when you created your deployment package to a location that is
accessible from the Compose machine.
2. Open Compose and choose one of the following methods:
l
In the main Compose window, select the desired project. Then, click the Deployment
toolbar button and select Deploy from the drop-down menu.
l
In the project window, select Deployment > Deploy from the project drop-down
menu.
The Deploy window opens.
3. Either drag and drop the file on the window.
-OR-
Click Select and browse to the location of the deployment package. In the Open window,
either double-click the deployment package ZIP file or select the file and click OK.
The package details will be displayed.
4. Click Deploy to deploy the package. When prompted to replace the existing project, confirm
the operation.
The project will be deployed.
When deploying a project defined with multiple Replicate Servers to any of the following:
l
A project without any Landing Zone databases
l
A project which is missing one or more Landing Zone databases defined in the
source project
Then the Landing Zone settings from the source project will be used, but the missing
databases will be created without a password and Replicate Server. These will need to
be configured manually.
Exporting and importing projects using the CLI
Compose CLI requires Administrator permission. To grant Administrator permission,
select "Run as administrator" when opening the command prompt.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
298

6 Data Lake projects
Under normal circumstances, use the deployment options described in
Project deployment (page
297)
to export and import projects. For deployment automation or control by another tool, you can
use the command line interface (CLI) to perform the following tasks:
l
Exporting a project (page 299)
l
Importing a project (page 301)
l
Exporting the project configuration (page 302)
l
Importing the Project Configuration (page 304)
To export or import a project or project configuration including passwords, you first need
to change the default Master User Password.
For more information on changing the master user password, see Changing the master
user password (page 29).
See also: Migrating projects from the test environment to the production environment
(page 305) and Import/Export scenarios: When is a password required? (page 305)
Before running any command, you must run the
Connecting to Qlik Compose server (page 77)
command.
To get help when using the command line, you can run the Help command. For example, for help
about exporting a project, issue the following command:
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository --help
This brings up a list of help parameters.
Exporting a project
You can use the export_project_repository CLI to export a project.
Exported projects include the following:
l
Data zone connections
l
Metadata definitions (entities and attributes)
l
Mappings between Landing Zone and Storage Zone table columns.
l
Storage Zone ETL tasks
l
Project settings
Existing Storage Zone tables and generated task statements are not exported.
Notifications and schedules are also not exported as they are considered to be
environment-specific.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository --project
project_name
--outfile
output_file
[--is_
without_credentials] [--password
password
] [--master_user_password
master_user_password
]
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
299

6 Data Lake projects
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--outfile The path to and name of the output file. This file is in JSON format
(e.g.
C:\file.json
).
--is_without_credentials Use this parameter to specify that you want to export the project
settings without the encrypted fields. When importing to a new
project, you will need to manually enter the project passwords (in
the Compose database connection settings) after the import
completes. In addition to eliminating the need to specify a
password when exporting or importing the project, the is_without_
credentials parameter also allows the project to be used in every
Compose installation, regardless of its master user password. It is
also useful in the event that you would like to keep the existing
passwords in the target environment (e.g. when exporting from a
testing environment to an existing project in the production
environment).
--password The password for encrypting the credentials in the exported
project. When used, this parameter must be used together with the
master_user_password parameter described below. Use the password
> parameter if you want to encrypt the credentials in the exported
project, but do not want the source master password to be used in
a different environment. The specified password must be at least
32 characters in length and can either be user-devised or
generated using the genpassword utility described in
Changing the
master user password (page 29)
.
--master_user_password The master user password defined for the source machine. When
used, this parameter must be used together with the password
parameter. Use the master_user_password > parameter if you want
to encrypt the credentials in the exported project, but do not want
the source master password to be used in a different environment.
In such a case, when you import the project to an environment that
has a different master password, you will only need to specify the
password qualifier.
For instructions on changing the master user password, see
Changing the master user password (page 29)
.
See also:
Moving projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 85)
and
Import/export scenarios -
When is a password required? (page 86)
Example
Export project without a password
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
300

6 Data Lake projects
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository --project MyProject --outfile file.json --is_without_
credentials
Export project with a password
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository --project MyProject --outfile file.json --password
MyPassword --master_user_password MyMasterUserPassword
Importing a project
You can use the import_project_repository CLI to import a project. If you import to an existing
project, all of the project settings, except the project configuration items will be overridden. For
information on the project configuration items, see
Exporting the project configuration (page 302)
.
Imported projects include the following:
l
Data zone connections
l
Model definitions (entities and attributes)
l
Mappings between Landing Zone and Storage Zone table columns.
l
Storage Zone ETL tasks
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe import_project_repository --project
project_name
--infile
input_file
[--
password
password
] [--is_without_credentials] [--override_configuration] [--dont_backup_
existing_project]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--infile The full path to the input file, including the file name. This
file is in JSON format (e.g.
C:\file.json
).
--password The password specified with the password parameter
during export.
For instructions on changing the master user password,
see
Changing the master user password (page 29)
.
See also:
Moving projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 85)
and
Import/export
scenarios - When is a password required? (page 86)
--is_without_credentials Use this parameter to specify to import the project settings
without the encrypted fields. In this case, you will need to
manually enter the project passwords in the Compose
database connection settings.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
301

6 Data Lake projects
Parameter Description
--override_configuration Use this parameter to override the existing project
configuration. When importing a project, the default setting
is not to override the existing project configuration.
--dont_backup_existing_project Use this parameter to specify not to back up the existing
project. By default, existing projects are backed up to the
following location (and automatically restored if the import
fails):
<product_dir>\data\projects\<project_name>_backup_
<timestamp>
Example
ComposeCli.exe import_project_repository --project MyProject --infile file.json --password
MyPassword --override_configuration --autogen
Existing Storage Zone tables and generated task statements are not imported. After the
import completes, you must perform step 3 below. You may also need to perform step 1
or 2, depending on whether you changed the Storage Zone connection settings (step 1)
or kept the existing connection settings (step 2).
1. If you changed the Storage Zone connection settings after importing the project,
then you need to create the tables in the new Storage Zone.
2. If you edited the Metadata in a testing environment and then imported the project
into a production environment, you need to validate and adjust the Storage Zone.
3. Generate the Data Storage task statements.
For information on validating the Storage Zone and generating the task statements, see
Creating
and Managing Storage Zone Tasks (page 347)
.
Exporting the project configuration
You can use the Compose CLI to export the configuration settings of an existing project. This
includes Landing and Storage Connections, scheduling jobs, and notifications. This is helpful, for
example, when you need to migrate configuration settings from a test environment to the
production environment.
For information about migrating projects, see
Migrating projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 305)
.
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository_config --project
project_name
--outfile
output_file
[-
-is_without_credentials] [--password
password
] [--master_user_password
master_user_password
]
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
302

6 Data Lake projects
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--outfile The path to and name of the output file. This file is in JSON format
(e.g.
C:\file.json
).
--is_without_credentials Use this parameter to specify that you want to export the project
settings without the encrypted fields. When importing to a new
project, you will need to manually enter the Landing Zone(s) and
Storage Zone passwords (in the Connections panel) after the
import completes. In addition to eliminating the need to specify a
password when exporting or importing the project, the is_without_
credentials parameter also allows the project to be used in every
Compose installation, regardless of its master user password. It is
also useful in the event that you would like to keep the existing
passwords in the target environment (e.g. when exporting from a
testing environment to an existing project in the production
environment).
--password The password for encrypting the credentials in the exported
project. When used, this parameter must be used together with the
master_user_password parameter described below. Use the password
> parameter if you want to encrypt the credentials in the exported
project, but do not want the source master password to be used in
a different environment. The specified password must be at least
32 characters in length and can either be user-devised or
generated using the genpassword utility described in
Changing the
master user password (page 29)
.
--master_user_password The master user password defined for the source machine. When
used, this parameter must be used together with the password
parameter. Use the master_user_password > parameter if you want
to encrypt the credentials in the exported project, but do not want
the source master password to be used in a different environment.
In such a case, when you import the project to an environment that
has a different master password, you will only need to specify the
password qualifier.
For instructions on changing the master user password, see
Changing the master user password (page 29)
.
See also:
Moving projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 85)
and
Import/export scenarios -
When is a password required? (page 86)
Example
Export project configuration without a password
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
303

6 Data Lake projects
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository_config --project MyProject --outfile file.json --is_
without_credentials
Export project configuration with a password
ComposeCli.exe export_project_repository_config --project MyProject --outfile file.json --
password MyPassword --master_user_password MyMasterUserPassword
Importing the Project Configuration
You can use the Compose CLI to import the configuration settings of an existing project. This
includes Data Zone definitions, scheduling jobs, and notifications. This is helpful, for example, when
you need to migrate configuration settings from a test environment to the production environment.
For information about migrating projects, see
Migrating projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 305)
.
Before you can import the project configuration, you must first run the
import_
project_repository
command described in Importing a project (page 301).
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe import_project_repository_config --project
project_name
--infile
input_file
[--
password
password
] [--is_without_credentials]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--infile The full path to the input file, including the file name. This file is in
JSON format (e.g.
C:\file.json
).
--password The password specified with the password parameter during
export.
For instructions on changing the master user password, see
Changing the master user password (page 29)
.
See also:
Moving projects from the test environment to the
production environment (page 85)
and
Import/export scenarios -
When is a password required? (page 86)
--is_without_credentials Use this parameter to specify to import the project settings without
the encrypted fields. In this case, you will need to manually enter
the project's Landing Zone and Storage Zone passwords in the
Data Zone Connection settings.
Example
ComposeCli.exe import_project_repository_config --project MyProject --infile file.json --
password MyPassword
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
304

6 Data Lake projects
Migrating projects from the test environment to the production environment
After successfully creating and testing projects in the test environment, you now want to move
those projects to the production environment. You also need to propagate updates from the testing
environment to the production environment as necessary. Although it sounds complicated, moving
new and updated projects from the test environment to the production environment is actually
quite straightforward, as explained below.
See also
Import/Export scenarios: When is a password required? (page 305)
.
Landing and Storage Connections (landing, storage and provisioning) will not be
overridden when moving to a production environment. This also includes the file format
set in the provisioning task.
The Landing Zone and Storage Zone display names must be identical in both the testing
and the production environments.
To perform the initial migration from the testing environment to the production environment:
1. Export the project from the test environment as described in
Exporting a project (page 299)
.
2. Import the test project to the production environment as described in
Importing a project
(page 301)
.
3. Edit the connection settings to point to the production Landing Zone and Storage Zone.
For more information, see
Defining Landing Zones (page 323)
and
Defining a connection to
the Storage Zone (page 314)
respectively.
4. Configure notifications and scheduling as needed.
For more information, see
Scheduling tasks (page 368)
and
Notifications (page 370)
respectively.
To propagate updates from the testing environment to the production environment:
1. Export the project from the test environment as described in
Exporting a project (page 299)
.
2. Import the test project to the production environment as described in
Importing a project
(page 301)
.
Import/Export scenarios: When is a password required?
The following section describes which of the various export/import scenarios require a password to
be specified.
In all scenarios, if you import a project to an existing project, the credentials of the
existing projects are preserved (as they are part of the project configuration).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
305

6 Data Lake projects
Scenario 1: Moving a project or project configuration between two Compose machines without
retaining the project credentials. This is useful when importing to a new project that will have
different project credentials.
In such a scenario, simply add the is_without_credentials parameter to either the export or the
import command.
Scenario 2: Moving a project or project configuration between two Compose machines that
have the same Master User Password.
In such a scenario, neither the export command nor the import command need to include a
password. If you do not want the source and target projects to have the same credentials (for Data
Zone connectivity, etc.), then you also need to specify the is_without_credentials parameter
in either the export or the import command.
Scenario 3: Moving a project or project configuration between two Compose machines that
have a different Master User Password, but without revealing the Master User Password of
the source machine.
In such a scenario, the export command must include the password and master_user_password
parameters while the import command must include the password parameter. The same password
(specified with the password parameter) must be used for both export and import.
Scenario 4: Moving a project or project configuration between two Compose machines that
have a different Master User Password.
In such a scenario, the export command does not need to include a password, but the import
command should specify the Master User Password of the source machine (using the password
parameter).
Generating projects using the CLI
The instruction below explain how to automatically generate projects using the CLI. This can be
especially useful when deploying projects between different environments.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe generate_project --project
project_name
[--database_already_adjusted]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--database_already_adjusted An optional parameter that should only be included if
the data warehouse and data marts were adjusted
outside of Compose.
Example
ComposeCli.exe generate_project --project MyProject --database_already_adjusted
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
306

6 Data Lake projects
When the command is run, Compose will:
l
Validate the metadata.
l
Create any storage tables that do not exist.
l
Validate the storage.
l
Adjust the storage if needed.
l
If an Adjust script is needed and --database_already_adjusted is included in
the command, the script (DDL) will not be run as it is assumed that the user
ran it manually.
l
If the "Adjust" cannot be performed automatically, the process will be
stopped.
l
Generate all storage tasks.
If Compose encounters an error while generating a storage task, it will skip the
problematic task and continue with the remaining tasks.
Viewing and downloading DDL scripts
In the DDL Script Files window, you can view and download the Storage Zone DDL script files. By
default, Compose executes the Create, Adjust and Drop statements immediately upon user
request. However, when the Generate DDL scripts but do not run them option is enabled,
Compose will only generate the scripts but not execute them.
For more information on the Create DDL scripts only option, see
Project settings (page 291)
.
To open the DDL Script Files window:
1. Open your project as described in
Managing and monitoring projects (page 290)
.
2. Click the downward arrow to the right of the project name and select Show DDL Scripts
from the drop-down menu.
The DDL Script Files window opens.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
307

6 Data Lake projects
3. To view a script, select the desired script in the Script Files pane on the left. The script will
be displayed on the right.
4. To download a script, select the desired script in the Script Files pane on the left. Then click
the download button in the top right of the window.
5. To search for an element in the script, start to type in the search box. All strings that match
the search query will be highlighted blue.
You can navigate between search query matches using the arrows to the right of the search
box. Use the right and left single arrows to navigate matches sequentially. Use the right and
left double arrows to jump to the last and first match respectively.
6. To reset the search, either delete the search query or click the "x" in the right of the search
box.
Project versioning
Compose provides built-in project version control using the Git engine. Version control enables
Compose developers to commit project revisions to both a local and a remote Git repository. If a
mistake is made, Compose developers can easily roll back to earlier versions of the project while
minimizing disruption to all team members.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
308

6 Data Lake projects
Revisions only store metadata and mapping information. After you revert to a saved
revision, you will need to recreate the data warehouse and data mart tables.
Configuring version control settings
To define Version Control Settings:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Version Control > Settings.
The Version Control Settings - Git window opens.
The Local Commits area shows the local root folder where project revisions are committed.
The first time a project revision is committed, Compose creates a JSON file with the current
project settings. The <project_name>.json file is archived to a ZIP file (<project_name>_
deployment.zip), which is located in a project-specific folder under the source-control folder.
2. To enable commits to a remote Git database, select Enable remote commits and then
provide the following information:
l
URL - The address of the remote Git database.
l
User name - Your user name for accessing the remote Git database.
l
Password - Your password for accessing the remote Git database.
Committing projects
You can commit a project using the console or using the CLI:
To commit a project to Version Control using the web console:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Version Control > Commit.
The Commit - <Project_Name> window opens.
2. Enter a message in the Message box and optionally select the Remote push check box.
Note that the Remote push check box will be disabled if the Enable remote commits option
described above is not selected.
To commit a project to Version Control using the CLI:
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe commit --project
project_name
[--message
message
] [--remote]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--message An optional message to accompany the commit.
--remote This parameter is required if you want to commit the project to a
remote Git repository (see above). By default, the project will be
committed locally to
<product_dir>\data\source-control
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
309

6 Data Lake projects
Example
ComposeCli.exe commit --project MyProject --remote
To revert to a saved revision:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Version Control > Revisions history.
The Revision History - <Project_Name> window opens.
By default, the last 10 revisions are shown. You can change this number by selecting one of
the available options from the Show drop-down list.
2. Optionally, use the Search box to find a specific revision.
3. Select the desired revision and then click the Deploy to Revision toolbar button.
4. When prompted to confirm the operation, click Yes.
The existing project will be replaced.
5. Click Close to close the Revision History - <Project_Name> window.
To download a saved revision:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Version Control > Revisions history.
The Revision History - <Project_Name> window opens.
By default, the last 10 revisions are shown. You can change this number by selecting one of
the available options from the Show drop-down list.
2. Optionally, use the Search box to find a specific revision.
3. Select the desired revision and then click the Download Revision as Package toolbar
button.
The package will be saved as a ZIP file in your browser's default download location.
Creating a diagnostics package
To assist in troubleshooting esoteric issues, a Qlik Support Engineer may ask you for a diagnostics
package. The diagnostics package contains the following information:
l
The project "data" directory
l
Java logs and workflow logs
l
.NET logs
l
Deployment package file
As a prerequisite to creating a diagnostics package, the project must have at least one
database connection configured.
To create a diagnostics package:
1. From the Project menu, select Create Diagnostics Package.
2. A zip file in the following format will either be downloaded to your computer or you will be
prompted to download it (according to your browser settings):
Compose_Diagnostics_<project_name>_<timestamp>.zip
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
310

6 Data Lake projects
6.3 Getting started with Data Lake projects
This section provides an overview of the Data Lake project workflow, familiarizes you with the
console elements and explains how to set up a task in Qlik Replicate.
In this section:
l
High-level flow (page 311)
l
Console elements (page 311)
High-level flow
A Qlik Compose workflow is typically set up as follows (simplified):
1. In Replicate, define a task that replicates the source tables to a specific target. The target
should be defined as the Landing Zone in your Qlik Compose project.
2. In Compose:
a. Configure access to your Storage Zone and your Landing Zone(s).
b. Use the "Discover" option to auto-generate the metadata from the source tables
located in the Landing Zone(s). You can even create the Metadata manually if you
prefer.
c. Optionally, create the Storage Zone tables and then generate the ETL statements that
will be executed when the task runs.
d. Run the separate Full Load and CDC tasks (in that order) that were automatically
created when the source tables were discovered.
See also
Introduction (page 13)
.
Console elements
This section will familiarize you with the elements that comprise the Qlik Compose UI.
To open Qlik Compose:
From the Windows Start menu, select All Programs > Qlik Compose > Qlik Compose Console.
The Qlik Compose Console opens in Management view.
Qlik Compose Console - Management View
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
311

6 Data Lake projects
Management View
In Management view, you can manage the following:
l
Qlik Compose projects
For more information, see
Adding and managing data warehouse projects (page 35)
.
l
The product license
l
Replicate Server connections
l
Compose Agent connection
l
Log levels and cleanup options
l
Email settings
l
User permissions
For more information, see
Managing Compose (page 378)
.
Designer View
When you add a new project or open an existing project, the console switches to Designer view.
You can switch back and forth between Designer view and Monitor view by clicking the Designer
and Monitor tabs in the top right of the console.
Designer view comprises the following panels:
l
Landing and Storage Connections - Configure access to your Landing Zone(s) and Storage
Zone.
For more information, see
Defining Landing Zones (page 323)
and
Defining a connection to
the Storage Zone (page 314)
respectively.
l
Storage Zone - In the Storage Zone, you can:
l
Discover and manage the source table metadata.
l
Define data storage tasks that move the data from the Landing Zone(s) to the Storage
Zone.
For more information, see
Selecting source tables and managing metadata (page 325)
and
Creating and Managing Storage Zone Tasks (page 347)
.
In Designer view, each of the panels has a bar below the panel name. The bar can be empty, half-
filled or completely filled, according to the current configuration status of the panel properties, as
follows:
No fill (gray) - Not configured
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
312

6 Data Lake projects
Partially filled - Configuration is not complete
Completely filled - Fully configured
Monitor View
To switch to Monitor view, click the Monitor tab in the top right of the console.
Monitor View
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
313
6 Data Lake projects
In Monitor view, you can view the status of Qlik Compose tasks, schedule their execution (either
individually or as a workflow), view logs, and create notifications.
For more information, see
Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows (page 365)
.
6.4 Setting up landing and storage connections
This topic explains how to configure connectivity to your Storage Zone and Landing Zone(s).
In this section:
l
Defining a Storage Zone (page 314)
l
Defining Landing Zones (page 323)
l
Managing Landing and Storage connections (page 325)
Defining a Storage Zone
This section explains how to set up Storage Zone connectivity in a Qlik Compose project.
In this section:
l
Defining a connection to the Storage Zone (page 314)
l
Supported data types (page 322)
l
Required permissions (page 314)
Required permissions
The following permissions are required:
l
Metadata: Read and Write
l
Tables: Insert and Update, and Delete.
Defining a connection to the Storage Zone
As the server connection settings for the Landing Zone are derived from the Storage
Zone settings, you must define a Storage Zone before defining a Landing Zone.
For more information on adding data sources, see
Defining Landing Zones (page 323)
.
To define the Storage Zone connection:
1. Open your project and click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Either, click the Add New Database link in the middle of the window.
-OR-
Click the New toolbar button.
The New Storage window opens. The settings will be relevant for the compute platform you
selected when you set up your project. The sections below detail the settings according to
each of the available compute platforms.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
314

6 Data Lake projects
To use AVRO file format with Hive 3.x, you must set the following parameter:
metastore.storage.schema.reader.impl=org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.SerDeStorageSc
hemaReader
Cloudera Compute Platform
Security
Use SSL - Select to connect using SSL.
l
Use self-signed certificate - Select to connect using a self-signed certificate.
l
Trusted store full path - Enter the full path to the store containing your trusted certificates.
l
Trusted store password - Enter the password for your trusted certificate store.
Authentication Type:
l
User name - Select to connect to the Hadoop cluster with only a user name. Then, in the
User name field, specify the name of a user authorized to access the Hadoop cluster.
l
User name and password - Select to connect to the Hadoop cluster with a user name and
password. Then, in the User name and Password fields, specify the name and password of a
user authorized to access the Hadoop cluster.
l
Knox - Select this option if you need to access the Hortonworks Hadoop distribution through
a Knox Gateway. Then, provide the following information:
l
Host - The FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) of the Knox Gateway host.
l
Knox port - The port number to use to access the host. The default is "8443".
l
Knox Gateway path - The context path for the gateway. The default is "gateway".
The port and path values are set in the gateway-site.xml file. If you are
unsure whether the default values have been changed, contact your IT
department.
l
Cluster name - The cluster name as configured in Knox. The default is "Default".
l
User name - Enter your user name for accessing the Knox gateway.
l
Password - Enter your password for accessing the Knox gateway.
l
Kerberos - Select to authenticate against the Hadoop cluster using Kerberos. Then, provide
the following information:
l
Realm: The name of the realm in which your Hadoop cluster resides.
For example, if the full principal name is [email protected], then EXAMPLE.COM
is the realm.
l
Principal: The user name to use for authentication. The principal must be a member of
the realm entered above. For example, if the full principal name is
[email protected], then john.doe is the principal.
l
Keytab file: The full path of the Keytab file. The Keytab file should contain the key of
the Principal specified above.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
315

6 Data Lake projects
The krb5.ini file should be located in C:\Windows (according to the Java
default). However, if Replicate is installed on the same machine as
Compose, the file might be in C:\Program Files\MIT\Kerberos. In such a
case, simply copy the file to C:\Windows.
l
Host: The FQDN that will be used to locate the correct Principal in Kerberos. This is
only required if the IP address of the Hive machine is not known to Kerberos.
l
Service name: The default is "hive". You should only change this if you are sure that
the service name is different.
In case of an issue with the Kerberos authentication, do the following:
1. Test the connection to the Hive machine with Kerberos.
2. Check the Kerberos configuration on HDFS.
If you are unsure about any of the above, consult your IT administrator.
Hive Access
l
Use ZooKeeper - Select if your Hive machines are managed by Apache ZooKeeper.
l
ZooKeeper hosts - The machines that make up the ZooKeeper ensemble (cluster). These
should be specified in the following format:
host1:port1,host2:port2,host3:port3
l
ZooKeeper namespace - The namespace on ZooKeeper under which the HiveServer2
znodes are located.
l
Host - If you are not using ZooKeeper, specify the IP address of the Hive machine. This
should be the same as the host name or IP address specified in the Cloudera Data Platform
Private Cloud or Hortonworks Data Platform target endpoint settings in the Replicate task.
l
Port - If you are not using ZooKeeper, optionally change the default port.
l
Database name - Specify the name of the Hive target database. This must be different from
the database specified in the Landing Zone settings.
If the database does not exist Compose will try and create it. This requires the
Compose user to be granted the necessary permission to create the database.
l
JDBC parameters - Additional parameters to add to the default Simba JDBC connection
string. These should be key values separated by a semi-colon.
Example:
KEY=VALUE;KEY1=VALUE1
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
316

6 Data Lake projects
l
You can set Hive parameters in the JDBC parameters. For example:
l
mapred.job.queue.name=<queuename>
l
hive.execution.engine=<enginename>
l
To distinguish Compose Hive sessions from other Hive Sessions, if Tez is
being used, you can define a JDBC parameter to change the query
description, as follows:
hive.query.name=my_description
Amazon EMR Compute Platform
Security
l
Use SSL - Select to connect using SSL.
Authentication type:
l
User name - Select to connect to the Hadoop cluster with only a user name. Then, in the
User name field, specify the name of a user authorized to access the Hadoop cluster.
l
User name and password - Select to connect to the Hadoop cluster with a user name and
password. Then, in the User name and Password fields, specify the name and password of a
user authorized to access the Hadoop cluster.
If you are unsure about any of the above, consult your IT administrator.
Hive Access
l
Host - Specify the IP address of the Hive machine. This should be the same as the host name
or IP address specified in the Amazon EMR target endpoint settings in the Replicate task.
l
Port - Optionally change the default port.
l
Database name - Specify the name of the Hive target database. This must be different from
the database specified in the Landing Zone settings.
If the database does not exist Compose will try and create it. This requires the
Compose user to be granted the necessary permission to create the database.
l
JDBC parameters - Additional parameters to add to the default Simba JDBC connection
string. These should be key values separated by a semi-colon.
Example:
KEY=VALUE;KEY1=VALUE1
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
317

6 Data Lake projects
l
You can set Hive parameters in the JDBC parameters. For example:
l
mapred.job.queue.name=<queuename>
l
hive.execution.engine=<enginename>
l
To distinguish Compose Hive sessions from other Hive Sessions, if Tez is
being used, you can define a JDBC parameter to change the query
description, as follows:
hive.query.name=my_description
l
Hive metadata storage type - Select one of the following storage mediums for your Hive
metadata:
l
Hive Metastore - This is the default metadata storage type.
l
AWSGlue Data Catalog - You can choose to store Hive metadata using the AWSGlue
Data Catalog. AWS Glue allows you to store and share metadata in the AWS Cloud in
the same way as in a Hive metastore.
When using AWSGlue Data Catalog for metadata storage, Compose
control tables will be created with the data type STRING instead of
VARCHAR (LENGTH).
Databricks Compute Platform
If you use Replicate November 2022 to land data in Databricks, only the Databricks
(Cloud Storage) target endpoint can be used. If you are using an earlier supported
version of Replicate, you can continue using the existing Databricks target endpoints.
Security
All connections to Databricks use SSL.
l
Authentication type - "Databricks Delta". This cannot be changed.
l
User name - The default user name is "token", which requires you to specify your personal
access token in the Password field. Although it's strongly recommended to use a token, you
can also access your Databricks account using a standard user name and password.
l
Password - If you are using a personal access token, this will be the token value. Otherwise,
specify the password for accessing your Databricks account.
l
HTTP Path - The HTTP path to your Databricks compute resources.
Example:
sql/protocolv1/o/8388045294310983/0123-xxxxxx-xxxxxxx
If you are unsure about any of the above, consult your IT administrator.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
318

6 Data Lake projects
Hive Access
l
Host - Specify the IP address of the Hive machine. This should be the same as the host name
or IP address specified in the Databricks target endpoint settings in the Replicate task.
l
Port - Optionally change the default port.
l
Catalog - If you want the storage tables to be created in Unity Catalog, specify the catalog
name.
If the Replicate task is Full Load and Store Changes, the storage catalog name can
be whatever you choose. However, both the catalog name defined in the
Replicate Databricks (Cloud Storage) target endpoint and the catalog name
defined in the landing settings must be hive_metastore.
l
Database name - Select the Hive target database. This must be different from the database
specified in the Landing Zone settings. If you specified a catalog (above), only databases in
the catalog will be available for selection.
l
If the database does not exist Compose will try and create it. This requires
the Compose user to be granted the necessary permission to create the
database.
l
To prevent table name conflicts when using Databricks, the Landing Zone
and Storage Zone databases should be different.
l
JDBC parameters - Additional parameters to add to the default Simba JDBC connection
string.
The following parameters are set by default and should not be changed:
l
UseNativeQuery=1
This is required for reading Compose tables or views in landing or storage on
Databricks, from outside of Compose. It is related to the way that the logical partitions
are created in the Replicate Change tables (as Databricks does not support partitions).
l
spark.sql.crossJoin.enabled=true
This parameter controls Spark SQL’s behavior when encountering queries that could
potentially result in a Cartesian product (cross join).
Additional parameters should be added as key value pairs separated by a semi-colon.
Example:
KEY=VALUE;KEY1=VALUE1
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
319

6 Data Lake projects
l
You can set Hive parameters in the JDBC parameters. For example:
l
mapred.job.queue.name=<queuename>
l
hive.execution.engine=<enginename>
l
To distinguish Compose Hive sessions from other Hive Sessions, if Tez is
being used, you can define a JDBC parameter to change the query
description, as follows:
hive.query.name=my_description
HDInsight Compute Platform
Security
All connections to HDInsight use SSL.
l
User name - Specify the name of a user authorized to access the Hadoop cluster.
l
Password - Specify the password of the user specified in the User name field.
Hive Access
l
Host - Specify the IP address of the Hive machine. This should be the same as the host name
or IP address specified in the Microsoft Azure HDInsight target endpoint settings in the
Replicate task.
l
Port - Optionally change the default port.
l
Database name - Specify the name of the Hive target database. This must be different from
the database specified in the Landing Zone settings.
If the database does not exist Compose will try and create it. This requires the
Compose user to be granted the necessary permission to create the database.
l
JDBC parameters - Additional parameters to add to the default Simba JDBC connection
string. These should be key values separated by a semi-colon.
Example:
KEY=VALUE;KEY1=VALUE1
l
You can set Hive parameters in the JDBC parameters. For example:
l
mapred.job.queue.name=<queuename>
l
hive.execution.engine=<enginename>
l
To distinguish Compose Hive sessions from other Hive Sessions, if Tez is
being used, you can define a JDBC parameter to change the query
description, as follows:
hive.query.name=my_description
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
320

6 Data Lake projects
Dataproc Compute Platform
Security
l
Use SSL - Select to connect using SSL.
Authentication type:
l
User name - Select to connect to the Hadoop cluster with only a user name. Then, in the
User name field, specify the name of a user authorized to access the Hadoop cluster.
l
User name and password - Select to connect to the Hadoop cluster with a user name and
password. Then, in the User name and Password fields, specify the name and password of a
user authorized to access the Hadoop cluster.
If you are unsure about any of the above, consult your IT administrator.
Hive Access
l
Host - Specify the IP address of the Hive machine. This should be the same as the host name
or IP address specified in the Google Dataproc target endpoint settings in the Replicate task.
l
Port - Optionally change the default port.
l
Database name - Specify the name of the Hive target database. This must be different from
the database specified in the Landing Zone settings.
If the database does not exist Compose will try and create it. This requires the
Compose user to be granted the necessary permission to create the database.
l
JDBC parameters - Additional parameters to add to the default Simba JDBC connection
string. These should be key values separated by a semi-colon.
Example:
KEY=VALUE;KEY1=VALUE1
l
You can set Hive parameters in the JDBC parameters. For example:
l
mapred.job.queue.name=<queuename>
l
hive.execution.engine=<enginename>
l
To distinguish Compose Hive sessions from other Hive Sessions, if Tez is
being used, you can define a JDBC parameter to change the query
description, as follows:
hive.query.name=my_description
After defining your Storage Zone connection parameters:
1. Click Test Connection to verify that Compose is able to establish a connection with the
specified database.
2. Click OK to save your settings. The database is added to the list on the left side of the
Manage Databases window.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
321

6 Data Lake projects
Supported data types
The following table shows the default mapping from Compose data types to Apache Hive and
Databricks data types.
Compose Data Types Hive Data Types Databricks Data Types
INTEGER INT INT
DATETIME TIMESTAMP TIMESTAMP
TIME TIMESTAMP TIMESTAMP
DATE DATE DATE
BIGINT REAL BIGINT
BYTE ARRAY STRING STRING
DECIMAL DECIMAL (P,S) DECIMAL (P,S)
GUID VARCHAR (38) STRING
VARCHAR VARCHAR (LENGTH) VARCHAR (LENGTH)
STRING STRING STRING
Data type mappings
Working with views
Compose creates the Storage Zone with both storage tables and storage views. The storage tables
are created in the database that you defined in your storage settings while two separate database
are created for the views:The exposed views database and the internal views database. The
exposed views database is the primary views database and contains all view types. The internal
views database is used to store updates to ODS Live Views and HDS Live Views. The exposed
views database and the internal views database share the same name as the Storage Zone
database, but are appended with a unique suffix (by default, _v and _v_internal respectively),
which is set in the project settings’ Naming tab. Consuming applications should be set up to read
from the exposed views database, which provide several benefits over tables including better
security (requiring read-only access only), data concurrency, and minimizing duplicate records in
projects defined with non-ACID storage.
There are four types of view, depending on the project-level or entity-level data store type:
l
ODS standard views – Created when the data store type is ODS only. These views will
always reflect the same data unless the storage task is run.
l
ODS Live Views – Created when the data store type is ODS only. As opposed to standard
views, these views always reflect any changes to the Replicate Change Tables and to the
Storage tables.
l
HDS standard views – Created when the data store type is ODS + HDS. These views contain
both current records and historical records and will only be updated if you run storage tasks.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
322

6 Data Lake projects
l
HDS Live Views – Created when the data store type is ODS + HDS. These views contain both
current records and historical records. As opposed to standard views, these views always
reflect any changes to the Replicate Change Tables and to the Storage tables.
When using live views, to ensure transactional consistency, it is recommended to turn
off Speed partition mode in the Replicate task settings. When set to off, Replicate will
close the partition only at the end of each transaction. This might require you to shorten
the partition interval in order for the changes to be propagated to Compose in a timely
manner. Shortening the partition interval might also require you to increase the partition
cleanup frequency to prevent too many files from accumulating on the target and
degrading performance.
For information about turning off Speed partition mode, setting partitioning intervals,
and partition cleanup, see the
Replicate Help
.
Tables that were reloaded in Replicate will be automatically reloaded in Compose the
next time the task runs. To prevent data inconsistency, Live Views should not be read
while the tables are being reloaded.
Standard views contain data that was already applied to the storage tables, with mid to low-level
latency. As consuming data from standard views requires less computing resources, this should be
the first choice for downstream users. However, if latency is too high for some applications, Live
views can be used instead. Although using live views significantly reduces latency, doing so
requires greater computational resources. There is also the possibility that the date in live views
might be less consistent than the data in standard views as updates may not have been applied to
all the storage tables at the same time.
Although the views are in a separate database, you can use the suffixes (specified in the project
settings’ Naming tab) to help identify them.
Defining Landing Zones
This section explains how to set up Landing Zone connectivity in a Qlik Compose project.
In this section:
l
Landing Zone permissions (page 323)
l
Defining Landing Zones connections (page 324)
Landing Zone permissions
For proper operation, the Landing Zone database must be granted the following permissions:
l
Read metadata
l
Select from tables
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
323

6 Data Lake projects
For information on configuring the Landing Zone, see
Defining Landing Zones connections (page
324)
.
Defining Landing Zones connections
In a Data Lake project, you can define any number of Landing Zone connections. Defining multiple
Landing Zone connections is necessary if the data that you eventually want to be available in your
Storage Zone is located in several Landing Zones.
The Landing Zone connection settings tell Compose where the source tables from the Replicate
task are located. Since the Landing Zone is always located on the Storage Zone Server and the
Storage Zone connection details have already been defined, you do not need to provide them
again.
l
Before you can define a Landing Zone connection in a Data Lake project, you first
need to define a Storage Zone connection.
For more information on defining a Storage Zone connection, see
Defining a connection to the
Storage Zone (page 314)
.
To define a Landing Zone connection:
1. Open your project and click Manage in the Databases panel.
The Manage Databases window opens.
2. Click the New toolbar button.
The New Data Source window opens.
3. In the Name field, specify a display name for your Landing Zone.
4. From the Content type drop-down list, choose whether the content in the landing zone is
Full Load Only, Change Processing or Full Load and Change Processing (according to the
Qlik Replicate task definition).
5. Specify the name of the Unity Catalog in the Catalog field, according to the following
guidelines:
l
If the Replicate task is Full Load and Store Changes, both the catalog name defined in
the Replicate Databricks (Cloud Storage) target endpoint and the catalog name
defined in landing settings must be hive_metastore.
l
If the Replicate task is Full Load only, the name must be the same as the catalog name
defined in the Replicate Databricks (Cloud Storage) target endpoint.
l
Relevant for Databricks only.
l
If the storage connection settings were defined without a catalog, then the
landing connection settings must also be defined without a catalog.
6. In the Database name field, select the database that was defined in the Replicate target
endpoint settings. If you specified a catalog (above), only databases in the catalog will be
available for selection.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
324

6 Data Lake projects
For more information, see
Defining a Qlik Replicate task (page 33)
.
7. Associate with Replicate Task - This is required. Select this to associate your Data Lake
project with the related Replicate task. Replicate tasks replicate the relevant tables from the
source database to the Landing Zone. Specifying the Replicate task name will enable you to
monitor and control that task from within Compose.
Before you can choose a Replicate task however, you first need to define the
connection settings to the Qlik Replicate Server machine. To do this, click the
Replicate Server Settings link below the Task field and then configure the
settings as described in Replicate Server settings (page 382).
Once you have configured connectivity to at least one Replicate Server, you can then
proceed to select a Replicate task.
To select a Replicate task:
1. Click the browse button to the right of the Associate with Replicate task field.
The Select Replicate Task window opens.
2. Select a Replicate Server from the Server drop-down list.
The Replicate Tasks list is populated with all tasks defined on the selected server.
3. Select the task that is replicating the source tables to the landing zone and then click
OK.
The name of the selected task is shown as read-only in the Associate with Replicate task
field.
8. Click Test Connection and then, if the connection is successful, click OK to save your
settings.
Managing Landing and Storage connections
You can edit and delete Landing and Storage Connections as required. The table below describes
the available options.
To Do this
Edit a Data
Zone
connection
In the left side of the Manage Landing and Storage Connections window,
select the desired Data Zone (Landing Zone or Storage Zone) and then click the
Edit toolbar button.
Delete a Data
Zone
connection
In the left side of the Manage Landing and Storage Connections window,
select the desired Data Zone (Landing Zone or Storage Zone) and then click the
Delete toolbar button.
Click Yes when prompted to confirm the deletion.
6.5 Selecting source tables and managing metadata
This section describes how to select source tables and manage metadata. The source tables are
the tables that were replicated to the Landing Zone by the Replicate task (i.e. the target tables of
the Replicate task).
In this section:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
325

6 Data Lake projects
l
Reserved column names (page 326)
l
Selecting and adding the source tables (page 326)
l
Validating the metadata and storage (page 330)
l
Managing the metadata (page 332)
l
Schema evolution (page 337)
l
Creating transformations (page 339)
l
Reusable transformations (page 345)
Reserved column names
The following section lists the reserved column names. If the any of the discovered tables contain
columns with these names, you need to rename them in Compose. For information on renaming
columns, see
Managing attributes (page 333)
.
l
BIR_MAPPING_NR - internal mapping identifier used in staging tables for ETL
l
ROWNR - internal row identifier used in staging tables for ETL
l
RUNNO_INSERT - The task run number for INSERT operations.
l
RUNNO_UPDATE - The task run number for UPDATE operations.
l
OBSOLETE__INDICATION - Used to mark OBSOLETE records in data mart objects. See also:
The "Obsolete" indicator (page 262)
l
TR_ID - The unique Transaction ID for a fact table record.
l
BID_OCCS - Internal column used in ETL processing.
l
FD - This column is added to tables that contain attributes (columns) with a History Type 2.
The column is used to delimit the range of dates for a given record version. The column name
can be changed in the project settings.
If you change the "From Date" name in the project settings, the new name will
become a reserved word.
l
TD - This column is added to tables that contain attributes (columns) with a History Type 2.
The column is used to delimit the range of dates for a given record version. The column name
can be changed in the project settings.
If you change the "To Date" name in the project settings, the new name will
become a reserved word.
l
FKNR - Foreign key number column used in logging tables to report missing references
captured via the data warehouse ETL
Selecting and adding the source tables
This section explains how to select and add the source tables. Note that in the following
explanations, "table"refers to the physical database object whereas "entity" refers to the logical
object within Compose.
In this section:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
326

6 Data Lake projects
l
Discovering the Landing Zone (page 327)
l
Importing entities and mappings from another project (page 328)
l
Clearing the metadata cache (page 361)
See also
Managing entities (page 332)
for information on adding entities manually.
Discovering the Landing Zone
If you want the metadata to be created with Primary Keys, you need to associate a
Replicate task with the Landing Zone. For instructions on how to do this, see Defining
Landing Zones connections (page 324).
To discover the source tables:
1. Open your project.
2. In the Metadata panel, select Discover from the drop-down menu in the top right corner.
-OR-
In the Manage Metadata window, click the Discover toolbar button on the left.
The Discover window opens.
3. Select the desired source Landing Zone and then click OK.
The Source Tables/Views Selection - Name window opens.
4. Choose one of the following Search for options:
a. To search for tables only, select Tables.
b. To search for views only, select Views.
c. To search for tables and views, select All.
5. To include internal Qlik tables in the search results, select the Show Internal Qlik Tables
check box. This may be useful for debugging, but is not usually not necessary.
6. To only search for tables/views whose names contain a specific string, type the string in the
Name field.
For example, entering "ers" will return "customers" and "suppliers" in the search results.
7. Click the Search button.
The resulting tables/views will be displayed in the list in the left of the window.
8. Optionally, click the Clear Cache button to clear the Landing Zone's metadata cache (tables
and columns). This may be necessary, for example, if tables were added to the Landing Zone
or renamed. Such tables will not appear in the table list until the cache is cleared.
9. To add all of the resulting tables/views, click the >> button (Add All)
You can select multiple tables/views by holding down the [Shift] (sequential
selection) or [Ctrl] (non-sequential selection) button.
10. To add specific tables/views, select the desired tables and/or views and then click the >
(Add) button.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
327

6 Data Lake projects
If you add a table that already exists in the Metadata with the same name, then
the new table is added with the name: source_table_name_DISCOVERED (or
source_table_name_DISCOVERED_02 if the name source_table_name_
DISCOVERED already exists, and so on).
If the table contains attribute domains that differ from existing ones but have the
same name, they will also be appended with the _01 suffix.
11. Click OK to add the selected tables/views to the project.
The Generating Metadata from [Metadata Name] window opens.
A progress bar indicates the current metadata generation progress. For each stage of the
metadata generation process, a corresponding message appears in the Messages list.
12. After the metadata has been generated, click Close.
13. Repeat steps 2-12 to discover additional sources.
Importing entities and mappings from another project
You can import entities and mappings from another project with the same Storage Zone type. This
can be useful within a development environment, for example, if you need to integrate a private
developer's project with the main project.
To import entities and mappings
1. Open the Manage Metadata window as described in
Managing the metadata (page 332)
.
2. In the Entities toolbar, click the Import from Project button.
3. The Import from Project wizard opens.
4. In the Entities tab:
l
Select a project from the Import from Project drop-down list.
l
Optionally, search for specific entities.
l
Select which entities to import or select Select All to import all entities.
5. Click Next to select which mappings to import.
To create new entities and mappings if the selected entities and mappings
already exist, clear the Replace existing entities and mappings check box.
The new entities/mappings will be named
<existing_name>_IMPORTED
(or
<existing_name>_IMPORTED_<n+>
if the entity/mapping is imported more than
once).
6. In the Mappings tab:
Either click Finish to import all mappings for the selected entities (the default).
-OR-
Select which mappings you want to import and then click Finish to import the selected
entities and mappings.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
328

6 Data Lake projects
If you do not wish to import any mappings, clear the Mappings check box before
clicking Finish.
Clearing the metadata cache
To improve performance when reading from the Landing Zone or from the Storage Zone, Compose
caches both the Landing Zone metadata and the Storage Zone metadata. However,
synchronization issues may sometimes occur if the structure of the Landing Zone or the Storage
Zone metadata is altered outside of the Compose project.
If you aware of external changes to the metadata or if you notice any data synchronization
anomalies, Compose enables you to clear the metadata cache, either using the web console or
using the CLI.
Clearing the landing zone metadata cache
To clear the landing zone metadata cache and refresh the mappings on the next reading of the
metadata:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Storage Zone panel.
2. Click the Clear Landing Cache button in the Manage Storage Tasks window.
See also the section describing how to clear the cache before discover.
Clearing the storage zone metadata cache
To clear the storage zone metadata cache:
1. In the Storage Zone panel, select the Clear Metadata Cache item from the menu in the top
right corner.
2. Click Yes to clear the storage zone metadata.
3. When the storage zone metadata cache has been successfully cleared, click Close.
Clearing the metadata cache using the CLI
You can also clear the metadata cache using the CLI.
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe clear_cache --project
project_name
[--type landing|storage] [--landing_zone
source_name]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
329

6 Data Lake projects
Parameter Description
--type Which type of metadata cache to clear. Possible values are:
l
landing
l
storage
If --type
landing
and you want to clear a specific landing
zone, you must set the --landing_zone parameter as well. To
clear the metadata cache in all landing zones, specify --type
landing
and omit the --landing_zone parameter.
--landing_zone the name of the landing zone when --type landing_zone
Example
ComposeCli.exe clear_cache --project MyProject --type landing --landing_zone MySource1
Validating the metadata and storage
Once the table metadata has been generated, to prevent data inconsistency issues, it is strongly
recommended to check the validity of the metadata and the Storage Zone. For example, for the
metadata to be valid, each of the tables must have a Business Key.
Validating the metadata does not recalculate expressions for historical data that has
changed.
To validate the metadata:
1. Click the Validate button in the bottom right of the Metadata panel.
Compose will run validation checks and identify any entities which are not valid.
If the metadata is valid, the following message will be displayed:
Validation tests completed successfully. No issues were detected.
If the metadata is not valid, the Validating Storage Zone window opens. This window is
divided into the following columns:
l
Severity: Warning or Error.
l
Message: A message indicating why the entity is invalid.
l
Names:The names of the affected entities.
l
Resolve: To open the Manage Metadata window and manually resolve the issue, click
the Edit Entities button.
2. Resolve the issue (for example, by adding a Business Key) and then click Close.
The Validate Metadata window will open.
3. Click the Refresh button in the top left corner.
A message will confirm the metadata’s validity.
4. Click Close to exit the window.
To validate the Storage Zone:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
330

6 Data Lake projects
1. Click the Validate button in the bottom right of the Storage Zone panel, or select Validate
from the drop-down menu in the top right of the Storage Zone panel.
2. Compose will run a series of validation checks and the Validating the Storage window
opens.
If the Storage Zone metadata is not valid, the following message will be displayed:
The metadata is not valid.
If the Storage Zone is valid, the following message will be displayed:
The Storage Zone is valid.
If the metadata in the Manage Metadata window is not the same as the Storage Zone
metadata, the following message will be displayed:
The Storage Zone is different from the metadata.
3. This step is only applicable if the Storage Zone metadata differs from the metadata in
Compose. Review the report in the Metadata and Storage Comparison Report window and
then do one of the following:
l
If all the changes can be adjusted automatically, do one of the following according to
your configuration::
l
Click Adjust Automatically. The Adjust Storage Zone progress window opens.
When the "The Storage Zone was adjusted successfully." message is displayed,
close the window.
l
If the Generate DDL scripts but do not run them option is set, click Generate
Adjust Script.
Automatic adjust supports ADDENTITY, DROP ENTITY, and ADD
ATTRIBUTE (if it's the last attribute in the entity) only.
l
If some or none of the changes cannot be adjusted automatically, the Adjust
Automatically button will not be shown. In this case, do one of the following according
to your configuration:
l
Click Drop and Recreate Tables. You will be prompted to confirm this action.
Click Yes. The Dropping Storage Tables window opens. When the "The
Storage Zone tables were dropped and recreated successfully." message is
shown, close the window.
l
If the Generate DDL scripts but do not run them option is set, click Generate
DDL Script.
Clicking Generate Adjust Script or Generate DDL Script
When you click Generate Adjust Script or Generate DDL Script, the Generate DDL Scripts
window opens showing the progress of the script generation.
The generated scripts will be saved to:
<product_dir>\data\projects\<project_name>\ddl-scripts
Once the script(s) have been generated, close the Generate DDL Scripts window.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
331

6 Data Lake projects
When working with a Hive-based compute platform, after you close the Generate DDL
Scripts window, the DDL Script Files window opens automatically displaying the generated
scripts. The DDL Script Files window provides a read-only view that allows you to review the
scripts and download them.
The scripts need to be executed directly in your Storage Zone. Make sure that any
modifications that you make to the scripts are done prior to executing them.
When you run the adjust scripts, backup tables are created from the existing
tables. The backup table names are appended with an "_old" suffix and must be
deleted manually after the script completes.
Search for "TODO" in the script to locate the part of the script that needs
modifying.
4. Close any open validation windows.
See also:
Supported characters (page 408)
.
Managing the metadata
You can add, remove and edit the entities and attributes according to your needs. All management
tasks are performed in the Manage Metadata window, which you can open using one of the
following methods:
l
Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Metadata panel.
l
Click the Entities number in the Metadata panel.
l
Select Manage from the drop-down menu in the top right of the Metadata panel.
The Manage Metadata window is split into two tabs: The Logical Metadata tab and the Physical
Metadata tab. The Logical Metadata tab shows the entities and attributes as they appear in the
Metadata whereas the Physical Metadata tab provides a preview of the actual tables (and
columns) that will be created in the Storage Zone.
In the Logical Metadata tab, you can perform various management tasks such as adding and/or
editing entities and attributes.
In this section:
l
Managing entities (page 332)
l
Managing attributes (page 333)
l
Managing the Attributes Domain (page 336)
Managing entities
You can add, edit and remove entities as described in the table below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
332

6 Data Lake projects
Reducing the window size also shortens the toolbar. If the toolbar is too short to contain
all the buttons, the toolbar options will be displayed in the drop-down menu instead. The
shorter the toolbar, the more options will appear in the drop-down menu.
To Do This
Add an entity 1. Click the New Entity button in the Entities toolbar.
2. Provide a name and description (optional) for the entity and then click OK.
Edit an entity 1. Select the entity you want to edit and then select Edit from the drop-down
menu in the Entities toolbar.
2. Edit the entity’s name and description (optional) and then click OK.
Remove an
entity
1. Select the entity (or multiple entities) that you want to remove, and then
select Delete from the drop-down menu in the Entities toolbar.
2. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes.
Duplicate an
entity
1. Select the entity you want to duplicate and then select Duplicate from the
drop-down menu in the Entities toolbar.
2. Edit the entity’s name and description (optional) and then click OK.
The duplicated entity is added to the Entities list.
Import
entities from
another
project
See
Importing entities and mappings from another project (page 328)
.
Include
historical
records
Select the check box in the Save History column to the right of the desired
entity. Note that if you chose ODS +HDS as your data store, all of the Save
History check boxes will be selected by default.
Managing attributes
You can add, edit and remove attributes as required. All attributes in the Metadata belong to the
Attributes Domain. When adding a new attribute, you can either select an existing attribute from the
Attributes Domain or create a new Attributes Domain. Both of these options are described below.
To add an attribute from the attributes domain:
1. Click the New Attribute button in the Attributes toolbar.
The New Attribute window opens.
2. From the Attribute domain drop-down list, select the desired attribute.
3. To edit the selected attribute domain on-the-fly, click the edit button located after the
Attribute domain drop-down list. This will open the Edit -
AttributeDomainName
window.
Then, continue from Step 2 in Edit an attribute domain.
4. In the Attribute name field, optionally change the default instance name for the attribute
domain.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
333

6 Data Lake projects
The name cannot contain any of the following forbidden (by Hive) characters:
: ; . , ' "
You can create multiple instances of a single Attribute Domain. This is especially useful if you
want to use the same Attribute Domain across multiple tables, with each "instance" having its
own unique name. This also allows you to edit the properties of each attribute without
affecting the other attributes, even though all of the Attribute Domain instances share the
same parent Attribute Domain. For example, if the Attribute Domain name is "ID", you could
create one instance for it in the "Categories" entity named "CategoryID" and another
instance in the "Employees" entity named "EmployeeID". If, however, you edit the parent
Attribute Domain attribute, all instances of that attribute will be updated as well.
5. Data type: The data type of the Attribute Domain. This can only be edited by editing the
Attribute Domain.
6. To add a prefix to the attribute name, enter the desired prefix in the Prefix field.
Adding a prefix to an attribute name allows you to add multiple instances of the same
attribute domain. For example, the attribute "Employee" could become two different
attributes: "ReportsTo_Employee" and "HiredBy_Employee".
7. To create an expression for the attribute, click the fx button located after the Expression
field and then continue from
Creating transformations (page 339)
.
8. Click OK to save your settings.
To create a new attribute domain and add it to the Metadata:
1. Click the New Attribute button in the Attributes toolbar.
The New Attribute window opens.
2. Click the plus sign to the right of the Attribute domain drop-down list.
The New Attribute Domain window opens.
a. Specify a Name for the attributes domain.
The name cannot contain any of the following forbidden (by Hive)
characters:
: ; . , ' " :
b. From the Type drop-down list, select one of the available data types.
c. If the selected data type requires further configuration, additional fields will be
displayed. For example, when Decimal is selected, the Length and Scale fields will be
displayed. Set the values as desired.
d. Optionally, specify a Description.
e. Click OK to add the newly created attribute domain to the Attribute domain field and
close the New Attribute Domain window.
3. Continue from Step 4 in Add an existing attribute domain above.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
334
6 Data Lake projects
You can also add new attribute domains via the Manage Attribute Domains
window. For more information, see Managing the Attributes Domain (page 336)
To edit an attribute:
Method 1:
1. Select the attribute you want to edit and then click the Edit button in the Attributes toolbar.
The Edit Attribute Name window opens.
2. Edit the values as required and then click OK.
Method 2:
1. Double-click the attribute you want to edit.
The values in the attribute row become editable.
2. Edit the values as required and then click the tick button at the end of the row.
To remove an attribute:
1. Select the attribute(s) you want to delete.
2. Click the Delete button in the Attributes toolbar.
3. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes.
The Storage Zone needs to be "adjusted" when deleting an attribute from the metadata
and then adding the same attribute back to the metadata. However, the "Adjust"
operation will also delete the data from the corresponding Storage Zone column.
To change the attribute order:
l
Select the attribute you want to move and use the Move Up/Move to Top and Move Down
/Move to Bottom toolbar buttons to move the attribute
To manage the Attributes Domain:
l
See
Managing the Attributes Domain (page 336)
.
To create an expression for an attribute:
l
See Add an attribute from the attributes domain or Edit an attribute above.
To export the attributes to a TSV file:
l
Select an entity from the Entities list on the left of the Manage Metadata window and then
select Export to TSV from the drop-down menu in the Attributes toolbar.
Depending on your browser settings, you will either be prompted to download the
<entityname>_Attributes.tsv file or it will be downloaded to your default Downloads
location.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
335

6 Data Lake projects
Managing the Attributes Domain
The Attributes Domain provides a list of all the attributes available in the Compose metadata, as
well as their data type. You can add, edit and delete attributes according to your data warehousing
needs. The Attributes Domain also allows you to see which entities each attribute belongs to, as a
single attribute may be present in several entities.
To manage the Attributes Domain:
1. From the drop-down menu in the top right of the Storage Zone panel, select Manage
Attributes Domain.
2. Add, delete and edit attributes as describe in the table below.
To Do This
Add an
attributes
domain
1. Click the New Attributes Domain toolbar button.
The New Attribute Domain window opens.
2. In the Name field, specify a name for the attribute.
The name cannot contain any of the following forbidden (by
Hive) characters:
: ; . , ' " :
3. From the Type drop-down list, select one of the available data types.
4. If the selected data type requires further configuration, additional fields will
be displayed. For example, when Decimal is selected, the Length and
Scale fields will be displayed. Set the values as desired.
5. Optionally specify a Description.
6. Click OK to add the attribute and close the New Attribute Domain window.
Attribute domains names are case insensitive. For example, a project
cannot contain one attribute domain called date and another called
DATE.
Edit an
attribute
domain
1. Select the desired attribute and then click the Edit toolbar button.
The Edit: Name window opens.
2. Edit the attribute as described in steps 2-6 of Add an attributes domain
above.
Note that the Edit: Name window also contains a Used in Entities list.
Knowing which entities the attribute is used in may affect the type of
changes you make, as the planned changes may not be appropriate for all
entities.
Remove an
attribute
1. Select the attribute you want to delete and then click the Delete toolbar
button.
2. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
336

6 Data Lake projects
Schema evolution
Schema evolution allows users to easily detect structural changes to multiple data sources and
then control how those changes will be applied to your project. Schema evolution can be used to
detect all DDL changes that were made to the source database, although not all changes can be
applied automatically (see "Supported data changes" below). Schema evolution can be performed
using the web console or using the CLI as described below.
Required permission: Compose Designer or Admin.
Schema evolution requires certain options to be turned on in the Replicate task(s). For information
about which options need to be enabled in Replicate for schema evolution, see
Defining a Qlik
Replicate task (page 282)
.
Supported data source changes
The following changes are supported:
l
New columns - When this change is applied:
l
The new column will be added (as an attribute) to the end of the entity in the metadata
l
The column will be added to any mappings for that entity
l
The data warehouse will be adjusted
l
The storage task will be generated (but not run)
l
New tables - When this change is applied:
l
The new table will be added (as an entity) to the metadata
l
A default mapping will be created
l
In the case of multiple storage tasks, the mapping will be added to the first task
according to alphabetical order
l
The data warehouse will be adjusted
l
The storage task will be generated (but not run)
Data warehouse adjustment and storage task generation will only occur if the
appropriate apply option (see Step 5 below) was selected.
Schema evolution using the web console
1. Open the Schema Evolution window using one of the following methods:
l
Click the Schema Evolution button at the bottom of the METADATA panel.
l
Select Schema Evolution from the hamburger menu in the top right of the
METADATA panel.
l
Open the Manage Metadata window and click the Schema Evolution toolbar button
in the Logical Metadata tab.
2. Select which data sources to scan for changes. You can select either All data sources or
Selected data sources. If you choose the latter, select which data sources to scan for
changes.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
337

6 Data Lake projects
3. Click Scan for Changes.
During the scan, if a change is detected, the following message will be displayed:
Found new DDL changes for data source <name>
If no changes were detected, the following message will be displayed:
No new DDL changes were found for data source <name>
If unsupported changes were detected, one of the following messages will be displayed:
DDL type <type> is not supported and will be skipped
Column operation <operation> in data source <name> is not supported and
will be skipped
4. When the scan completes, click Close.
If changes were detected, the Schema Changes window opens showing the list of changes
since the last scan (via the web console or the CLI).
5. Click Apply Changes Options if you want to apply the changes or Ignore Changes to close
the window without applying the changes.
When you click Apply Changes Options, the Apply Schema Changes window opens,
showing the following apply options:
l
Apply changes to the metadata and the mappings - Select this option if you have
other changes you would like to make before adjusting the data warehouse. You may
even wish to undo some of the schema evolution changes as Compose does not allow
you to choose which changes to apply.
l
Apply changes to the metadata and the mappings, and adjust the data warehouse
- Select this option if you have other changes you would like to make before
generating the tasks.
l
Apply changes to the metadata and the mappings, adjust the data warehouse,
and generate relevant tasks - Select this option if you want to apply all the changes
and generate associated tasks without making any prior changes.
6. Choose one of the options and click Apply Changes.
The Applying Schema Changes window opens.
7. After the operations you selected in Step 5 have completed, click Close.
If, for whatever reason, Compose fails to add the changes to the metadata or the
mappings, the next time you perform a scan, the changes will be detected again.
However, if Compose succeeds to apply the changes but fails to adjust the data
warehouse or generate the tasks, the changes will not be detected again. In such
a case, you will need to manually adjust the data warehouse and/or generate the
tasks after resolving the issue that prevented these operations from being
performed automatically.
Schema evolution using the CLI
You can also use the Compose CLI to perform schema evolution. As opposed to the web console,
the CLI does not output a list of changes, which makes it more suited to customers that wish to
automate schema evolution through the use of scripts.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
338

6 Data Lake projects
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe schema_evolution --project
project_name
[--data_sources
data_source
] --action
apply_to_model_and_mappings|apply_to_model_mappings_adjust_storage|apply_to_model_mappings_
adjust_storage_generate_tasks|ignore_changes
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--data_sources A comma-separated list of data sources to scan for changes.
When omitted, all of the project’s data sources will be scanned. If
there are no changes, “0” will be returned.
To avoid errors, the data source names must be exactly as defined
in your project.
--action How (or whether) to apply the changes. Possible values are:
l
apply_to_model_and_mappings - Select this option if you have
other changes you would like to make before adjusting the
data warehouse. You may even wish to undo some of the
schema evolution changes, as Compose does not allow you
to choose which changes to apply.
l
apply_to_model_mappings_adjust_storage - Select this option
if you have other changes you would like to make before
generating the tasks.
l
apply_to_model_mappings_adjust_storage_generate_tasks -
Select this option if you want to apply all the changes and
generate associated tasks without making any prior
changes.
l
ignore_changes - Select this option to ignore all changes.
Example
ComposeCli.exe schema_evolution --project MyProject --data_sources mysource1,mysource2 --
action apply_to_model_mappings_adjust_storage
Creating transformations
Compose allows you to transform data using an expression either in Replicate or Compose,
according to your needs. The table below provides further information about creating
transformations.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
339

6 Data Lake projects
Where the
Transformation is
Created
Reasons to Create a Transformation There When the
Transformation is
Applied
Replicate
l
Filtering large amounts of data that is not
needed for the Storage Zone (in the present
or the future)
l
Obfuscation due to regulatory reasons or
internal policies
l
Data type conversion (e.g. converting a
source data type that is not supported on
the Storage Zone platform)
Before the data
reaches the landing
zone.
Metadata
l
The default location if you are not sure
where to put it
l
General business logic
l
Needed for several sources or several data
marts
Between the Landing
Zone and the Storage
Zone.
Storage Zone
l
Specific source preparation
l
Need to preserve the original unfiltered
source information in Hadoop
l
Needed for merging several sources
Between the Landing
Zone and the Storage
Zone.
Where to create a transformation
See also
Reusable transformations (page 345)
.
In this section:
l
Expression Builder overview (page 340)
l
Building Expressions (page 342)
l
You test your expression to check that results are as expected. The following figure is an
example of an expression that has been evaluated and tested. (page 343)
Expression Builder overview
The following section provides an overview of the Expression Builder functionality.
The Expression Builder enables you to create a transformation without needing to type anything
manually.
The Expression Builder can be opened in several places, depending on your needs. For more
information about where to create a transformation, see
Creating transformations (page 339)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
340

6 Data Lake projects
The Expression Builder consists of the following panels:
l
Tabs on the left of the Expression Builder: These tabs contains elements that you can add
to an expression. Select elements and add them to the Build Expression pane to create an
expression. For more information, see
Building Expressions (page 342)
.
The following tabs are available:
l
Parameters - Only displayed when opening the Expression Builder from within the
Reusable Transformations > Edit Transformation window.
For information on reusable transformations, see
Reusable transformations (page
345)
below.
l
Input Columns/Input Attributes - Columns/attributes that can be used to build your
expression.
l
Transformations - Contains a list of reusable transformations. The tab is not
displayed if no reusable transformations have been defined.
For information on reusable transformations, see
Reusable transformations (page
345)
below.
l
Operators - Operators that can be used to build your expression.
l
Functions - Functions that can be used to build your expression.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
341

6 Data Lake projects
The Operators and Functions displayed in the Expression Builder use SQL
format. As SQL support and implementation is different for each database
type and version, the database being used in your Compose project will
determine which Operators and Functions will be available.
Additionally, the list of Operators and Functions displayed in the Expression
Builder is not comprehensive. However, you can use any Operators and
Functions supported by the database, even if they are not included in the
list.
For an explanation of the available Operators and Functions, refer to the
Help for your data lake.
l
Build Expression Pane: The Build Expression pane is where you build your expression. You
can add elements, such as columns or operators to the panel as well as type all or part of the
expression. For more information, see
Building Expressions (page 342)
.
l
Parse Expression Pane: This pane displays the parameters for the expression. After you
build the expression, click Parse Parameters to list the expression parameters. You can then
edit the parameters, enter a value for each of the parameters and associate attributes with
them. For more information, see
Parsing expressions (page 343)
.
l
Test Expression Pane: This panel displays the results of a test that you can run after you
provide values to each of the parameters in your expression. For more information, see
You
test your expression to check that results are as expected. The following figure is an example
of an expression that has been evaluated and tested. (page 343)
.
Building Expressions
The first step in using the Expression Builder is to build an expression in the Build Expression pane.
To build an expression:
1. Hover the mouse cursor over the element that you want to add to your expression
(expressions usually start with an Input Column) and click the arrow that appears to its right.
2. Add Operators additional Input Columns and Functions as required.
To add operators to your expression, you can use the Operator tab on the left or the
Operator buttons located above the Build Expression pane or any combination of
these.
Example:
To create an expression that combines the FirstName name and LastName columns, do the
following:
1. Add the FirstName Input Column to the Build Expression pane.
2. In the Operator toolbar above the Build Expression pane, click the concatenate operator.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
342

6 Data Lake projects
3. Then add a space between single quote characters and click the concatenate (+) operator
again.
4. Add the LastName Input Column to the Build Expression pane.
The expression would look like this:
Parsing expressions
When you add operators to the expression, the expression’s parameters are usually added
automatically to the Parse Expression pane. However, when you complete your expression or edit
it, you may need to parse the expression see all of the parameters.
To parse the expression parameters:
l
Click the Parse Expression button below the Build Expression pane.
If the expression is
not
valid, a red error message will appear at the bottom of the Expression
Builder window.
If the expression is valid, the expression parameters and attributes (Input Columns) will be
displayed in the in the Parse Expression pane. See the figure
Test Expression (page 344)
.
Editing parameter names
By default, the parameter name is the same as the input column name. However, you can change
the parameter name as needed and then associate it with an input column. This is useful, for
instance, when you need to shorten attribute names. For example, EstimatedTimeOfArrival can
be abbreviated to ETA.
To edit a parameter and associate it with an input column:
1. In the Parse Expression pane, edit the parameter name as required.
2. From the Attribute drop-down list, select the desired input column.
Testing expressions
You test your expression to check that results are as expected. The following figure is an example
of an expression that has been evaluated and tested.
Testing an expression that contains an analytic function will validate the syntax without
actually executing the function. Additionally, the test will only be performed on a single
record.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
343

6 Data Lake projects
Compose does not check the data types of columns used in an expression for
compatibility. For example, if a column of type integer is used in an expression for a
column of type varchar, the expression will not be executed successfully.
Test Expression
To test an expression:
1. In the Expression Builder window, build an expression as described in
Building Expressions
(page 342)
.
2. Click Parse Expression as described in
Parsing expressions (page 343)
.
3. View the parameters that are displayed. If your expression is not valid, an error message is
displayed.
4. Optionally edit the parameters name(s) as described in
Editing parameter names (page 343)
.
5. Type values for each parameter and then click Test Expression to see the expression result.
For example, using the expression in
Test Expression (page 344)
, type Mike for FirstName
and Smith for LastName. The result displayed is Mike Smith.
6. This step is only available for transformations created in the Edit Mappings window. When
you create a transformation in the Edit Mappings window, an additional button called Show
Data appears to the left of the Test Expression button. You can click this button to see how
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
344

6 Data Lake projects
your expression translates into actual data.
For example, clicking the Show Data button for the expression UnitPrice*Quantity will
open the following window.
For more information on the Edit Mappings window, see
Column mappings (page 353)
in
Creating and Managing Storage Zone Tasks (page 347)
.
Reusable transformations
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
345

6 Data Lake projects
In a single Compose project there may be several processes that require similar data
transformations. For example a reusable transformation can be defined that concatenates first and
last names. This transformation could then be used both in the Customers mapping and in the
Employees mapping.
As opposed to stored functions or procedures which are environment dependent, reusable
transformations are environment agnostic, meaning that not only can they be used as required
within a Compose project, but they can also be used across different environments (using
Compose’s export/import function).
Centrally managed transformations increase efficiency by eliminating unnecessary duplication,
while at the same time, enabling the seamless propagation of changes to all transformation
instances.
Adding a reusable transformation
To define a reusable transformation:
1. From the drop-down menu in the top right of the Storage Zone panel, select Reusable
Transformations.
The Reusable Transformations window opens.
The window is split into the following panes:
l
Upper pane - Lists the reusable transformations that have been defined.
l
Lower pane - Provides additional information about transformation instances such as
where they are in use (e.g. mappings, metadata, etc.) and the expression that was
created using the transformation.
Select a transformation to see the additional information.
2. Click the New Transformation toolbar button.
The New Transformation window opens.
1. In the Name field, specify a name for the transformation.
2. In the Category field, specify a category name. If the category name already exists it
will be displayed below the field when you start to type the name. To group the new
transformation in the same category, simply select the existing name (unless of course
you wish to create a new category with a similar name).
In the Expression Builder, transformations are grouped according to their category
name, making it easier to find the transformation you want to use. Therefore, when
specifying a category name, it is recommended to choose a name that reflects the
purpose of the transformation. For example, if you create several transformations that
concatenate data, it would make sense to group those transformations under a
category called "Join".
3. To add a parameter to the transformation, click the New button to the right of the
Parameters heading.
A new row is added to the Parameters list.
4. Specify a name for the parameter, select an appropriate data type, and optionally
provide a description.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
346

6 Data Lake projects
If you add multiple parameters, you can change a parameter’s position by
selecting the parameter and then using the Up/Down arrows (above the
Parameters list) to reposition it.
5. Click the Create Expression button below the Parameters list.
The Edit Transformation window opens.
6. In the Edit Transformation window, create an expression using the parameters you
defined earlier.
For information on creating expressions, see
Creating transformations (page 339)
.
7. Click OK to save the transformation.
The transformation is added to the list in the upper pane.
Once a transformation has been defined, it will be available for selection as needed in the
Expression Builder’s Transformations tab.
For information on creating expressions, see
Creating transformations (page 339)
.
Managing reusable transformations
You can manage reusable transformation as described in the table below.
To Do This
Delete a
transformation
Select the transformation and then click the Delete toolbar button. When
prompted to confirm the action, click OK.
If the transformation is in use, you first need to delete the
transformation instances.
Edit a
transformation
Double-click the transformation or select the transformation and then click
the Edit toolbar button. Continue as described in
Reusable transformations
(page 345)
.
Any changes you make to a transformation will be propagated to
all instances of that transformation.
Edit a parameter Open the Edit Transformation window as described in
Reusable
transformations (page 345)
. Then, select the parameter you want to delete
and click the Delete button above the Parameters list.
6.6 Creating and Managing Storage Zone Tasks
Once the Metadata has been prepared, the next step in the Compose workflow is to create the
Storage Zone tables (optional), generate the task statements and run the Storage Zone task. Tasks
can either be run manually or scheduled to run periodically or in the future.
In this section:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
347

6 Data Lake projects
l
Defining and running data storage tasks (page 348)
l
Managing task definitions (page 351)
l
Viewing and exporting task statements (page 362)
l
Modifying task settings (page 363)
Defining and running data storage tasks
This section, describes how to create the Storage Zone tables, generate the task statements and
run a Data Storage task.
It contains the following topics:
l
Creating the Storage Zone (page 348)
l
Generating the task statements (page 348)
l
Controlling data storage tasks (page 349)
Creating the Storage Zone
If table(s) were reloaded in Replicate, the table(s) will also be (automatically) reloaded in
Compose the next time the task runs. During reload, Live Views should not be read.
To create the Storage Zone tables:
1. Click the Create button in the bottom right of the Storage Zone panel.
The Creating Storage Zone window opens.
A progress bar indicates the current progress. For each stage of the Storage Zone
generation process, a corresponding message appears in the Messages list.
2. When the process completes, click Close.
See also:
Supported characters (page 408)
.
Generating the task statements
After the Storage Zone tables have been created, you then need to generate the task statements
that will be used in the Storage Zone task. The task statements include the Mappings between the
Landing Zone tables and the Storage Zone tables. If you need to make changes to the Mappings,
continue from
Managing task definitions (page 351)
.
l
Changing a Primary Key in the source record will cause a new record to be
inserted in the storage table.
l
Regenerating the task statements after performing a non-supported change in
the metadata will appear to succeed without errors or warnings, but the task will
fail if run later.
l
Defining a single task that ingests data from several Landing Zones is not
supported. As a workaround, you can create a separate task for each Landing
Zone.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
348

6 Data Lake projects
To generate the Storage Zone task statements:
1. Click the Data Storage Tasks button in the bottom left of the Storage Zone panel.
The Manage Data Storage Tasks window opens.
2. If there are multiple tasks, in the left pane, select the desired task.
3. Click the Generate toolbar button, and select one of the following options:
l
With validation - This is the default option for generating storage tasks.
You can also generate storage tasks with validation (default option) by
clicking the Generate toolbar button.
l
Without Validation - Select this option if you are sure that the storage tables are
adjusted properly and the mapping is valid. The generation of storage tasks is much
faster. Note that you could have errors later when running the task if something is not
valid.
The Generating Statements for Task:
Name
progress window opens. When the "Generate
task finished successfully" message is displayed, close the window.
Only mappings associated with the task in the Manage Tasks window will be
generated.
Controlling data storage tasks
Once the Storage Zone tables have been created and the task statements have been generated,
you can then proceed to run the Storage Zone task. The Storage Zone task extracts data from the
Landing Zone tables and loads it into the Storage Zone tables.
Limitations and considerations
l
When task are reloaded in Replicate November 2020, Compose will also reload the task (i.e.
perform a Full Load) and only then apply the changes. Depending on the number of tables
involved, this may takes some time as two reloads will be performed (one in Replicate and
the other in Compose).
l
A storage directory may be used exclusively by only one Compose project.
l
Data storage tasks are optimized to run on relatively large batches of data. It is
recommended to specify a partition length in excess of one hour. Although specifying a
partition length of less than one hour may improve latency, creating many partitions on the
target may also impact (target) performance (especially in systems with large volumes of
changes).
l
Change Processing creates a new file on every write. This may cause many files to amass
and degrade performance. Therefore, it is recommended to monitor the storage directory
and periodically consolidate small files into larger ones and move/delete files that are no
longer required.
l
Storage directories and subdirectories are managed by Compose; you should not delete files
or write to them unless approved by Qlik Support or explicitly recommended in this guide.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
349

6 Data Lake projects
l
When using a Hive-based compute platform, for optimal performance, it is recommended to
allocate a dedicated queue to Compose tasks only.
l
When using a Hive-based compute platform, in order to see the delta of data changes in the
storage tables, you need to define the following commands so that Hive can read the
subdirectories:
set hive.supports.subdirectories=true;
set hive.input.dir.recursive=true;
Running a task
Storage Zone tasks can be run manually, scheduled to run periodically or run as part of a workflow.
The section below describes how to run a Storage Zone task manually. For information on
scheduling Storage Zone tasks or including them in a workflow, see
Controlling and monitoring
tasks and workflows (page 365)
.
If there is a Replicate source table with data, that:
l
Was not originally selected in the Replicate Full Load and Apply Changes task (i.e.
was added later).
-OR-
l
Was selected in a Replicate Full Load and Apply Changes task, but was not
selected in the mappings of the Compose Full Load and Change Processing data
storage tasks, and the tasks have already been run.
In any of the above scenarios, in order to get the data that was added later, you need to:
1. Duplicate the Compose Full Load and Change Processing tasks associated with
that table.
2. Run the duplicated Full Load task.
3. Run the duplicated Change Processing task.
Note that after running these tasks, duplicate records may exist in the Storage Zone, but
they will be removed when reading from the Storage Zone views.
To run a Storage Zone task:
1. Click the Manage button in the bottom left of the Storage Zone panel.
The Manage Storage Tasks window opens.
2. If multiple tasks have been defined, in the left pane, select the task that you want to run.
3. Click the Run toolbar button. The window switches to Monitor view and the following status
bars are displayed:
l
Completed - Shows the tables that have already been loaded into Hive
l
Loading - Shows the tables currently being loaded into Hive
l
Queued - Shows the tables waiting to be loaded into Hive
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
350

6 Data Lake projects
l
Error - Shows the tables that could not be loaded into Hive due to error. Click the
Show Details link below the bar to see more information about the statement(s) that
resulted in the error.
l
Canceled - The number of canceled tables (tables that were not processed due to the
task being aborted) does not appear as a separate status bar. To view the number of
canceled tables, click the Select All link above the status bars.
To see more information about tables in a particular status, click the relevant status bar. A list
of tables in the selected status will be shown.
When the task status is indicated by a icon, close the Manage Storage Tasks window.
You can stop the task at any time by clicking the Abort toolbar button. This may be
necessary if you need to urgently edit the task settings due to some unforeseen
development. After editing the task settings, simply click the Run button again to restart the
task.
You can also access the task log files by clicking the View Log button.
Aborting a task may leave the Storage Zone tables in an inconsistent state.
Consistency will be restored the next time the task is run.
Managing task definitions
Task definitions contain the mappings between the columns in the Landing Zone tables and the
columns in the Storage Zone tables(and any transformations applied to those mappings). The same
mappings can be used by several tasks. You can create new tasks, duplicate tasks and edit existing
tasks as required.
The following options are available:
l
Adding and duplicating tasks (page 352)
l
Column mappings (page 353)
l
For each Compose task, all of the mapping tables should be populated by
data from one Replicate task.
l
You must regenerate the task statements and then run a Storage Zone task
whenever the mappings are modified. Populating the Storage Zone can
either be done manually as described in Controlling data storage tasks
(page 349) or automatically as described in Scheduling tasks (page 368).
If you have already run the data mart tasks, then you also need to
regenerate the data mart ETLs and run the tasks again as described in
Managing task definitions (page 351).
l
Using lookup tables (page 357)
l
Dropping and recreating tables (page 359)
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
351

6 Data Lake projects
Adding and duplicating tasks
As the default task definitions are generated automatically (by discovering the Landing Zone
tables), there is usually no reason to manually create or duplicate an task. One possible reason to
duplicate an task is if your Metadata contains different types of tables and you want to manage
them in separate tasks. An exception to this is if you import your model from ERwin without first
defining global mappings. In such a case, you will need to manually add the Task and create the
mappings.
For more information on global mappings, see
Managing global mappings (page 161)
.
The following task types are available:
l
Full Load - Loads the selected tables from the Landing Zone into the Storage Zone.
l
Change Processing - Updates the Storage Zone tables with the Landing Zone changes.
l
Full Load and Change Processing - Loads the selected tables into the Storage Zone and
then updates them with the Landing Zone changes.
To Do This
Add a new
Task
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Storage Zone panel.
The Manage Tasks window opens.
2. Click the New Task toolbar button.
The Add New Task window opens.
3. Specify a name for the task.
Task names cannot contain the following characters:
/\,&#%$@=^*+"'`~?<>:;[]{} as well as all non-printable
characters (below 0x20). The task name can contain a single dot,
but it cannot be the first or last character.
4. Optionally, specify a description.
5. Choose Full Load and/or Change Processing as the task type.
6. Click OK.
7. Select the task name in the left pane and continue from
Column mappings
(page 353)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
352

6 Data Lake projects
To Do This
Duplicate a
Task
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Storage Zone panel.
The Manage Tasks window opens.
2. Select the task you want to duplicate and then click the Duplicate toolbar
button.
The Duplicate window opens.
3. Specify a Name for the new Task.
4. Select a Landing Zone.
5. Optionally change the default Schema.
6. Select the Task type according to your Replicate task type.
7. Click OK.
8. Select the task name in the left pane and continue from
Column mappings
(page 353)
.
Column mappings
For improved metadata performance during discovery and mapping, Compose caches
the metadata of the Landing Zones after reading them. However, synchronization issues
may arise if the Landing Zone is modified outside of Compose. In such cases, you should
click Clear Landing Cache in the Mappings tab of the Storage Zone panel in order to
refresh the cache on the next reading of the metadata.
For details on recreating the Storage Zone cache, see Clearing the metadata cache
(page 361).
The mappings show the current mapping between the Landing Zone tables and the Storage Zone
tables. By default, the columns names and data in the Landing Zone tables and the Storage Zone
tables will be identical. However, you can manually change the mappings according to your needs,
either by simply mapping a Landing Zone column to a different Storage Zone column and/or by
using an expression.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
353

6 Data Lake projects
Limitations and considerations
l
Creating multiple mappings for a single table is not supported.
l
Mapping from Views is not supported.
Editing column mappings
To edit column mappings:
1. Click the Manage button in the Storage Zone panel.
The Mappings tab is displayed. Each of the Storage Zone tables has a corresponding
mapping name.
2. In the Mappings column, click the mapping that you want to edit.
The Edit Mapping: Name window opens.
3. Edit the mapping as described in the table below.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
354

6 Data Lake projects
To Do This
Map a column in
a Landing Zone
table to a column
in a Storage
Zonetable
The mapping procedure differs depending on whether you
are in Standard View or Compact View. For information on
changing the view, see Change the view (page 356).
In Standard View:
1. Hover the mouse cursor over the Landing Zone column name as
shown in the image below.
A gray dot appears to the right of the column name.
2. Drag the mouse cursor from the gray dot to the desired column
in the Storage Zone table.
3. When the dotted line turns green (as shown below), release
your mouse button.
The mapping operation is completed.
Note that if the dotted line turns red (instead of a green), you
will not be able to map the Landing Zone column with the
desired Storage Zone column. A red dotted line indicates that
the Landing Zone and Storage Zone column data types are
incompatible with each other.
In Compact View:
1. Switch to Compact View as described in Change the view.
2. Drag the Landing Zone column to the cell located to the left of
the target Storage Zone column.
Auto-generate
mapping
Click the Auto-Map toolbar button.
Remove all
mappings
Click the Reset toolbar button.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
355

6 Data Lake projects
To Do This
Change the view Changing to a more compact view is recommended for Landing Zone
tables that have numerous columns. In compact view, the table
columns are organized in rows (instead of a single list), making it
easier to locate Landing Zone columns and map them to the desired
Storage Zone columns.
To change the view:
Click the Change View toolbar button. For information on creating
mappings in Compact view, see Map a column in a Landing Zone table
to a column in a Data Lake table.
Select a different
source database
Select a database from the Landing Zone Database drop-down list on
the left of the window.
Select a different
source schema
Select a schema from the Schema drop-down list on the left of the
window.
Select a different
table
Select a table from the Table drop down list on the left of the window.
Create a
column-level
transformation
1. Hover the mouse cursor over the Storage Zone Column for
which you want to create a transformation and then click the fx
button that appears to its right.
The Expression Builder opens.
2. Continue from
Creating transformations (page 339)
.
Adding, renaming and deleting mappings
You can add, rename and delete mappings as required. For example, if you want one of the Storage
Zone tables to contain columns from several tables in the Landing Zone, then you need to add a
new mapping for each of the Landing Zone tables.
To add, delete, and rename mappings:
1. Click the Manage button in the Storage Zone panel.
The Manage taskTasks window opens.
2. In the left pane, select the desired taskTask.
3. Select the Mappings tab.
4. Add or delete mappings as described in the following table.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
356

6 Data Lake projects
To Do This
Add a new
mapping
1. In the Data Lake Tables column, select the table that you want to
map.
2. Click the NewMapping button above the Delivery Tables column.
The New Mapping window opens.
3. Optionally change the default mapping name.
4. From the Entity drop-down list, select the entity in the Storage
Zone to which you want to map.
5. Click OK to save the mapping.
6. Enable the mapping.
Delete a
mapping
1. In the Mappings column, hover the mouse cursor over the
mapping you want to delete.
2. Click the Delete(x) button that appears to its right.
3. Click OK when prompted to confirm the deletion.
Rename a
mapping
1. In the Mappings column, hover the mouse cursor over the
mapping you want to rename.
2. Click the Rename (A) button that appears to its right.
The Rename window opens.
3. Specify a new name for the mapping and then click OK.
Using lookup tables
Lookup tables are useful for replacing source data with the actual data that you want to appear in
the Storage Zone. For example, a lookup table could be used to replace a zip code with a full
address or, conversely, to replace a full address with a zip code.
Lookup on a column which is mapped to the Compose "From__Date" column is not
supported.
Linking lookup tables
To link a lookup table column to a Storage Zone table column:
1. Click the link to the desired task in the Storage Zone panel.
The Manage Tasks window opens.
2. In the Mappings column, click the mapping for the Storage Zone table containing the result
column (with the data that you want to replace).
The Edit Mapping - Name window opens.
3. Hover the mouse cursor over the relevant Storage Zone column and then click the Lookup
button that appears to the right of the column name.
The Select Lookup Table window opens.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
357

6 Data Lake projects
1. From the Database drop-down list, select the database containing the lookup table.
The database must reside in your Landing Zone.
2. From the Schema drop-down list, select the schema containing your source lookup
tables.
3. Select either Table or View according to the lookup table type.
4. From the Table drop-down list, select the lookup table.
The right side of the Select Lookup Table window displays the lookup table columns
and their data types. To view the data in the lookup table, click the Show Lookup Data
button.
5. After you have selected the lookup table, click OK.
The Lookup Transformations - Table Name.Column Name window opens.
The window is divided into the following panes:
Upper pane: The upper part of the right pane (Condition) displays the condition expression,
which stipulates the condition(s) for performing the lookup.
Lower pane: The lower part of the right pane (Result Column) displays the column result
expression, which stipulates what data to replace in the target column.
4. To change the lookup table, click the Change Lookup Table button above the lookup table
columns and then perform steps a. to d. above.
5. To view the lookup table or landing table data, click the Show Lookup Data or Show Landing
Data buttons respectively.
6. To specify the condition(s) for performing the lookup, click the Create Expression button
(which changes to Edit Expression after an expression has been created) above the
Condition expression.
The Condition Expression - Column Name window opens.
7. Create an expression using the landing and lookup table columns on the left.
For an example, see
Using lookup tables (page 357)
.
For information on creating expressions, see
Creating transformations (page 339)
.
8. To specify what data to replace or add if the lookup conditions are met, click the Create
Expression button (which changes to Edit Expression after an expression has been created)
above the Result Column expression.
The Result Expression - Column Name window opens.
9. Create an expression using the landing and lookup table columns on the left.
For an example, see
Using lookup tables (page 357)
.
For information on creating expressions, see
Creating transformations (page 339)
.
10. To preview the results, click the Preview Results button.
11. Click OK to save your settings and close the Lookup Transformations - Table
Name.Column Name window.
Lookup example
The following example shows how a lookup table is used to concatenate a Dutch translation of the
category name (located in the lookup table) to the original category name located in the landing
table.
The lookup could be defined using the following expressions:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
358

6 Data Lake projects
1. Condition expression:
${Lookup.CategoryID}=${Landing.CategoryID}
Meaning: Perform the lookup only if the Category ID in the landing table and the lookup table
are the same.
2. Result column expression:
${Lookup.CategoryName} + ' is ' + ${Landing.CategoryName}
Meaning: Add the data in the CategoryName column in the lookup table to the data in the
CategoryName column in the landing table (separated by the word "is").
Assuming the result column name is "Split Name", clicking the Preview Results button would
display the following table:
Split Name Category Name
(Lookup)
Category Name
(Landing)
Category ID
(Lookup)
Category ID
(Landing)
dranken is Beverages dranken Beverages 1 1
Specerijen is
Condiments
Specerijen Condiments 2 2
Gebak is
Confectionary
Gebak Confectionary 3 3
Zuivelproducten is
Dairy Products
Zuivelproducten Dairy Products 4 4
Grains/Granen is
Grains/Cereal
Grains/Granen Grains/Cereal 5 5
Vlees/Gevolgete is
Meat/Poultry
Vlees/Gevolgete Meat/Poultry 6 6
Dropping and recreating tables
Compose enable you to drop and recreate the Storage Zone tables as required.
When changing certain project settings (e.g. table prefixes) drop and create is required. If you
change the Metadata after the Storage Zone tables and/or files were already created and loaded
with data, you should adjust the Storage Zone to reflect the modified Metadata (as described in
Validating the metadata and storage (page 330)
). Some changes however cannot be resolved by
adjusting the Storage Zone. In such cases, you can either revert the Metadata to its pre-modified
state or drop and (optionally) recreate the Storage Zone tables.
Note that dropping and recreating tables will delete
all
of the data in the tables and should only be
performed in lieu of a better option.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
359

6 Data Lake projects
l
In some scenarios, you need to edit the CREATE table statements before they are
run. This can be done using the
Generate DDL scripts but do not run them
option
in Project settings (page 37). For example, if you want to override the default
sorting of your Storage Zone tables or add specific formatting annotations, you
will need to edit the script to accomplish this.
l
The Change Processing context (i.e. the point in time when changes were last
captured) is deleted when dropping all tables but preserved when dropping
selected tables. Therefore after deleting selected tables, in order for Compose to
continue processing changes from when the tables were dropped, you need to
perform the following additional steps:
1. Duplicate the Full Load and Change Processing tasks.
2. Delete the old tasks (i.e. the tasks that were duplicated) making sure to select
the Delete mappings not used by other tasks option.
3. Run the Full Load and Change Processing tasks again. This may result in
duplicates in the Storage Zone tables, but the duplicates are excluded from
the Storage Zone Views and will not appear in any provisioned data.
To drop and recreate all storage tables:
1. In the Storage Zone panel, select the Drop and Recreate|Tables item from the menu in the
top right corner.
2. The Drop and Recreate Tables window opens.
3. Select Recreate to drop and recreate the storage tables or Drop to drop them only.
4. Click OK to perform the drop and/or recreate operation.
The tables will be dropped and/or recreated, unless the Generate DDL scripts but do not run
them option is enabled.
Dropping and recreating views
Generally speaking, you should not need to recreate the views very often. Usually, recreating the
views is only required after upgrading to a newer Compose version or patch release that contains
updates to the views. Although unlikely, you may also need to recreate the views if they were
accidentally deleted. If there is a need to recreate the views after upgrading, it will be clearly stated
in the release notes. The Views can be recreated using the Compose web console or using the
Compose CLI.
If Compose detects a mismatch between the Logical Metadata (defined via the Metadata panel)
and the Storage Zone metadata, the view recreation operation will fail and you will need to validate
and adjust the storage before retrying the operation.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
360

6 Data Lake projects
Recreating the Views with the web console
To recreate the Views using the web console, simply select Recreate Views from the menu in the
top-right of the STORAGE ZONE panel. You will be prompted to confirm the operation as it might
take some time, during which the Views data might not be accessible.
Recreating the Views with the CLI
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe recreate_views--project
project_name
Where:
--project is the name of the project.
Example
ComposeCli.exe recreate_views --project MyProject
See also:
Validating the metadata and storage (page 330)
Clearing the metadata cache
To improve performance when reading from the Landing Zone or from the Storage Zone, Compose
caches both the Landing Zone metadata and the Storage Zone metadata. However,
synchronization issues may sometimes occur if the structure of the Landing Zone or the Storage
Zone metadata is altered outside of the Compose project.
If you aware of external changes to the metadata or if you notice any data synchronization
anomalies, Compose enables you to clear the metadata cache, either using the web console or
using the CLI.
Clearing the landing zone metadata cache
To clear the landing zone metadata cache and refresh the mappings on the next reading of the
metadata:
1. Click the Manage button at the bottom left of the Storage Zone panel.
2. Click the Clear Landing Cache button in the Manage Storage Tasks window.
See also the section describing how to clear the cache before discover.
Clearing the storage zone metadata cache
To clear the storage zone metadata cache:
1. In the Storage Zone panel, select the Clear Metadata Cache item from the menu in the top
right corner.
2. Click Yes to clear the storage zone metadata.
3. When the storage zone metadata cache has been successfully cleared, click Close.
Clearing the metadata cache using the CLI
You can also clear the metadata cache using the CLI.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
361

6 Data Lake projects
Command syntax:
ComposeCli.exe clear_cache --project
project_name
[--type landing|storage] [--landing_zone
source_name]
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--type Which type of metadata cache to clear. Possible values are:
l
landing
l
storage
If --type
landing
and you want to clear a specific landing
zone, you must set the --landing_zone parameter as well. To
clear the metadata cache in all landing zones, specify --type
landing
and omit the --landing_zone parameter.
--landing_zone the name of the landing zone when --type landing_zone
Example
ComposeCli.exe clear_cache --project MyProject --type landing --landing_zone MySource1
Viewing and exporting task statements
You can view the task statements that were run during the Storage Zone task. You can also export
the task statements to a TSV file for reviewing and sharing.
To view the task statements :
Click the Task Statements toolbar button.
The Task Statements - <
Source_Landing_Zone_Name
> window opens in List View. The
Description column provides a description of each operation that was performed on the target
tables. Each operation has a different process number (displayed in the Process Number column).
For additional details about an operation, double-click the operation.
-OR-
Click the Item View button and navigate through the statements using the navigation buttons at
the bottom of the Task Statements - <
Source_Landing_Zone_Name
> window.
To jump to a specific statement, type the statement's number in the Go To field at the
bottom of the window and then press [Enter].
To export the task statements to a TSV file:
In List View, click the Export to TSV File button located to the left of the search field.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
362

6 Data Lake projects
A file named "<name>_Task_Instructions.tsv" will be saved to your default "Downloads" location or
you will be prompted to save it (according to your browser settings).
To hide non-SQL steps from the display, select the Filter non-SQL steps check box
Modifying task settings
For each task, you can modify the settings according to your needs.
To modify task settings:
1. In the Manage Storage Tasks window, select a task in the left pane and then click Settings.
The Setting - <Task_Name> window opens.
2. In the General tab, you can change the logging granularity. In the Log level drop-down list,
the following options are available:
l
INFO (default) - Logs informational messages that highlight the progress of the task at
a coarse-grained level.
l
DEBUG - Logs fine-grained informational events that can be used to debug the task.
l
TRACE - Logs finer-grained informational events than the DEBUG level.
Note that the log levels DEBUG and TRACE impact performance. You should only
select them for troubleshooting if advised by Qlik Support.
3. In the Advanced tab, the following settings are available:
l
Sequential Processing: Select this option if you want all the Storage Zone processes
to run sequentially, even if they can be run in parallel. This may be useful for
debugging or profiling, but it may also affect performance.
l
Maximum number of database connections: Enter the maximum number of
database connections that Compose is allowed to open for the task. The default
number is 10.
l
JVM memory: Edit the memory for the java virtual machine (JVM) if you experience
performance issues. Xms is the minimum memory; Xmx is the maximum memory. The
JVM starts running with the Xms value and can use up to the Xmx value.
Only the following characters are supported (shown as a regular
expression):/^[-a-zA-Z0-9:]*$/
l
Position in default workflow: Select where you want the Storage Zone tasks to
appear in the default workflow. For more information on workflows, see
Workflows
(page 372)
.
4. To save your changes, click OK.
6.7 Creating and managing command tasks
Command tasks enable you to incorporate custom processes into your Compose workflow. This is
especially useful if you need to leverage external tools to transfer files, validate data, and so on. A
Command task can run any script or executable supported by the operating system including batch
files, Python scripts, PowerShell scripts, executables and so on.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
363

6 Data Lake projects
For security reasons, command tasks are blocked by default. To enable command tasks,
a Compose administrator needs to run the following commands in the Compose CLI:
ComposeCli.exe connect [--url connection-url]
Where --url connection-url is only required if the Compose Server is on a different
machine.
To enable task commands:
ComposeCli.exe allow_user_scripts --enable
To disable task commands:
ComposeCli.exe allow_user_scripts --disable
In this section:
l
Defining Command tasks (page 364)
l
Managing Command tasks (page 365)
l
Controlling and monitoring Command tasks (page 365)
Defining Command tasks
This section explains how to define a command task. You can define as many command tasks as
you need and execute them at different stages of a Compose workflow.
For security reasons, before you define a command task, make sure that the executable
or script file that you want to run resides in the following directory on the Compose
server machine:
PRODUCT_DIR\data\projects\YOUR_PROJECT\scripts
To define a command task:
1. From the project drop-down menu, select Manage Command Tasks.
The Manage Command Tasks window opens.
2. Provide a name for the task.
Task names cannot contain the following characters: /\,&#%$@=^*+"'`~?<>:;[]{}
as well as all non-printable characters (below 0x20). The task name can contain a
single dot, but it cannot be the first or last character.
3. Optionally, enter a description.
4. In the Script/Executable File field, specify the name of the files that you want to run.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
364

6 Data Lake projects
5. In the Parameters field, specify any parameters required by the command. Parameters
should be separated by a space.
6. The user context is the user account under which the Task will run. To change the current
user context, provide the User, Password and Domain of the account under which you want
the Task to run.
7. Click Save to save your changes or Discard to discard any unsaved changes.
The task will be added to the list of tasks in the left of the window.
Managing Command tasks
The table below describes the task management options.
To Do This
Edit a
task
Select the task in the tasks list in the left of the Manage Command Tasks window
and edit it as described in
Defining Command tasks (page 364)
.
Delete a
task
Select the task in the tasks list in the left of the Manage Command Tasks window
and then click the Delete toolbar button. When prompted to confirm the deletion,
click OK.
Search
for a task
Enter part of the task name in the search box above the task list. The list of tasks will
be filtered to show only tasks that include the search term in their name.
Controlling and monitoring Command tasks
Command Tasks can be run from the Manage Command Tasks window or from the main Compose
Monitor view. Although they can be run individually, command tasks are usually run as part of a
workflow.
For information on defining workflows, controlling and monitoring tasks, and controlling and
monitoring workflows, see
Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows (page 365)
.
To run a command task from the Manage Command Tasks window:
1. Open the Manage Command Tasks window and select the task you want to run.
2. Click the Run toolbar button.
3. The Manage Command Tasks window switches to Monitor view.
In Monitor view the following information is available:
l
The task ID
l
The current status
l
When the task started and ended
l
The overall task progress
6.8 Controlling and monitoring tasks and workflows
The Compose monitor shows the current status of all your tasks and enables you to drill-down for
additional information about each task. Task instances can be run immediately or scheduled to run
in the future (either once or at set intervals).
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
365

6 Data Lake projects
In this section:
l
Viewing information in the monitor (page 366)
l
Running and controlling tasks (page 368)
l
Notifications (page 370)
l
Workflows (page 372)
l
Monitoring and controlling Replicate tasks (page 376)
Viewing information in the monitor
As well as providing a high-level summary of all your tasks, the monitor also lets you view more
detailed information about specific tasks.
To switch to monitor view:
1. Open a Compose project and click the Monitor icon in the top right of the console.
A list of tasks is displayed for the current project. The left pane of the monitor allows you to
filter the task list by status as well as indicating the current number of running, failed and
completed tasks.
For each task, the monitor displays the following information:
l
Status - Running, Completed, Failed or Aborted.
l
Task - The task name.
Type - The following task types are available:
l
Storage Full Load - Moves the data in its entirety from the Landing Zone to the Storage
Zone.
l
Storage Change Processing - Moves changes to the data from the Landing Zone to
the Storage Zone.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
366

6 Data Lake projects
l
Workflow - Executes several tasks in succession. See also
Adding and designing
workflows (page 372)
.
l
Command - For information about Command Tasks, see
Creating and managing
command tasks (page 363)
l
Replicate - The Qlik Replicate task that moves the data from the source database to
the Landing Zone.
l
Started and Ended - The date and time the task started and completed (according to
the server time). If the task is running, the Ended column will display the current
progress. In the case of a Replicate task performing Change Processing, Running CDC
will be displayed.
l
Next Instance - The next time the task is due to run (if the task is scheduled).
l
Elapsed Time - The time it took for the task to complete or - if the task is still running -
how long the task has been running.
l
Updated Tables - The number of tables updated in the Storage Zone.
l
Scheduled - Whether the task has been scheduled. "N/A" indicates that the task has
never been scheduled whereas a check box indicates that the task has been
scheduled. Clear the check box to disable the scheduling.
2. To view additional information about a task, select the task. The information is displayed in
the following tabs in the lower pane of the monitor:
l
Details - The Details tab shows the following status bars:
l
Completed - Shows the tables that have already been loaded into Hive.
l
Loading - Shows the tables currently being loaded into Hive.
l
Queued - Shows the tables waiting to be loaded into Hive.
l
Error - Shows the tables that could not be loaded into Hive due to error. Click
the Show Details link below the bar to see more information about the
statement(s) that resulted in the error.
To see more information about tables in a particular status, click the status bar. A list
of tables in the selected status will be shown.
You can also click the Task Commands button for more information about the
operations performed during the task.
l
Progress Status - The Progress Status tab shows the task’s current progress as well
as the sub-status (Waiting/Standby, Running, Failed, etc.) of operations within the
task. To see details about a specific operations, click the number to the right of the
operation status.
For example, to view more information about an operation with an error status, click
the number to the right of the Failed bar.
l
History - The History tab provides a list of previous task instances.
To view a task instance’s log file, select the task and click the View Log button.
To view more details about a task instance, either double-click the instance or select
the instance and then click the View Instance Details button. The Details tab is
shown.
3. To run a task immediately, select the task and then click the Run toolbar button.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
367

6 Data Lake projects
4. To view and manage a task’s settings, select the task and then click the Open toolbar button.
For more information about the settings, see the relevant topic in this guide.
Running and controlling tasks
You can run and stop tasks/workflow manually or you can schedule them using the scheduling
options described in
Scheduling tasks (page 368)
.
Running and aborting tasks manually
You can run tasks manually and abort them if required.
To run a task manually:
l
Select the task and click the Run toolbar button.
To abort a task:
l
Select the task and click the Abort toolbar button.
The task process is aborted. Note that aborting a task may leave the Storage Zone or data
mart tables in an inconsistent state. Consistency will be restored the next time the task is
run.
Scheduling tasks
Scheduling tasks is a convenient way of continually updating the Storage Zone and associated data
mart(s). For instance, you could schedule a data warehouse task to run at 4:00 pm and then
schedule a data mart task to run at 5:00 pm.
Note that as Compose does not provide a task-chaining option (i.e. run another task as soon as the
current task completes), it may be better to schedule tasks using an external tool that supports this
capability.
You can also use the command line interface (CLI) to run a task. For details, see
Running tasks using
the CLI (page 369)
.
To schedule a task:
1. Click the Schedule toolbar button.
2. In the <Name> Scheduler window, choose one of the following options from the Run Job
drop-down list.
l
Once - to run the job once on a specific date and time.
l
Every - to run the job at set intervals.
l
Daily - to run the job every day at a specific time.
l
Weekly - to run the job on selected days at a specific time
l
Monthly - to run the job on the
n
th of every month at a specific time
l
Advanced - to use a Cron expression. For a description of allowed cron formats
together with usage examples, see
Cron format and examples (page 405)
.
3. Set the scheduling parameters according to the selected scheduling option.
4. Click OK to save your settings.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
368

6 Data Lake projects
The date and time the next instance is scheduled to run will appear in the Next Instance
column.
5. To disable a scheduled job, select the task and click the Edit Scheduling toolbar button.
Then, select the Disable check box in the <Name> Scheduler window.
6. To cancel a scheduled job for a task, select the task and click the Edit Scheduling toolbar
button. Then, in the <Name> Scheduler window, click Delete.
Running tasks using the CLI
You can also run tasks using the CLI. This is especially useful if you wish to run Compose tasks from
external schedulers such as HP OpenView or Control-M. Before you can run a task, you must first
run the Connect command as described in
Connecting to Qlik Compose server (page 77)
.
As Compose CLI requires Administrator permission, make sure to select "Run as
administrator" when opening the command prompt.
The run_task command populates the Storage Zone with data. The task can also be run using the
Run toolbar button located in Monitor view as well as in the Manage Task window.
When this command succeeds, it returns 0.
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe run_task --project
project_name
--type
storage|workflow
--task
task_name
--wait
timeout_in_sec
Parameters
Parameter Description
--project The name of the project.
--type The type of task that you want to run you want to run.
l
storage - data storage task.
l
workflow - workflow task.
--task The name of the task that you want to run.
--wait The wait time specified in seconds.
The command line can run in sync or async mode. A value of 0
(seconds) indicates sync mode. This means that as soon as the
task finishes, the command line returns to prompt. The default
mode is async, with a value of -1. This is also applied if you leave
this parameter empty. Other negative values are not permitted.
Note that if wait is excluded from the command, the task may
appear to complete successfully even if it encountered an error.
Example
ComposeCli.exe run_task --project MyProject --type workflow --task DL1 --wait 1
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
369

6 Data Lake projects
Notifications
You can select events, on the occurrence of which, a notification will be sent to the specified
recipients.
Notifications will not be sent unless the
mail server settings
are correctly defined.
Setting notifications
To set a notification rule:
1. Switch to Monitor view.
2. Click the Notifications toolbar button.
The Notification Rules window opens.
3. Click the New toolbar button.
The New Notification wizard opens.
4. In the Events screen:
l
Specify a name for the notification
l
Choose for which type of events you want the notification to be sent, both at the task
level and at the workflow level.
5. Click Next. In the Recipients screen:
l
Select Windows Event to send the notification to Windows Event Log and/or
Recipients to send the notification to a list of email recipients.
See also:
Notifications (page 370)
.
l
If you selected Recipients, enter the recipient email addresses in the To, Cc (optional)
and Bcc (optional) boxes. Multiple addresses must be separated by a semi-colon.
6. Click Next. In the Message screen, optionally, edit the default notification message. You can
add variables to the message by selecting the variable on the right and then clicking the
arrow to the left of the variables list.
The following variables are available:
Variable Description
${PROJECT} The name of the Compose project in which the event
occurred.
${TASK_NAME} The name of the task in which the event occurred.
${INSERTED} The number of rows inserted in the Storage Zone.
${UPDATED} The number of rows updated in the Storage Zone.
${DELETED} The number of rows deleted from the Storage Zone.
${ERROR_CODE} The error code if an error was encountered during the
task.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
370

6 Data Lake projects
Variable Description
${ERROR_DETAILS} The error message if an error was encountered during the
task.
${EVENT_TYPE} The event type (Started, Error or Completed).
${EVENT_TYPE_
DESCRIPTION}
${EVENT_TIME} The date and time the event occurred.
${LINK} A link to the relevant Compose project.
7. Click Next. In the Apply to screen, select whether to apply the rule to all tasks of to selected
tasks. If you chose Selected Tasks, select which tasks to apply the rule to.
8. Click Next to see a summary of the notification settings or Finish to save your settings and
exit the wizard.
9. If you clicked Next, review your settings and then click Finish to save the notification rule
and exit the wizard or Prev to edit your settings. You can also click the headings on the right
of the wizard to go directly to a specific window.
The notification will be added to the list of notifications in the Notification Rules window.
Managing notification rules
In the Notification Rules window, you can edit, delete and enable/disable notification rules as
described in the table below.
To Do This
Delete a
Rule
Select the rule and then click the Delete toolbar button. When prompted to confirm
the deletion, click Yes.
Edit a
Rule
Either double-click the rule you want to edit or select the rule and click the Edit
toolbar button. Continue from
Notifications (page 370)
.
Disable a
Rule
Select the rule you want to disable and then either click the Disable toolbar button or
clear the check box in the Enabled column.
Enable a
Rule
Select the rule you want to enable and then click the Enable toolbar button or select
the check box in the Enabled column.
Event IDs in Windows Event Log
The table below lists the Event IDs for Compose events in Windows Event Log.
If a notification is set for several events, the event ID will be 0 for each of the events.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
371

6 Data Lake projects
Event ID Description
261 The task ended with error
400 The task has started.
406 The task completed successfully.
Windows Event Log IDs
Workflows
Workflows enable you to run tasks both sequentially and in parallel. You can either schedule
workflows as described in
Scheduling tasks (page 368)
or run them manually using the Run toolbar
button or Compose CLI.
You can create your own workflow and/or use the built-in workflow. The built-in workflow enables
you to run all of your tasks as a single, end-to-end process. The built-in workflow appears in the
Type column as "Default Workflow".
When you create your
own
workflow, you decide which tasks to include in the workflow and the
order in which they will be run.
In this section:
l
Adding and designing workflows (page 372)
l
Validating workflows (page 375)
l
Managing workflows (page 375)
l
Running and monitoring workflows (page 376)
Adding and designing workflows
This section provides instructions for adding and creating workflows.
Adding a workflow
To add a workflow:
1. Switch to Monitor view by clicking the Monitor button in the top right of the Compose
console.
2. Click the New Workflow toolbar button.
The New Workflow window opens.
3. To create a workflow with all current tasks, select Create default workflow and then click
OK. Otherwise, continue from Step 4 below. Separate workflows will be created for Full Load
and Change Processing tasks. The default workflow cannot be edited and will appear as
Default Workflow in the list of monitored tasks.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
372

6 Data Lake projects
Any tasks you create after adding the default workflow will not be automatically
included in the default workflow. If you want to create a default workflow that
includes newly added tasks, simply delete the existing default workflow and
create another one in its place.
4. Specify a name for your workflow.
5. To create a workflow based on an existing workflow, select the Duplicate from check box
and then select an existing workflow from the drop-down list.
6. Click OK to save your settings.
The <workflow_name> window opens.
7. Continue from Designing a workflow below.
Designing a workflow
The workflow window is divided into two panes. The pane on the left (hereafter referred to as the
Elements pane) is where you design your workflow and contains two default elements: Start and
End.
The Elements pane contains gateways and tasks that you can use in your workflow. The following
elements are available:
l
Tasks - All existing Data Warehouse tasks, Data Mart tasks, and Command tasks.
l
Gateways - There are two types of gateway: Parallel Split and Synchronize. Use the
Parallel Split gateway to create parallel paths. This is useful, for example, if you want two or
more tasks to run in parallel.
Use the Synchronize gateway to merge parallel paths. The workflow waits for all the Tasks
that precede the gateway to complete before continuing the flow.
To design a workflow:
1. Drag the desired workflow elements from the Elements pane to the pane on the left.
2. Arrange the elements in the order that you want them to run.
3. Connect the elements to each other by dragging the connector from the gray dot (that
appears on the right of an element when you hover the mouse cursor over it) to the target
element. When a blue outline appear around the target element, release the mouse button.
4. Optionally add error paths to the workflow. The workflow will follow the error path if a task
encounters an error. For example, if an error occurs with one task, you may want to run
another task in its place.
To add an error path, hover your mouse cursor over the task element. A red dot will appears
below the element. Drag the connector from the red dot to the target element, as shown
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
373

6 Data Lake projects
below.
Connecting two error paths to the same task should be avoided as the workflow will fail
if the task tries to run twice.
Continuing a workflow in the event of parallel task failure
In a workflow, all task elements have an error port. This allows you to change the course of the
workflow in the event of a task failure, as described in Step
Adding and designing workflows (page
372)
above. Similar to Task elements, the Synchronize gateway also has an error port which can be
used to reroute the workflow if any of the tasks between the Parallel Split and Synchronize
gateways should fail.
By default, a workflow will end with an error if one or more parallel tasks do not complete
successfully. However, in certain cases you may want the workflow to continue, even if one or more
of the parallel tasks failed.
To do this, you need to connect the error port of the relevant task(s) directly to the Synchronize
gateway. You can also design the workflow so that it follows the path leading from the Synchronize
error port, instead of continuing its normal flow.
In the example below, the error port of the MyCommandTask is connected to the Synchronize
gateway, meaning that even if MyCommandTask task fails, the workflow will continue. However, if
the MyCommandTask task fails, the workflow will not proceed directly to the End element. Instead,
it will follow the Synchronize gateway’s error path to the Source task.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
374

6 Data Lake projects
Validating workflows
It is strongly recommended to validate your workflow before running it. This will prevent errors from
occurring during runtime due to an invalid workflow.
Workflow rules include:
l
All elements must be connected to each other
l
A workflow must contain Start and End elements and at least one task.
l
A workflow cannot contain a Parallel Split gateway without a Synchronize gateway and vice
versa.
l
Storage Zone tasks that update the same tables cannot run in parallel.
l
A workflow cannot contain a Parallel Split gateway without a Synchronize gateway and vice
versa.
l
The execution order of elements must be sequential and not cyclic. For example an element
cannot loop back to an element that precedes it the execution order.
To validate your workflow:
l
Click the Validate Flow toolbar button.
If the workflow is valid, a "<workflow_name> is valid." message will be appear at the top of the
window. If the workflow is not valid, a message describing the problems will appear instead.
Managing workflows
The table below describes the options available for managing workflows.
To Do This
Delete a
Workflow
In Monitor view, select the workflow in the Task column and then click the
Delete Workflow toolbar button.
Edit a
Workflow
In Monitor view, either double-click the workflow you want to edit or select the
workflow and click the Open toolbar button. Continue from
Adding and
designing workflows (page 372)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
375

6 Data Lake projects
To Do This
Delete an
element in
workflow
Either right-click the element and select Delete or select the element and then
click the Delete toolbar button.
Reset the
workflow view
Click the reset button to the right of the slider at the top of the window.
Zoom in
to/zoom out of
the workflow
Move the slider at the top of the window to the left or right as required.
Running and monitoring workflows
You can either schedule workflows as described in
Scheduling tasks (page 368)
or run them
manually using the Run toolbar button. The Run toolbar button appears both in the main Monitor
view and in the workflow design window. Note that when you run a workflow from the workflow
design window, a new Monitor tab is added to the window and the view automatically switches to
the Monitor tab.
You can monitor the workflow either in the Monitor tab or in the Progress Status tab. During
runtime, the workflow elements fill with blue providing a graphic indication of progress. If a task
encounters an error, the task element will appear with red fill instead of blue.
Monitoring and controlling Replicate tasks
Before you can create a Compose project, you need to define a Replicate task that replicates the
relevant source tables from the source database to the Landing Zone. You can define a different
task for each project or the same task can serve several projects. You can also define multiple tasks
for a single project. The tasks can either reside on the same Replicate server or on several Replicate
servers distributed throughout your organization.
Monitoring and controlling Replicate tasks from within Compose involves the following steps:
l
Step 1: Configure Qlik Compose to connect to the Qlik Replicate machine(s) as described in
Replicate Server settings (page 382)
.
l
Step 2: Add the Replicate task name to the source Landing Zone settings as described in
Defining Landing Zones connections (page 324)
.
l
Step 3: Monitor and control the Replicate task as described below.
The image
Replicate Task in the Compose Monitor (page 377)
shows how the Replicate task
appears in the Compose Monitor. You can stop and start the Replicate task using the Abort and
Run toolbar buttons.
If a task is stopped from within Replicate, the task status in Compose for Data Lakes will
be "Completed" instead of "Aborted".
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
376

6 Data Lake projects
You can also define notifications for the task and add the task to a workflow. For more information,
see
Notifications (page 370)
and
Workflows (page 372)
respectively.
The monitor provides various information about the task. For details, see
Viewing information in the
monitor (page 366)
.
Replicate Task in the Compose Monitor
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
377

7 Managing Compose
7 Managing Compose
Qlik Compose management options can be accessed from the Management menu located at the
top of the Compose main page.
In this section:
l
License settings (page 378)
l
Logging settings (page 379)
l
Mail server settings (page 382)
l
Running tasks on a remote Compose server (page 382)
l
Replicate Server settings (page 382)
l
User permissions (page 384)
l
Audit trails (page 392)
7.1 License settings
You need to register a valid license in order to use Qlik Compose. The license file contains details
such as the product expiration date, the date the license was issued, which source databases can
be used, and so on.
License enforcement
The license is enforced only when trying to generate, run, or schedule a task (via the web console
or API ). Other operations such as Test Connection may also fail if you do not have an appropriate
license.
Registering a license
This section describes how to register your Compose license. You can register the license either
using the console or using a command line.
To register a license using the console:
1. Copy the license file to the computer on which Compose is installed or to any computer in
your network that can be accessed from the Compose computer.
2. Click Load and browse to find and select the license file. The license text is displayed in the
window. Check to be sure that the details are correct.
3. Click Register License to register the license. A message indicating the license was
registered successfully is displayed.
To register a license using the command line:
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe register_license --infile|license_text
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
378

7 Managing Compose
Parameters
Parameter Description
--infile The full path to the Qlik Compose license file.
--license_text A string in JSON format. When specifying a JSON string, any quote
symbols should be escaped using a backslash (\).
Example
Register a license with --infile:
ComposeCli.exe register_license --infile c:\Admin\Temp\lic.txt
Register a license with --license_text:
ComposeCli.exe register_license --license_text "{ \"$type\": \"ComposeLicense\", \"product\":
\"Compose\", \"issued_to\": \"qa\", \"issued_by\": \"Qlik\", 07-21\", \"hosts\": \"\",
\"product_version\": \"2.8\", \"notes\": \"\", \"host_role\": \"\", \"source_db_types\": \"\",
\"dwh_type\": \"\", \"number_of_dms\": \"0\", \"managed_dwh_size\": \"0\",
LcVLPfXvD4wY5ZyUYlasdjtOvQd1Hwk5UzT7xe5+pqhZtB1dfUUyl50+7zKju7vm1kkPnz3I+L5LbLm3FpvqxIxOFrj2LQ
Bk1LoUxMN+v06vI+w5aMSGQw6fttUgbYohFCIOduk8=\"}"
7.2 Viewing a license
You can view the license information in the Qlik Compose Console at any time.
To view the license information:
1. From the Management menu, select License|View License.
2. The License window opens. All of the license information is displayed in the License window.
7.3 Logging settings
You can set the server logging level, configure automatic roll over and cleanup, and view and
download log files.
Setting the logging level
The logging level determines what type of information is written to the log files. The log files provide
information about Qlik Compose Server and Qlik Compose Agent processes.
The following logging levels are available (ordered from the lowest level to the highest level):
1. Errors
2. Warnings
3. Info
4. Trace
5. Verbose
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
379

7 Managing Compose
The higher levels always include the messages from the lower levels. Therefore, if you select Error,
only error messages are written to the log files. However, if you select Info, informational
messages, warnings, and error messages will be included. Selecting Verbose writes all possible
messages to the log.
To set the server logging level:
1. From the Management menu, select Logs|Log Management. The Log Management
window opens displaying the Server Log tab.
2. To set a global logging level, move the top slider to the desired logging level. All of the sliders
for the individual modules move to the same level that you set in the main slider.
3. To set a logging level for individual Compose components, select a module and then move its
slider to the desired logging level.
4. Click OK to save your changes and close the Log Management window.
To set the Qlik Compose Agent level:
1. From the Management menu, select Logs|Log Management. The Log Management
window opens displaying the Server Log tab.
2. Select the Qlik Compose Agent log tab, and then move the slider to the desired logging
level.
3. Click OK to save your changes and close the Log Management window.
Changes to the logging level take place immediately. There is no need to restart the Qlik
Compose service.
Setting automatic roll over and cleanup
You can define when log files should be automatically rolled over as well as how many log files to
keep. Rolling over log files keeps any single log file from becoming too large and provides an easy
way to identify files that are no longer being used so that an automated script can clean the logging
directory. Automatic deletion of old log files ensures that the logs do not take up too much disk
space when there is a lot of activity in the system.
To set the log file roll over and cleanup options:
1. From the Management menu, select Logs|Log Management. The Log Management
window opens.
2. Select the Log Settings tab.
3. The following options are available:
l
Enable automatic roll over: Select this check box to determine the maximum size a
log file can reach before it is rolled over. The current log file is called Compose.log and
saved (older) log files are called Compose_xxxxxxxxxxxx.log where xxxxxxxxxxxx
represents a 12-digit timestamp.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
380

7 Managing Compose
l
Roll over the log if the log file is larger than (MB): Use the counter or type in
the maximum amount of megabytes for a specific log file. When the log file
reaches the specified size, the old log is saved with a timestamp appended to
its name and a new log file is started. The default value is 10 megabytes.
The scheduled job that checks the log size runs every five minutes.
Consequently, the actual size of the log when rolled over might be larger
than specified.
l
Enable automatic cleanup: Select this check box to define the maximum number of
log files to keep.
l
Maximum number of log files to keep: Use the counter or type in the
maximum number of log files to keep. When the number of log files reaches the
specified maximum, Compose will delete the oldest log file whenever a new log
file is created, thereby ensuring the number of log files never exceeds the set
limit. The default is 45.
4. Click OK to save your settings and close the Log Management window.
Viewing and downloading Compose log files
This section explains how to view and download Compose log files.
The logs are in four different locations:
l
<product_dir>\data\logs – Server log file
l
<product_dir>\java\data\logs – Compose Agent log file
l
<product_dir>\data\projects\<project_name>\logs – project logs , workflow logs,
and command task logs
To view Compose log files:
1. From the Management menu, select Logs|View Logs. The Log File Viewer opens.
2. Select the log file you want to view from the list in the Log Files pane.
The contents of the log file will be displayed in the right pane. When you select a row in the
log file, a tooltip will display the full message of the selected row.
3. Browse through the log file using the scroll bar on the right and the navigation buttons at the
top of the window.
4. To search for a specific string in the log file, enter the search string in the search box at the
top of the window. Any terms that match the specified string will be highlighted blue.
To download Compose log files:
1. From the Management menu, select Logs|View Logs. The Log File Viewer opens.
2. From the list in the Log Files pane, select the log file you want to download.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
381

7 Managing Compose
3. Click the Download Log File button in the top right of the window. The log file is
downloaded.
7.4 Mail server settings
The mail parameters define the mail server used to send notifications.
To configure the mail server settings:
1. From the Management menu, select Mail Server Settings. The Mail Settings window
opens.
2. Configure the settings as follows:
l
Mail server: Specify the outgoing mail server that will be used to send Qlik Compose
notifications, for example, smtp.example.com.
l
Port: Enter the mail server port number. The default value is 25.
l
Use secure email (SMTPS): Select this to connect to the mail server using TLS.
l
Anonymous login: Enable this to allow Qlik Compose to access the mail server
without having to provide any user credentials.
l
User name: Specify the user name for the account that will be used to send
notifications.
l
Password: Specify the password for the account that will be used to send
notifications.
l
Sender email address: Enter the email address that sends the email notifications. This
is the address that appears in the From field of the email notification.
l
Send Test Mail: You this option to validate your mail server settings. Click Send Test
Mail to open the Send Test Email window. In the Email address for test email, enter
the email address to which you want the test email to be sent and then click Send.
3. Click OK to save your settings and close the Mail Settings window.
7.5 Running tasks on a remote Compose server
You can run Compose tasks either locally (the default) or on a remote Compose server.
To run tasks on a remote server:
1. From the Management menu in the projects view, select Compose Agent Settings.
2. In the Compose Agent Settings window, select Remote server and provide the required
connection details.
3. Click OK to save your settings.
7.6 Replicate Server settings
Before you can create a Compose project, you need to define at least one Replicate task that
replicates the relevant source tables from the source database to the Landing Zone.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
382

7 Managing Compose
If you want to monitor the Replicate tasks, you need to provide the information that Compose needs
in order to establish a connection to the Replicate Server on which the tasks are running. After
providing this information, you will then be able to associate a source Landing Zone with a specific
Replicate task.
To configure the Replicate Server connection settings:
1. Open the Manage Replicate Servers window using any of the following methods:
l
From the Management drop-down menu in the main toolbar, select Manage
Replicate Servers.
l
In the New Data Source window, click the Replicate Server Settings link below the
Associate with Replicate task field.
The Manage Replicate Servers window opens.
2. Click Add Replicate Server.
The Add Server window opens.
3. Enter the following information:
l
Name: A display name for the server.
l
Description: (Optional) A description for the server.
l
Host: The IP address or host name of the Qlik Replicate machine.
When Replicate Server is installed on Linux, enter the IP address of the
Windows machine on which the Replicate UI Server is running.
l
Port: Optionally, change the default port (443). You should only change the default
port if you are certain that a different SSL port is being used.
l
User Name and Password: Your credentials for logging in to the Qlik Replicate
machine.
When Replicate Server is installed on Linux, enter the user name and
password for the Windows machine on which the Replicate UI Server is
running.
l
Get metadata timeout - The time to wait when discovering a task’s source database
or refreshing the metadata cache before returning a timeout error.
l
Get task timeout - The time to wait when starting a Replicate task before returning a
timeout error.
In environments with complex networks, operations related to Replicate
may exceed the default timeout limit. If you experience frequent timeouts
starting tasks, discovering a task’s source database, or refreshing the
metadata cache, increasing these values may help.
4. Click Test Connection and then click OK if the connection is successfully verified.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
383

7 Managing Compose
The server is added to the Manage Replicate Servers window. Click Close to close the
window.
7.7 User permissions
Security roles allow you to grant Qlik Compose users different roles according to the tasks you
want them to perform. Qlik Compose comes with the following predefined security roles: Admin,
Designer, Operator and Viewer. Each role has its own set of permissions, as described in
Default
user permissions according to role (page 384)
.
You can associate a user with a security role by adding the user to the appropriate Active Directory
group or by assigning a role directly to the user. By default, the user under whose account you
install Qlik Compose is an Admin. You can also fine-tune access control per user or group. For more
information, see
Granular access control (page 386)
As a user with the relevant permissions, you can view and change the permissions for existing users
or groups, or add users or groups that do not yet exist in Qlik Compose.
The advantage of adding groups over users is that you can assign a security role to a group as a
whole, instead of to individual users, and any new user that is added to an existing group
automatically acquires the security role granted to that group.
To set user permissions using Active Directory groups, you can either create Active Directory
groups with the names listed in the table below, or you can create Active Directory groups with
different names. Then, add users to the groups according to the role you want them to perform.
If you create your own Active Directory groups, you need to add them to the User Permissions tab
in the Settings window and set their permissions as described in
Managing user permissions (page
389)
.
Role Active Directory Group
Administrator QlikComposeAdmins
Designer QlikComposeDesigners
Operator QlikComposeOperators
Viewer QlikComposeViewers
Predefined user permission roles
Default user permissions according to role
In the Qlik Compose Console, the menus, buttons, and options can be accessed only by users who
have the relevant permissions. For example:
l
The Project view is available to all roles, but Designers only have read-access to user
permissions, and operators cannot add projects – they can only view the different settings
but not edit them. Viewers cannot edit settings, add, edit, or delete a project, or register a
license.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
384

7 Managing Compose
l
The Model view for the Data Warehouse is available to all roles, but only Designers can
create and manage the model, import entities and mappings from other projects (including
models created in ERwin), manage global mappings, validate, define reusable
transformations, add Date and Time entities for the model, and so on.
The following table lists the permissions granted to each of the predefined security roles:
Permission Admin Designer Operator Viewer
Projects:View projects and logs, generate
documentation
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Projects: Define and manage command
tasks
Yes Yes Yes No
Projects:Create, design, reset, define
settings for, control versions, commit,
revert, delete, create deployment package
Yes Yes No No
View databases and model Yes Yes Yes Yes
Model: Add, edit, delete, discover, import
from other tools (e.g. ERwin), validate
Yes Yes No No
Data Warehouse: View data and logs, tasks,
commands and mapping
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Data Warehouse: Create, edit, delete source
and target Data Warehouse databases
Yes Yes No No
Data Warehouse: Manage settings, populate
tasks, cleaning and validation rules
Yes Yes No No
Data marts: View details and logs Yes Yes Yes Yes
Populate data marts Yes Yes Yes No
Data marts: Create, edit, delete, edit
expressions and filters, import and add
dimensions, generate tasks
Yes Yes No No
Monitor tasks (in Monitor view) Yes Yes Yes Yes
Workflow operations: Create, edit, populate,
notification rules, run Replicate and
command tasks
Yes Yes Yes No
Perform runtime operations such as starting
and aborting tasks.
Yes Yes Yes No
Define table creation modifiers Yes Yes No No
Permission access properties
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
385

7 Managing Compose
Permission Admin Designer Operator Viewer
Manage Compose (e.g. license registration,
email settings, and so on)
Applies only if the user is an
Admin at the Compose level.
Yes No No No
Granular access control
For each user, Qlik Compose lets you set granular access permissions for different hierarchy levels
in the system and for different objects at the same hierarchy level. This granular access control
facilitates the decentralization of control, effectively preventing the same user from, for example,
designing the model and managing the mappings. As such, granular access control lets you create
a buffer between those who can create and design models and those who can create and run the
mappings.
Qlik Compose handles permission management as follows:
l
Admins can add, remove, and change permissions.
l
Designers and Operators can view permissions.
l
Viewers cannot view permissions.
By default, each object inherits its permissions from its parent.
User permissions can be assigned to individual Data Warehouse projects as well as across all
projects. The following hierarchy is in place, whereby:
l
Compose User Permissions are applied globally. Changes to Compose permissions will
affect any level that inherits those permissions. At Compose root level, users must have at
least Viewer permissions.
Only Admin users at the Compose level can perform logging actions, such as,
changing the logging level and rolling over logs.
l
All Projects User Permissions apply to all projects. When inheritance is enabled (the default),
permissions will be inherited from the “Compose” root level.
A user that is assigned All Projects User Permissions but not Compose User
Permissions is not authorized to log in to Compose.
l
Project User Permissions apply to a specific project. When inheritance is enabled (the
default), permissions will be inherited from the “All Projects” level.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
386

7 Managing Compose
Supported with Data Warehouse projects only.
l
Model User Permissions apply to the model unless overridden at any of the lower levels.
When inheritance is enabled (the default), permissions will be inherited from the “Project”
level.
l
Not applicable to Data Lake projects
l
If user permissions are other than None at the Project level, in the Model
level the user must have at least Viewer permissions.
Inheritance and overrides
Group permission may contradict the permission that a particular user was granted. In this case, the
higher permission overrides the lower permission, as illustrated in the following figure:
Effective permissions are the permissions that take effect when a user is part of more than one
group, or when there is a conflict between the user's permission and the group's permission, or in
the hierarchy.
By default, the permission of a user or group object is inherited from the access control list (ACL)of
the object's parent. However, a lower or higher permission may override this permission. In this
case, the overriding higher permission is the effective permission for the object, stopping
inheritance from the parent. As a result, any changes to the parent no longer affect this user or
group.
In the User Permissions window, inheritance is indicated by a check mark in the Inherited column.
By default, inheritance is enabled for all users and groups on any level. Changing permissions by
using the slider automatically stops inheritance for the selected user or group. Qlik Compose also
lets you disable inheritance by disconnecting the entire authorization level from the parent level.
For information on how to do this, see
Managing user permissions (page 389)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
387

7 Managing Compose
Managing user and group roles using the Compose CLI
You can set and update user and group roles using the Compose CLI. You can also remove users
and groups from a role in one of the available scopes (for example, Admin in All Projects). This is
especially useful if you need to automate project deployment. Before you can use the CLI, you must
first run the Connect command as described in
Connecting to Qlik Compose server (page 77)
.
Adding or updating roles
You can add a new user or group and assign a role to that user/group, or you can update the role of
an existing user or group. If the specified user or group does not exist, they will be added to
Compose.
Syntax
composecli set_user_or_group_role --scope global|allprojects|project [--
project_name project-name] --role admin|designer|operator|viewer|none --user_
name netbios\user|--group_name netbios\group
Parameters
Parameter Description
scope The scope of the user or group: global, allprojects, or project.
role Required. The role that you want to assign the user or group: none, viewer,
operator, designer, or admin.
project_
name
The name of the project to assign the role on. Only required if --scope
project.
user_name The name of the user to add or update. Required if no group is specified.
Users must be specified in the following format:
NetBIOS-name\user
Example:
qa\mike
group_name The name of the group to add or update. Required if no user is specified.
Users must be specified in the following format:
NetBIOS-name\group
Example:
qa\admins
Example
composecli set_user_or_group_role --scope project --project_name myproject --
role admin --group_name qa\admins
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
388

7 Managing Compose
Revoking roles
You can revoke a user or group's role from a particular project, from all projects, or from Compose.
Syntax
composecli remove_user_or_group_role --scope global|allprojects|project [--
project_name project-name] --user_name netbios\user|--group_name
netbios\group
Parameters
Parameter Description
scope The scope of the user or group to remove: global, allprojects, or project.
project_
name
The name of the project to remove the user or group from. Only required if --
scope project.
user _name The name of the user to remove. Required if no group is specified.
Users must be specified in the following format:
NetBIOS-name\user
Example:
qa\mike
group_name The name of the group to remove. Required if no user is specified.
Users must be specified in the following format:
NetBIOS-name\group
Example:
qa\admins
Example
composecli remove_user_or_group_role --scope project --project_name myproject
--user_name qa\mike
Managing user permissions
This section explains how to access user permissions at different levels in the hierarchy, edit user
permissions, add and remove users or groups, disable or enable inheritance, restore inherited
permissions if they were overridden, and view effective permissions for a user.
By default, inheritance is enabled for all objects (users and groups). This means that permissions
are automatically carried over from the parent object. You can turn inheritance on or off for all
objects at the current level. Effective permissions are the permissions that are in effect for a user at
any particular level.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
389

7 Managing Compose
For more information on the underlying concepts, see
Granular access control (page 386)
and
Inheritance and overrides (page 387)
.
To access user permissions at the Compose level
l
In the Qlik Compose Console, from the Management menu, select User Permissions.
By default, the User Permissions window opens at Console root level, displaying the currently
assigned user role permissions for each defined user/group. These permissions apply globally
unless they are overridden at any of the lower levels.
Changes to Compose permissions will affect any level inheriting those permissions.
To access user permissions at the All Projects level
l
In the User Permissions window, select the All Projects tab.
The All Projects User Permissions window displays the currently assigned user role permissions
for each defined user/group. These permissions apply to all projects unless they are overridden at
any of the lower levels.
When inheritance is enabled, permissions will be inherited from the Compose root level.
To access user permissions for a specific project:
l
In the Qlik Compose Console, select the required project, and then select User Permissions
from the context menu.
The Project User Permissions window shows the user role permissions that apply to the specific
project '{project name}' for each defined user/group. These permissions apply to the specific
project unless overridden at any of the lower levels.
When inheritance is enabled, permissions will be inherited from the All Projects level.
To access user permissions for a Model:
l
In the User Permissions for project: '{project name}' window, click the Model tab. The
Model User Permissions windowshows the user role permissions that apply to the specific
project model for each defined user/group.
When inheritance is enabled, these permissions will be inherited from the Project
level.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
390

7 Managing Compose
To edit user permissions:
1. In the User Permissions window, adjust the permission slider for a user or group as required.
Adjusting the slider stops inheritance from the parent object.
2. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To add a user or group:
1. In the User Permissions window, click Add.
2. In the Add User/Group window, select User or Group.
3. Enter the name for the new user or group in the following format:
NetBIOS_name\user (for example:qa\qa)
4. Click OK to add the user/group and close the window.
5. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To remove a user or group:
1. In the User Permissions window, select the user or group you want to remove.
2. Click Remove.
3. When prompted, click Yes to confirm.
4. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To disable inheritance:
1. In the User Permissions window, click Disable Inheritance.
This option disconnects the entire authorization level from the parent level.
2. In the Disable Inheritance window, select whether you want to:
l
Convert inherited permissions on this object into explicit permissions: This option
changes inherited permissions to explicit permissions. Any new users or groups will
not inherit permissions from the parent.
l
Remove all inherited permissions from this object: This option removes all existing
permissions inherited from the parent level. Any new users or groups will not inherit
permissions from the parent.
3. Click Disable. If you chose to convert inherited permissions, the check mark in the Inherited
column changes into an X. If you chose to remove inherited permissions, all users and groups
disappear from the list.
4. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To enable inheritance:
1. In the User Permissions window, click Enable Inheritance.
This option enables inheritance for all users and groups on this level.
2. In the Enable Inheritance window, select whether you want to:
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
391

7 Managing Compose
l
Inherit all permissions from parent and override any definition manually made at
this level: This option reinstates inherited permissions for all users and groups that
are already defined, and new users and groups will inherit their permissions from the
parent level.
l
Inherit all permissions from parent but keep definitions manually made at this
level: This option preserves the permissions already defined for the existing users and
groups, and adds all permissions from the parent level. New users and groups will
inherit permissions from the parent level.
3. Click Enable.
4. Click Save or OK to accept the changes, or Discard Changes or Cancel to undo them.
To restore inherited permissions for a single user or group if they were overridden:
1. In the User Permissions window, select the user or group.
2.
Click Restore Inheritance . The check mark returns to the Inherited column to indicate
that permissions for this user or group are inherited from the parent.
To view effective permissions for a user:
1. In the User Permissions window, do one of the following:
l
Select a user in the list on the left.
l
If a user does not appear in the list but exists in the system and is part of a group, enter
the user name in the text field in the Effective Permissions pane on the right. Make
sure to use the following format:
NetBIOS_name\user (for example: qa\qa)
2. Click Get Effective Permissions. The effective permissions for the user you entered appear
below the button.
7.8 Audit trails
The information provided in an Audit Trail can be leveraged for user accountability, reconstruction
of events, intrusion detection, and other operational issues. As such, Audit Trails are an
indispensable tool for regulatory compliance (e.g. SOX).
For operations performed by users with Operator privileges or later, the Compose Audit Trail shows
which user performed the operation, when it was performed, and on which objects.
By default, Compose retains audit files for one week or until they reach a total size of 100 MB (10
files). You can change these settings through the command line interface (CLI) as described in
Exporting Audit Trail files (page 393)
below.
Audit Trail files are located in the following folder:
<Installation_Directory>\data\AuditTrail\audit_service
You can also export an audit trail file for a specific time range, as described in
Exporting Audit Trail
files (page 393)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
392

7 Managing Compose
Audit trail information
Audit Trail files provide all or some of the following information:
l
Timestamp - The time when the row was inserted into the Audit Trail.
l
User - The user that performed the operation.
l
Node - The IP of the server on which the operation was performed.
l
Requested Action - The API method/function that was called.
l
Required Permission - The minimum role of the user that can perform the operation.
l
Effective Permission - The actual role of the user that performed the operation.
l
Security Result - Whether the user is allowed to perform the operation.
l
Action Result - The completion status of the operation (success of failure).
l
Error Message - The error message if the operation failed.
l
Task - The name of the task where relevant.
l
Notification - The notification defined for the operation (if defined).
l
Payload - A URL. To view payload information, simply copy the link from the Payloadcolumn
and paste it into your browser's address bar.
Payloads for some operations (e.g. RegisterLicense) contain sensitive information and need
to be decoded. For information on decoding payloads, see
Decoding an encoded payload
(page 395)
.
l
Project Name - The name of the Compose project.
Audit Trail files are compressed and tamper-protected.
Exporting Audit Trail files
You can export an audit trail file with a record of activity for a specific time range. In Compose, there
are two way of doing this:.
l
Using the management console
l
Using the CLI
You can also export audit trails using the ExportAuditTrail API method. For further
information, see the Qlik Enterprise Manager Help and API Guide.
Exporting an Audit Trail file via the management console
You can use the Compose management console to export the audit trail as a CSV file.
To do this:
1. From the Management drop-down menu, select Audit Trail. The Audit Trail window opens.
2. From the Time Range drop-down list, select the desired time range. If you select Custom,
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
393

7 Managing Compose
set From and To values as well.
3. Click Generate.
Depending on your browser settings, you will either be prompted for a download location or the file
will be downloaded automatically to your preferred location.
Exporting an Audit Trail file via the CLI
You can use the Compose CLI to export the audit trail as a JSON file.
Run the following command from the Compose bin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCli.exe generate_audit_trail --start_timestamp
timestamp
[--end_timestamp
timestamp
] --
outfile
full_path
Parameters
Parameter Description
--start_timestamp The date and time from which you want the audit trail to start, in
UTC format.
--end_timestamp The date and time on which you want the audit trail to end, in UTC
format. When not specified, the file will end at the latest audit trail
record.
--outfile The full path to the output file. If the path contains spaces, it
should be enclosed in quotation marks.
Example
ComposeCli.exe generate_audit_trail --start_timestamp 2020-06-30T16:15:00Z --end_timestamp
2020-07-14T16:15:00Z --outfile "C:\compose audit trails\audit.json"
Configuring Audit Trail size and retention
Run the following command from the Composebin directory:
Command syntax
ComposeCtl.exe audit_trail_control --age
weeks
--size
megabytes
Parameters
Parameter Description
--age The number of weeks to retain the audit trail file (default 1 week).
--size The maximum size of the audit file to retain (default 100 MB).
Example
ComposeCtl.exe audit_trail_control --age 4 --size 1000
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
394

7 Managing Compose
Decoding an encoded payload
Some audit records (e.g. RegisterLicenses) may contain an encoded payload. Encoded payloads
are displayed as byte arrays and need to be decoded using Base64.
To decode an encoded stream payload:
1. Locate the payload URL in the audit record.
2. Copy the URL into your browser's address bar and press [Enter]. A byte array will be
displayed.
3. Copy the byte array into a Base64 decoder and decode it.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
395

8 Setting up Compose on a Windows HA cluster
8 Setting up Compose on a Windows HA
cluster
This section describes how to set up Compose in a Windows Server High Availability Cluster
environment. For instructions on how to set up a Windows clustering environment, refer to the
Microsoft Help.
When building failover cluster solutions with Compose using Windows Server Failover
Cluster (WSFC) or a Linux failover cluster software, Qlik recommends using a block
device (physical, virtual or iSCSI-based) for the shared Compose DATA folder. Using
NFS or SMB-based storage is not supported due to the associated latency which could
greatly degrade the data transfer performance, as well as due to reduced reliability and
compatibility issues. When building a cloud-based high availability solution that needs to
span different availability zones, it is recommended to use a Storage-as-a-Service
solution that can handle the block-level replication of the storage and that is integrated
with the chosen failover clustering software.
All commands described in this section must be run as administrator.
In this section:
l
Step 1: Installing Compose in the cluster (page 396)
l
Step 2: Adding the Compose service (page 398)
l
Step 3: Defining the service dependencies (page 398)
l
Step 4: Defining the URLfor the cluster (page 399)
l
Upgrading Compose on the cluster (page 400)
8.1 Step 1: Installing Compose in the cluster
This topic describes how to install Compose in a high availability cluster environment.
Preparation
Allocate two shared folders for Compose: one for the Compose server and the other for the
Compose agent
The setup instructions below assume that the Compose data folder is
F:\Compose-server-data
and
the Compose Agent data folder is
F:\Compose-agent-data
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
396

8 Setting up Compose on a Windows HA cluster
Primary node setup
1. Install Compose.
2. Generate a 32 character random master key by running the following command from
<PRODUCT_DIR>\bin:
ComposeCtl.exe utils genpassword
The setup instructions below assume that your key is
WdAHWEwXSvwxDFetcl7TVVFfSXPbMrFx
3. Stop the Compose service.
4. Edit the service executable path as follows:
SC CONFIG QlikCompose binPath= "<PRODUCT_DIR>\bin\ComposeCtl.exe -d
F:\server-server-data service run”
Example:
SC CONFIG QlikCompose binPath="\"C:\Program
Files\Qlik\Compose\bin\ComposeCtl.exe\" -d \"F:\Compose-server-data\"
service run"
5. Run the following commands from
<PRODUCT_DIR>\bin
:
ComposeCtl.exe -d "F:\Compose-server-data" setup install
ComposeCtl.exe -d "F:\Compose-server-data" masterukey set -p
WdAHWEwXSvwxDFetcl7TVVFfSXPbMrFx
6. Edit <PRODUCT_DIR>\java\bin\acjs.bat and immediately below the line with SET JAVA_
LIB_PATH, add the following:
set AT_DATA=-d F:\Compose-agent-data
7. Start the Compose service and then stop it. This will create the java repository.
This step should be performed on the primary node only.
8. Run the following command from
<PRODUCT_DIR>\java\bin
:
acjs.bat masterukey set WdAHWEwXSvwxDFetcl7TVVFfSXPbMrFx
9. Start the Compose service and then stop it.
10. In the Cluster Manager, move to the secondary node.
Secondary node setup
1. Install Compose.
2. Stop the Compose service.
3. Edit the service executable path as follows:
SC CONFIG QlikCompose binPath= "<PRODUCT_DIR>\bin\ComposeCtl.exe -d
F:\server-server-data service run”
Example:
SC CONFIG QlikCompose binPath="\"C:\Program
Files\Qlik\Compose\bin\ComposeCtl.exe\" -d \"F:\Compose-server-data\"
service run"
4. Run the following commands from
<PRODUCT_DIR>\bin
:
ComposeCtl.exe -d "F:\Compose-server-data" setup install
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
397

8 Setting up Compose on a Windows HA cluster
ComposeCtl.exe -d "F:\Compose-server-data" masterukey set -p
WdAHWEwXSvwxDFetcl7TVVFfSXPbMrFx
5. Edit <PRODUCT_DIR>\java\bin\acjs.bat and immediately below the line with SET JAVA_
LIB_PATH, add the following:
set AT_DATA=-d F:\Compose-agent-data
6. Run the following command from
<PRODUCT_DIR>\java\bin
:
acjs.bat masterukey set WdAHWEwXSvwxDFetcl7TVVFfSXPbMrFx
7. Start the Compose service and then stop it.
8. In the Cluster Manager, move to the next nodes if your cluster has more than two nodes.
8.2 Step 2: Adding the Compose service
After installing Compose in the cluster, you need to add the Compose service as a resource to the
role.
To add the Compose service:
1. In the left pane of the Failover Cluster Manager, select Roles. The available roles will be listed
in the right pane of the console. Right-click the role you are working with and point to Add a
resource. Then select Generic Service.
2. In the Select Service screen of the New Resource wizard, select Qlik Compose from the list.
3. Click Next and follow the instructions in the wizard to create the resource. For information on
how to use this wizard, see the Microsoft online help.
Compose must be installed on the computer where you defined the service in order for
the service to be available in the list.
8.3 Step 3: Defining the service dependencies
You need to define dependencies for the Compose service that will enable the Storage and
Network names to start up before the service. If these resources do not start before the service,
Compose will not be able to start as it will be searching for the data location.
To define the service dependencies:
1. In the left pane of the Failover Cluster Manager console, select Roles.
2. From the list of available roles in the right pane of the console, select the role you are working
with.
3. In the bottom right pane, select the Resource tab. From the list of the available roles, select
Compose.
4. Right-click the Compose role and select Properties.
5. In the Compose Properties window, select the Dependencies tab.
6. Click Insert. A new line is added to the Resource list.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
398

8 Setting up Compose on a Windows HA cluster
7. In the Resource column, click the arrow and select the Compose Data storage resource from
the list.
8. Click Insert and add the Network Name resource (it should have the same name as the
cluster).
9. Start the Service using the Failover Cluster Manager and access the console using the
Network name.
10. Register the license. The license should contain all host names of the cluster.
To open the Compose Console, it is recommended to use an address that
includes the name or IP address of the cluster machine (as opposed to the
specific node name).
Example:
https://cluster_name_ip/qlikcompose/
8.4 Step 4: Defining the URLfor the cluster
By default, the Compose service generates the URL when it starts, according to the host name of
the machine on which Compose is installed.
In a cluster environment, this is not good practice because the URL will change each time the
cluster is rolled over. To resolve this issue, you need to set the cluster name as the Compose URL.
To set the cluster name as the Compose URL:
1. In the left pane of the Failover Cluster Manager, select Nodes.
The right pane of the Console displays a list of cluster nodes.
2. Select a node to see the cluster name. This is the name you want to set (for example:
Cluster_Network_1).
The cluster name must be registered in DNS, before you can set it.
3. Run the following command from the primary node:
<PRODUCT_DIR>\bin>ComposeCtl.exe -d <COMPOSE_SERVER_DATA_FOLDER> configuration set --
address <CLUSTER_NAME>
Example:
ComposeCtl.exe -d "F:\Compose-server-data" configuration set --address QlikCluster
The host configuration will be updated.
4. Restart the Compose service for the changes to take effect.
5. To make sure Compose is now using the correct URL, check
F:\Compose-server-
data\logs\compose.txt
or use the
<COMPOSE_DATA_FOLDER>\service.url
shortcut to
check the cluster name in the service Properties.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
399

8 Setting up Compose on a Windows HA cluster
6. Try to open Compose from a remote browser using
<COMPOSE_DATA_
FOLDER>\service.url
.
8.5 Upgrading Compose on the cluster
To upgrade Compose on a Windows Server High Availability Cluster:
1. Make sure you are on the primary node.
2. In the left pane of the Failover Cluster Manager, select Roles. From the list of available roles
in the right pane, right-click the Compose role you are working with and change it to offline.
3. Run the standard upgrade procedure.
Make sure the Compose role is offline, as the upgrade should bring the services
online.
4. As the upgrade process overrides the acjs.bat file, when the upgrade completes, add the
following row to the <PRODUCT_DIR>\java\bin\acjs.bat file:
SET AT_DATA=-d <agent data path>
If the above string already exists in acjs.bat, you can skip this step.
5. Bring the Compose role back online and make sure there are no connection errors.
6. Upgrade the projects by running the following command on the primary node only:
ComposeCtl.exe -d <server data path> setup postupdate
7. Repeat steps 2-5 on the secondary node.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
400

A Impact of DST change on Qlik Compose
A Impact of DST change on Qlik Compose
This topic describes how Qlik Compose is affected by Daylight Saving Time (DST) and provides
guidelines for handling changes brought about by DST.
There are two types of DST changes:
l
DST On - Occurs approximately when Summer starts (actual date is country specific). Its
impact on local time is that local time is moved one hour forward (so, for example, 01:00AM
becomes 02:00AM). This DST change does not impact Qlik Compose as it does not result in
time overlap.
l
DST Off - Occurs approximately when Winter starts (actual date is country specific). Its
impact on local time is that local time is moved back one hour (so, for example, 02:00AM
becomes 01:00AM). This DST change results in time overlap where local time travels over the
same hour twice in a row.
The comments below assume that the customer has not changed the time but rather the timezone
or the DST setting. Changing the actual time (not for minor time adjustments) is a sensitive
operation and is best done when Qlik Compose is stopped.
There are two places where DST may have an effect:
l
Timestamps in logs and audit messages are in local time. As a result, when Winter time starts,
the logs will show the time going back an hour; conversely, when Summer time starts, the
logs may appear to be missing one hour.
l
Statistics shown on the console are also sensitive to local time, and thus may also show
confusing/inaccurate data in the overlap period (going in to Winter time) or for the skipped
period (going into Summer time).
In general, it is recommended to avoid non-critical task design changes during the first overlap
period (going in to Winter time) so as to prevent confusion about when the changes took place.
In addition to Qlik Compose, other components are also affected including:
l
The source endpoint system
l
The target endpoint system
l
The local operating system
l
The task design (specifically using timestamp based variables)
The Scheduler is not adjusted to take into account daylight saving time (DST). For
example, a daily job which was scheduled to run at 11 PM should be rescheduled to run
at 11 PM after DST comes into effect.
Given the complexity of the topic and the involvement of many independent components and
settings, Qlik generally recommends that customers first verify the impact of DST changes in their
test environment.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
401

B Support matrix
B Support matrix
In addition to listing the platforms on which Qlik Compose can be installed, this topic also specifies
which source and target database versions can be used in a Qlik Compose task.
B.1 Supported Windows platforms
Qlik Compose can be installed on any of the following Windows platforms:
l
Windows Server 2016 (64-bit)
l
Windows Server 2019 (64-bit)
l
Windows Server 2022 (64-bit)
B.2 Supported browsers
The Qlik Compose Web UI supports the following browsers:
l
Microsoft Edge (with automatic updates turned on)
l
Mozilla Firefox (with automatic updates turned on)
l
Google Chrome (with automatic updates turned on)
B.3 Supported Qlik Replicate and Enterprise Manager
versions
Qlik Replicate is required for landing data into the data warehouse or storage while Qlik Enterprise
Manager allows you to monitor and control Compose tasks running on different servers. This
section lists the supported versions for each of these products.
Qlik Compose November 2023 is compatible with the following Replicate and Enterprise Manager
versions:
l
Qlik Replicate: May 2022, November 2022 and its service releases, and November 2023
l
Enterprise Manager: November 2023
B.4 Supported Databases for Data Warehouse Projects
Supported data sources
Any data source supported by Qlik Replicate can be used as a data source in Qlik Compose. When
using a Qlik Replicate data source, discovery needs to be performed on the landing zone. Replicate
data sources (endpoints) that can be discovered directly from Qlik Compose are described in the
table below.
For more information on discovering data sources, see
Discovering the Source Database or Landing
Zone (page 156)
.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
402

B Support matrix
Data Source (Endpoint) Version
Microsoft SQL Server 2016, 2017, 2019, and 2022
MySQL 8.0 and 8.1
Oracle
Note: All Oracle editions are supported.
19.x, and 21c
IBM DB2 for LUW 9.x, 10.x, and 11.x
Supported data sources and versions
Supported data warehouses
The table below lists the data warehouse versions supported in a Data Warehouse project.
Data Warehouse Version
Microsoft SQL Server 2016, 2017, 2019, and
2022
Microsoft Azure SQL Database (via the Microsoft SQL Server database
connection settings)
Same as Microsoft
SQL Server.
Microsoft Azure SQL Managed Instance (via the Microsoft SQL Server
database connection settings)
Same as Microsoft
SQL Server.
Oracle
All Oracle editions are supported.
19.x, and 21c
Amazon Redshift N/A
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics (formerly known as Microsoft Azure
SQL Server Data Warehouse)
N/A
Snowflake N/A
Google Cloud BigQuery N/A
Supported data warehouses and versions
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
403

B Support matrix
B.5 Supported hive distributions for Data Lake projects
The table below lists the supported hive distributions for Data Lake projects.
l
For all hive distributions, fully binary compatible versions are also supported.
l
All major versions and selected minor versions are certified for use with Compose.
l
For information about supported drivers, see Prerequisites (page 284).
Hive Distribution Version
Amazon EMR 6.x
Cloudera 7.x
Microsoft Azure HDInsight 4.x
Google Dataproc (non ACID) 2.0
Databricks on AWS 9.1 (LTS), 10.4 LTS, 12.2 (LTS), 14.3 LTS, and SQL warehouse
cluster
Databricks on Azure 9.1 (LTS), 10.4 LTS, 12.2 (LTS), 14.3 LTS, and SQL warehouse
cluster
Databricks on Google Cloud 9.1 (LTS), 10.4 LTS, 12.2 (LTS), 14.3 LTS, and SQL warehouse
cluster
Supported databases for Data Lake projects
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
404

C Cron format and examples
C Cron format and examples
Cron expressions can be used to schedule a Compose task. This appendix describes the Cron
format used in Compose (Quartz), provides a description of the special characters that can be used
in an expression and ends with some examples of Cron usage.
In this appendix:
C.1 Cron format
A cron expression is a string comprised of five fields separated by a white space. Fields can contain
any of the allowed values, along with various combinations of the allowed special characters for
that field. The fields are described in the table below.
Field Name Mandatory Allowed Values Allowed Special Characters
Seconds
0-59 , - * /
Minutes
0-59 , - * /
Hours
0-23 , - * /
Day of month
1-31 , - * ? / L W
Month 1-12 or JAN-DEC
, - * /
Days of week 1-7 or SUN-SAT
, - * ? / L #
Cron expression field values
C.2 Special characters
The following special characters are supported:
l
* ("all values") Used to select all values within a field. For example, "*" in the minute field
means "every minute".
l
? ("no specific value") Useful when you need to specify something in one of the two fields in
which the character is allowed, but not the other. For example, if I want my task to run on a
particular day of the month (say, the 10th), but don't care what day of the week that happens
to be, I would put "10" in the day-of-month field, and "?" in the day-of-week field. See the
examples below for clarification.
l
- Used to specify ranges. For example, "10-12" in the hour field means "the hours 10, 11 and
12".
l
, Used to specify additional values. For example, "MON,WED,FRI" in the day-of-week field
means "the days Monday, Wednesday, and Friday".
l
/ Used to specify increments. For example, "0/15" in the seconds field means "the seconds 0,
15, 30, and 45". And "5/15" in the seconds field means "the seconds 5, 20, 35, and 50". You
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
405

C Cron format and examples
can also specify '/' after the '' character - in this case '' is equivalent to having '0' before the
'/'. '1/3' in the day-of-month field means "run every 3 days starting on the first day of the
month".
l
L ("last") Has a different meaning in each of the two fields in which it is allowed. For example,
the value "L" in the day-of-month field means "the last day of the month" - day 31 for
January, day 28 for February on non-leap years. If used in the day-of-week field by itself, it
simply means "7" or "SAT". But if used in the day-of-week field after another value, it means
"the last xxx day of the month" - for example "6L" means "the last friday of the month". You
can also specify an offset from the last day of the month, such as "L-3" which would mean
the third-to-last day of the calendar month. When using the 'L' option, it is important not to
specify lists, or ranges of values, as you'll get confusing/unexpected results.
l
W ("weekday") Used to specify the weekday (Monday-Friday) nearest the given day. As an
example, if you were to specify "15W" as the value for the day-of-month field, the meaning is:
"the nearest weekday to the 15th of the month". So if the 15th is a Saturday, the trigger will
run on Friday the 14th. If the 15th is a Sunday, the trigger will run on Monday the 16th. If the
15th is a Tuesday, then it will run on Tuesday the 15th. However if you specify "1W" as the
value for day-of-month, and the 1st is a Saturday, the trigger will run on Monday the 3rd, as it
will not 'jump' over the boundary of a month's days. The 'W' character can only be specified
when the day-of-month is a single day, not a range or list of days. ** The 'L' and 'W'
characters can also be combined in the day-of-month field to yield 'LW', which translates to
"last weekday of the month".
l
# Used to specify "the nth" XXX day of the month. For example, the value of "6#3" in the day-
of-week field means "the third Friday of the month" (day 6 = Friday and "#3" = the 3rd one in
the month). Other examples: "2#1" = the first Monday of the month and "4#5" = the fifth
Wednesday of the month. Note that if you specify "#5" and there is not 5 of the given day-of-
week in the month, then no firing will occur that month. ** The legal characters and the
names of months and days of the week are not case sensitive. MON is the same as mon.
C.3 Usage examples
Here are some examples of cron expressions and their effect.
Cron
expression
example
Trigger frequency
0 0 12 * * ? 12 pm (noon) every day
0 15 10 ? * * 10:15am every day
0 15 10 * * ? 10:15am every day
0 15 10 * * ? * 10:15am every day
0 15 10 * * ?
2005
10:15am every day during the year 2005
Cron expression usage examples
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
406

C Cron format and examples
Cron
expression
example
Trigger frequency
0 * 14 * * ? Every minute starting at 2pm and ending at 2:59pm every day
0 0/5 14 * * ? Every 5 minutes starting at 2pm and ending at 2:55pm every day
0 0/5 14,18 * *
?
Every 5 minutes starting at 2pm and ending at 2:55pm every day, ANDevery 5
minutes starting at 6pm and ending at 6:55pm every day
0 0-5 14 * * ? Every minute starting at 2pm and ending at 2:05pm every day
0 10,44 14 ? 3
WED
At 2:10pm and at 2:44pm every Wednesday, in the month of March
0 15 10 ? *
MON-FRI
At 10:15am every day from Monday - Friday
0 15 10 15 * ? 10:15am on the 15th day of every month
0 15 10 L * ? 10:15am on the last day of every month
0 15 10 ? * 6L 10:15am on the last Friday of every month
0 15 10 ? * 6L
2002-2005
10:15am on the last Friday of every month, during the years 2002-2005
0 15 10 ? * 6#3 10:15am on the third Friday of every month
0 0 12 1/5 * ? 12pm (noon) every 5 days every month, starting on the first day of the month
0 11 11 11 11 ? 11:11am on every November 11th
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
407

D Supported characters
D Supported characters
To prevent character validation errors, Compose best practice is to only use alphanumeric
characters, underscores and hyphens in table and column names. This is because object naming
rules are always determined by the database type, of which there may be several in a single
Compose project.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
408

E Glossary
E Glossary
A
Attribute
In the Compose model, an attribute is a logical representation of a
physical column in a source database (or Landing Zone) table.
Attributes Domain
A list of all the attributes available in the Compose model. You can add,
edit and delete attributes according to your data warehousing needs. The
Attributes Domain also shows you which entities each attribute is used in,
as a single attribute may be used in several entities.
C
Change Tables
Change Tables are created in the Landing Zone when the Replicate task is
defined as Full Load and Store Changes or Store Changes only. When the
Store Changes replication option is enabled in the Replicate task, any
changes to the source tables will be replicated to the Change Tables in
the Landing Zone. The Change Table name format comprises the original
table name appended with a "__ct".
E
Entity
In the Compose model, an entity is a logical representation of a physical
source database/Landing Zone table or view.
ETL Task
In a project, the following ETL tasks can be run: - An ETL task that
extracts data from the Landing Zone, performs user-defined
transformations on the data, and loads it into the data warehouse tables. -
An ETL task that extracts data from the data warehouse, performs user-
defined transformations on the data, and loads it into the data mart
tables. Depending on the ETL task type and specific settings within
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
409

E Glossary
Compose, only changes to the existing data will be populated or all of the
data (regardless of whether any changes were made to the source).
F
Full Load
A Full Load replication task is a Replicate task that replicates all of the
selected source tables to the Landing Zone and populates them with data
from the source database. When you duplicate an existing data
warehouse ETL, you can set the ETL type to Full Load and Change Tables
(i.e. initially extract all the data from the Landing Zone tables and then
only the changes), Full Load Only (i.e. extract all the data from the Landing
Zone tables) or Change Tables Only (i.e. extract only the changes to the
Landing Zone tables).
H
History
Model attributes (and their corresponding data warehouse columns) can
either be defined as history Type 1 or history Type 2. When an attribute is
defined as history type 1, no history of the data is kept since old data will
always be overwritten with new data. When an attribute is defined as
history Type 2, a new record is added each time the record is updated.
This is especially useful for Slowly Changing Dimensions (SCDs). For
example, defining the Address attribute in the Customers table as Type 2
would enable you to retrieve data based on the customer’s location during
a certain time period. Attributes defined as history Type 1 will always exist
in hub tables whereas attributes defined as history Type 2 will always
exist in satellite tables.
Hub
A table in the data warehouse containing history Type 1 columns. When a
column is defined as history type 1, no history of the data is kept since old
data is overwritten with new data.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
410

E Glossary
I
Incremental loading
The activity of loading only new or updated records from the data
warehouse into the data mart(s), using Full Load formatted data. The
input data may include all of the records (full) or only added and updated
records (partial). As opposed to CDC, incremental loading does not
indicate wether the change is an UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE.
L
Landing Zone
The area in the data warehouse to which the source tables are replicated.
This is also the target endpoint in a Replicate task.
Lineage
A visual representation of the data flow of a particular table or column
from its source to its current location. Before editing an entity or attribute,
you may want to see which other entities/attributes or tables/columns will
be impacted by the change. For example, removing the "Discount"
attribute from a table will affect the "Total Price". Additionally, a single
attribute may have multiple names depending on its location.
M
Model
The business information model of an enterprise. Usually an ERD (Entity-
Relationship Diagram), the model should contain all of the information
needed to create the data warehouse. Models can be imported from
ERwin or generated automatically by discovering (otherwise known as
reverse engineering) the source database or Landing Zone.
R
Relationship
Similar to a foreign key, a relationship "attribute" is a special type of
attribute that points to another entity in the same model.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
411

E Glossary
S
Satellite
A table in the data warehouse containing history Type 2 columns. When a
column is defined as history type 1, a new record is added whenever a
record is updated (instead the existing record being overwritten). Satellite
tables also contain two additional columns: FD (From Date) and TD (To
Date). For old records, these columns show the dates between which a
particular record was current (i.e. before a new record rendered it
obsolete). The TD column will only contain a date if the record has been
succeeded by a newer record. In Compose, you can set a satellite number
(1 and above) for attributes in the model. This is a good way of ensuring
that similar attributes (or columns in the data warehouse) appear in the
same satellite table. For example, setting the same satellite number for
the "Total" and "Discount" attributes ensures that both attributes will be
included in the same satellite table.
Setup and User Guide - Qlik Compose, November 2023 and Service
Release 1
412
