
Semi-industrial
LoRaWAN
®
Gateway
UG65
User Guide

2
Preface
Thanks for choosing Milesight UG65 LoRaWAN
®
gateway. UG65 delivers tenacious
connection over network with full-featured design such as automated failover/failback,
extended operating temperature, dual SIM cards, hardware watchdog, VPN, Gigabit
Ethernet and beyond.
This guide shows you how to configure and operate the UG65 LoRaWAN
®
gateway. You
can refer to it for detailed functionality and gateway configuration.
Readers
This guide is mainly intended for the following users:
- Network Planners
- On-site technical support and maintenance personnel
- Network administrators responsible for network configuration and maintenance
©2011-2023 Xiamen Milesight IoT Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved.
All information in this user guide is protected by copyright law. Whereby, no organization or
individual shall copy or reproduce the whole or part of this user guide by any means
without written authorization from Xiamen Milesight Iot Co., Ltd.
Related Documents
Document
Description
UG65 Datasheet
Datasheet for UG65 LoRaWAN
®
gateway.
UG65 Quick Start Guide
Quick Installation Guide for UG65 LoRaWAN
®
gateway.
Declaration of Conformity
UG65 is in conformity with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of the
CE, FCC, and RoHS.

3
For assistance, please contact
Milesight technical support:
Email: iot.support@milesight.com
Support Portal: support.milesight-iot.com
Tel: 86-592-5085280
Fax: 86-592-5023065
Address: Building C09, Software Park III,
Xiamen 361024, China
Revision History
Date
Doc Version
Description
Aug. 31, 2020
V1.0
Initial version
Dec. 10, 2020
V2.0
Layout replace
Apr. 30, 2021
V2.1
1. Support LoRaWAN
®
Class B
2. Add Node-RED feature
3. Add Noise-Analyzer feature
4. Add Multicast Group feature
5. Add application examples
Aug. 24, 2021
V2.2
1. Support Yeastar Workplace platform integration
2. Delete Package Forward status page
3. Phone & Email webpage update
Dec. 15, 2021
V2.3
1. Add AS923-3&AS923-4
2. Change network server channel mask box to channel
3. Add device channel setting in profile
Feb. 18, 2022
V2.4
1. Add batch backup
2. Log in webpage update
3. Change default antenna type to external antenna
4. Adjust time of Class C ACK timeout
Jun. 1, 2022
V2.5
1. Support VLAN Trunk client
2. Add System Name in SNMP
3. Add Use L2TP Peer DNS option
Dec.26, 2022
V2.6
1. Add BACnet Server feature
2. Add Payload Codec feature
3. Add Reset and all flows export feature on Node-RED
4. Add data retransmission feature on Packet Forward

4
Contents
Chapter 1 Product Introduction ...................................................................................................7
1.1 Overview ..........................................................................................................................7
1.2 Advantages .....................................................................................................................7
1.3 Specifications .................................................................................................................8
1.4 Dimensions (mm) .........................................................................................................10
Chapter 2 Access to Web GUI ...................................................................................................11
2.1 Wireless Access ...........................................................................................................11
2.2 Wired Access................................................................................................................12
Chapter 3 Web Configuration ....................................................................................................15
3.1 Status............................................................................................................................15
3.1.1 Overview .............................................................................................................15
3.1.2 Cellular ............................................................................................................... 15
3.1.3 Network ..............................................................................................................17
3.1.4 WLAN................................................................................................................. 18
3.1.5 VPN .....................................................................................................................19
3.1.6 Host List .............................................................................................................20
3.2 LoRaWAN ......................................................................................................................21
3.2.1 Packet Forwarder .............................................................................................. 22
3.2.1.1 General .................................................................................................... 22
3.2.1.2 Radios ......................................................................................................22
3.2.1.3 Noise Analyzer ........................................................................................24
3.2.1.4 Advanced ................................................................................................ 25
3.2.1.5 Custom .................................................................................................... 27
3.2.1.6 Traffic ...................................................................................................... 28
3.2.2 Network Server .................................................................................................. 29
3.2.2.1 General .................................................................................................... 29
3.2.2.2 Application .............................................................................................. 31
3.2.2.3 Payload Codec ........................................................................................34
3.2.2.4 Profiles .................................................................................................... 37
3.2.2.5 Device ...................................................................................................... 39
3.2.2.6 Multicast Groups .................................................................................... 41
3.2.2.7 Gateway Fleet ......................................................................................... 43
3.2.2.8 Packets ....................................................................................................44
3.3 Protocol Integration ..................................................................................................... 47
3.3.1 BACnet Server ....................................................................................................47
3.3.1.1 Server .......................................................................................................47
3.3.1.2 BACnet Object .........................................................................................48
3.4 Network .........................................................................................................................49
3.4.1 Interface .............................................................................................................49
3.4.1.1 Port .......................................................................................................... 49
3.4.1.2 WLAN .......................................................................................................52

5
3.4.1.3 Cellular .....................................................................................................55
3.4.1.4 Loopback .................................................................................................58
3.4.1.5 VLAN Trunk .............................................................................................58
3.4.2 Firewall ...............................................................................................................59
3.4.2.1 Security ....................................................................................................59
3.4.2.2 ACL .......................................................................................................... 59
3.4.2.3 DMZ ......................................................................................................... 61
3.4.2.4 Port Mapping .......................................................................................... 61
3.4.2.5 MAC Binding ........................................................................................... 62
3.4.3 DHCP ..................................................................................................................63
3.4.4 DDNS .................................................................................................................. 64
3.4.5 Link Failover.......................................................................................................65
3.4.5.1 SLA ...........................................................................................................65
3.4.5.2 Track ........................................................................................................66
3.4.5.3 WAN Failover .......................................................................................... 67
3.4.6 VPN .....................................................................................................................68
3.4.6.1 DMVPN ....................................................................................................68
3.4.6.2 IPSec ........................................................................................................69
3.4.6.3 GRE .......................................................................................................... 72
3.4.6.4 L2TP ........................................................................................................ 73
3.4.6.5 PPTP ........................................................................................................75
3.4.6.6 OpenVPN Client ...................................................................................... 77
3.4.6.7 OpenVPN Server ..................................................................................... 78
3.4.6.8 Certifications ...........................................................................................80
3.5 System .......................................................................................................................... 82
3.5.1 General Settings ................................................................................................ 82
3.5.1.1 General .................................................................................................... 82
3.5.1.2 System Time ........................................................................................... 83
3.5.1.3 SMTP ....................................................................................................... 85
3.5.1.4 Phone .......................................................................................................85
3.5.1.5 Email ........................................................................................................86
3.5.2 User Management .............................................................................................87
3.5.2.1 Account ................................................................................................... 87
3.5.2.2 User Management .................................................................................. 87
3.5.3 SNMP ................................................................................................................. 88
3.5.3.1 SNMP .......................................................................................................88
3.5.3.2 MIB View ................................................................................................. 89
3.5.3.3 VACM .......................................................................................................89
3.5.3.4 Trap ..........................................................................................................90
3.5.3.5 MIB ...........................................................................................................91
3.5.4 Device Management ......................................................................................... 91
3.5.5 Events .................................................................................................................92
3.5.5.1 Events ......................................................................................................92
3.5.5.2 Events Settings ....................................................................................... 93

6
3.6 Maintenance .................................................................................................................95
3.6.1 Tools ...................................................................................................................95
3.6.1.1 Ping ..........................................................................................................95
3.6.1.2 Traceroute ...............................................................................................95
3.6.1.3 Qxdmlog .................................................................................................. 96
3.6.2 Schedule .............................................................................................................96
3.6.3 Log......................................................................................................................96
3.6.3.1 System Log ............................................................................................. 96
3.6.3.2 Log Settings ............................................................................................ 97
3.6.4 Upgrade ..............................................................................................................98
3.6.5 Backup and Restore.......................................................................................... 99
3.6.6 Reboot ................................................................................................................99
3.7 APP............................................................................................................................. 100
3.7.1 Python .............................................................................................................. 100
3.7.1.1 Python ................................................................................................... 100
3.7.1.2 App Manager Configuration ................................................................ 101
3.7.1.3 Python App ............................................................................................102
3.7.2 Node-RED .........................................................................................................103
3.7.2.1 Node-RED .............................................................................................. 103
Chapter 4 Application Examples .............................................................................................105
4.1 Restore Factory Defaults ...........................................................................................105
4.1.1 Via Web Interface............................................................................................ 105
4.1.2 Via Hardware................................................................................................... 106
4.2 Firmware Upgrade ......................................................................................................106
4.3 Ethernet Connection .................................................................................................. 107
4.4 Cellular Connection ....................................................................................................108
4.5 Wi-Fi Application Example .........................................................................................109
4.5.1 AP Mode .......................................................................................................... 109
4.5.2 Client Mode......................................................................................................111
4.6 Packet Forwarder Configuration ...............................................................................112
4.7 Connect to Milesight IoT Cloud ................................................................................ 114
4.8 Application Configuration ..........................................................................................115
4.9 Device Configuration ................................................................................................. 118
4.10 Send Data to Device .................................................................................................119
4.11 Node-RED ................................................................................................................. 121
4.11.1 Start the Node-RED ....................................................................................... 121
4.11.2 Send Data by Email ....................................................................................... 122

7
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
1.1 Overview
UG65 is a robust 8-channel indoor LoRaWAN
®
gateway. Adopting SX1302 LoRa chip and
high-performance quad-core CPU, UG65 supports connection with more than 2000 nodes.
UG65 has line of sight up to 15 km and can cover about 2 km in urbanized environment,
which is ideally suited to smart office, smart building and many other indoor applications.
UG65 supports not only multiple back-haul backups with Ethernet, Wi-Fi and cellular, but
also has integrated mainstream network servers (such as TTI, ChirpStack, etc.) and built-in
network server and Milesight IoT Cloud for easy deployment.
Figure 1-1
1.2 Advantages
Benefits
- Built-in industrial CPU and big memory
- Ethernet, 2.4GHz Wi-Fi and global 2G/3G/LTE options make it easy to get connected
-
Embedded network server and compliant with several third party network servers
- MQTT, HTTP or HTTPS protocol for data transmission to application server
-
Rugged enclosure, optimized for wall or pole mounting
- 3-year warranty included
Security & Reliability
- Automated failover/failback between Ethernet and Cellular
-
Enable unit with security frameworks like IPsec/OpenVPN/GRE/L2TP/PPTP/ DMVPN
- Embedded hardware watchdog to automatically recover from various failure and
ensure highest level of availability

8
Easy Maintenance
- Milesight DeviceHub provides easy setup, mass configuration, and centralized
management of remote devices
- The user-friendly web interface design and various upgrading options help
administrator to manage the device as easy as pie
- Web GUI and CLI enable the admin to achieve quick configuration and simple
management among a large quantity of devices
- Users can efficiently manage the remote devices on the existing platform through the
industrial standard SNMP
Capabilities
- Link remote devices in an environment where communication technologies are
constantly changing
- Industrial quad core 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53 processor, high-performance operating up
to 1.5 GHz with low power consumption, and 8GB eMMC available to support more
applications
- Support wide operating temperature ranging from -40°C to 70°C/-40°F to 158°F
1.3 Specifications
Hardware System
CPU
Quad-core 1.5GHz, 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53
Memory
8 GB eMMC Flash, 512 MB DDR4 RAM
LoRaWAN
Antenna
Fully Integrated and Internal Antenna
(Optional: 1 × 50 Ω N-Female External Connector)
Channel
8
Frequency Band
CN470/IN865/EU868/RU864/US915/AU915/KR920/AS923-1&2&3&
4
Sensitivity
-140dBm Sensitivity @292bps
Output Power
27dBm Max
Protocol
V1.0 Class A/Class B/Class C and V1.0.2 Class A/Class B/Class C
Ethernet
Ports
1 × RJ-45 (PoE PD supported)
Physical Layer
10/100/1000 Base-T (IEEE 802.3)

9
Physical Characteristics
Ingress Protection
IP65
Dimensions
180 x 110 x 56.5 mm
Mounting
Desktop, Wall or Pole Mounting
Others
Reset Button
1 × RST
Data Rate
10/100/1000 Mbps (auto-sensing)
Interface
Auto MDI/MDIX
Mode
Full or half duplex (auto-sensing)
Wi-Fi Interfaces
Antenna
Fully Integrated and Internal Antenna
Standards
IEEE 802.11 b/g/n, 2.4 GHz
Tx Power
802.11b: 18 dBm +/-2.0 dBm (11 Mbps)
802.11g: 15 dBm +/-2.0 dBm (6 Mbps)
802.11g: 15 dBm +/-2.0 dBm (54 Mbps)
Cellular Interfaces (Optional)
Antenna
Internal Antenna
SIM Slots
1
Software
Network
Protocols
PPPoE, SNMP v1/v2c/v3, TCP, UDP, DHCP, DDNS, HTTP, HTTPS,
DNS, SNTP, Telnet, SSH, MQTT, etc.
VPN Tunnel
DMVPN/IPsec/OpenVPN/PPTP/L2TP/GRE
Firewall
ACL/DMZ/Port Mapping/MAC Binding
Management
Web, CLI, SMS, On-demand dial up, DeviceHub, Milesight IoT Cloud,
Yeastar Workplace Platform
App
Python SDK, Node-RED
Power Supply and Consumption
Power Supply
1. DC Jack Connector for 9-24 VDC power supply
2. 1 × 802.3 af PoE input
Consumption
Typical 2.9W, Max 4.2W

10
LED Indicators
1 × POWER, 1 × STATUS, 1 × LoRa, 1 × Wi-Fi, 1 × LTE, 1 × ETH
Built-in
Watchdog, RTC, Timer
Environmental
Operating
Temperature
-40°C to +70°C (-40°F to +158°F)
Reduced cellular performance above 60°C
Storage
Temperature
-40°C to +85°C (-40°F to +185°F)
Ethernet Isolation
1.5 kV RMS
Relative Humidity
0% to 95% (non-condensing) at 25°C/77°F
1.4 Dimensions (mm)

11
Chapter 2 Access to Web GUI
This chapter explains how to access to Web GUI of the UG65.
Username: admin
Password: password
2.1 Wireless Access
1. Enable Wireless Network Connection on your computer and search for access point
“Gateway_******” to connect it.
2. Open a Web browser on your PC (Chrome is recommended) and type in the IP address
192.168.1.1 to access the web GUI.
3. Enter the username and password, click “Login”.
If you enter the username or password incorrectly more than 5 times, the login page
will be locked for 10 minutes.
4. After logging the web GUI, follow the guide to complete the basic configurations. It’s
suggested that you change the password for the sake of security.

12
5. You can view system information and perform configuration of the gateway.
2.2 Wired Access
Connect PC to UG65 ETH port directly or through PoE injector to access the web GUI of
gateway. The following steps are based on Windows 10 system for your reference.
1. Go to “Control Panel” → “Network and Internet” → “Network and Sharing Center”, then
click “Ethernet” (May have different names).
2. Go to “Properties” → “Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4) ”and select “Use the
following IP address”, then assign a static IP manually within the same subnet of the
gateway.

13
3. Open a Web browser on your PC (Chrome is recommended) and type in the IP address
192.168.23.150 to access the web GUI.
4. Enter the username and password, click “Login”.
If you enter the username or password incorrectly more than 5 times, the login page
will be locked for 10 minutes.
5. After logging the web GUI, follow the guide to complete the basic configurations. It’s
suggested that you change the password for the sake of security.

14
6. After guide complete, you can view system information and perform configuration of
the gateway.

15
Chapter 3 Web Configuration
3.1 Status
3.1.1 Overview
You can view the system information of the gateway on this page.
Figure 3-1-1-1
System Information
Item
Description
Model
Show the model name of gateway.
Region
Show the LoRaWAN
®
frequency region of gateway.
Serial Number
Show the serial number of gateway.
Firmware Version
Show the currently firmware version of gateway.
Hardware Version
Show the currently hardware version of gateway.
Local Time
Show the currently local time of system.
Uptime
Show the information on how long the gateway has been
running.
CPU Load
Show the current CPU utilization of the gateway.
RAM (Capacity/Available)
Show the RAM capacity and the available RAM memory.
eMMC (Capacity/Available)
Show the eMMC capacity and the available eMMC memory.
Table 3-1-1-1 System Information
3.1.2 Cellular
You can view the cellular network status of gateway on this page.

16
Figure 3-1-2-1
Modem Information
Item
Description
Status
Show corresponding detection status of module and SIM card.
Model
Show the model name of cellular module.
Version
Show the version of cellular module.
Signal Level
Show the cellular signal level.
Register Status
Show the registration status of SIM card.
IMEI
Show the IMEI of the module.
IMSI
Show IMSI of the SIM card.
ICCID
Show ICCID of the SIM card.
ISP
Show the network provider which the SIM card registers on.
Network Type
Show the connected network type, such as LTE, 3G, etc.
PLMN ID
Show the current PLMN ID, including MCC, MNC, LAC and Cell ID.
LAC
Show the location area code of the SIM card.
Cell ID
Show the Cell ID of the SIM card location.
Table 3-1-2-1 Modem Information

17
Figure 3-1-2-2
Network Status
Item
Description
Status
Show the connection status of cellular network.
IP Address
Show the IP address of cellular network.
Netmask
Show the netmask of cellular network.
Gateway
Show the gateway of cellular network.
DNS
Show the DNS of cellular network.
Connection Duration
Show information on how long the cellular network has been connected.
Table 3-1-2-2 Network Status
3.1.3 Network
On this page you can check the Ethernet port status of the gateway.
Figure 3-1-3-1
Network
Item
Description
Port
Show the name of the Ethernet port.
Status
Show the status of the Ethernet port. "Up" refers to a status that WAN
is enabled and Ethernet cable is connected. "Down" means Ethernet
cable is disconnected or WAN function is disabled.
Type
Show the dial-up type of the Ethernet port.
IP Address
Show the IP address of the Ethernet port.
Netmask
Show the netmask of the Ethernet port.

18
Gateway
Show the gateway of the Ethernet port.
DNS
Show the DNS of the Ethernet port.
Duration
Show the information about how long the Ethernet cable has been
connected to the Ethernet port when the port is enabled. Once the port
is disabled or Ethernet cable is disconnected, the duration will stop.
Table 3-1-3-1 WAN Status
3.1.4 WLAN
You can check Wi-Fi status on this page, including the information of access point and
client.
Figure 3-1-4-1
WLAN Status
Item
Description
Wireless Status
Show the wireless status.
MAC Address
Show the MAC address.
Interface Type
Show the interface type, such as "AP" or “Client".
SSID
Show the SSID.
Channel
Show the wireless channel.
Encryption Type
Show the encryption type.
Status
Show the connection status.
IP Address
Show the IP address of the gateway.
Netmask
Show the wireless MAC address of the gateway.
Gateway
Show the gateway address in wireless network.
Connection Duration
Show information on how long the Wi-Fi network has been connected.
Table 3-1-4-1 WLAN Status

19
Figure 3-1-4-2
Associated Stations
Item
Description
IP Address
Show the IP address of access point or client.
MAC Address
Show the MAC address of the access point or client.
Connection Duration
Show information on how long the Wi-Fi network has been
connected.
Table 3-1-4-2 WLAN Status
3.1.5 VPN
You can check VPN status on this page, including PPTP, L2TP, IPsec, OpenVPN and
DMVPN.
Figure 3-1-5-1

20
Figure 3-1-5-2
Figure 3-1-5-3
VPN Status
Item
Description
Name
Show the name of the VPN tunnel.
Status
Show the status of the VPN tunnel.
Local IP
Show the local tunnel IP of VPN tunnel.
Remote IP
Show the remote tunnel IP of VPN tunnel.
Table 3-1-5-1 VPN Status
3.1.6 Host List
You can view the host information on this page.

21
Figure 3-1-6-1
Host List
Item
Description
DHCP Leases
IP Address
Show IP address of DHCP client
MAC Address
Show MAC address of DHCP client
Lease Time Remaining
Show the remaining lease time of DHCP client.
MAC Binding
IP & MAC
Show the IP address and MAC address set in the Static IP
list of DHCP service.
Table 3-1-6-1 Host List Description
3.2 LoRaWAN

22
3.2.1 Packet Forwarder
3.2.1.1 General
Figure 3-2-1-1
General Settings
Item
Description
Gateway EUI
Show the unique identifier of the gateway and it’s non-editable.
Gateway ID
Fill in the corresponding ID which you’ve used for registering
gateway to the remote network server, such as TTN. It is usually the
same as gateway EUI and can be changed.
Frequency-Sync
Sync frequency configurations from the network server by selecting
the corresponding multi-destination ID.
Data
Retransmission
When the
gateway connects to a single Chirpstack/Semtech/Remote Embedd
ed NS type package forwarder, it supports data storage up to 1GB w
hen network is disconnected and re-transmits the data after network
recovery.
Multi-Destination
The gateway will forward the data to the network server address
that was created and enabled in the list.
Connection
Status
Show the connection status of package forwarder.
Table 3-2-1-1 General Setting Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Packet fowarder configuration
3.2.1.2 Radios

23
Figure 3-2-1-2
Figure 3-2-1-3
Radios-Radio Channel Setting
Item
Description
Antenna
Type
Select the transmission type of antennas.
Region
Choose the LoRaWAN
®
frequency plan used for the upstream and downlink
frequencies and datarates. Available channel plans depend on the gateway’s
model.
Center
Frequency
Change the frequencies to receive packets from LoRaWAN
®
nodes.
Table 3-2-1-2 Radio Channels Setting Parameters
Figure 3-2-1-4
Radios-Multi Channel Setting

24
Item
Description
Enable
Click to enable this channel to transmit packets.
Index
Indicate the ordinal of the list.
Radio
Choose Radio 0 or Radio 1 as center frequency.
Frequency/MHz
Enter the frequency of this channel.
Range: center frequency
±
0.4625.
Table 3-2-1-3 Multi Channel Setting Parameters
Figure 3-2-1-5
Radios-LoRa Channel Setting
Item
Description
Enable
Click to enable this channel to transmit packets.
Radio
Choose Radio 0 or Radio 1 as center frequency.
Frequency/MHz
Enter the frequency of this channel.
Range: center frequency±0.9.
Bandwidth/MHz
Enter the bandwidth of this channel.
Spread Factor
Choose the selectable spreading factor. The channel with large
spreading factor corresponds to a low rate, while the small one
corresponds to a high rate.
Table 3-2-1-4 LoRa Channel Setting Parameters
Figure 3-2-1-6
Radios-FSK Channel Setting
Item
Description
Enable
Click to enable this channel to transmit packets.
Radio
Choose Radio 0 or Radio 1 as center frequency.
Frequency/MHz
Enter the frequency of this channel.
Range: center frequency±0.9.
Bandwidth/MHz
Enter the bandwidth of this channel.
Recommended value: 125KHz, 250KHz, 500KHz
Data Rate
Enter the data rate. Range
:
500-25000.
Table 3-2-1-5 FSK Channel Setting Parameters
3.2.1.3 Noise Analyzer
Noise analyzer is used for scanning the noise of every frequency channel and giving a
diagram for users to analyze the environment interference condition and select best
deployment. RSSI indicates the sensitivity for every channel. Lower the RSSI value, better

25
the signal. It’s not suggested to enable this feature when using package forwarder since it
will affect the downlink transmission.
Figure 3-2-1-7
Noise Analyzer
Item
Description
Default
Enable
Click to enable noise analyzer feature.
Disabled
Sweep Freq
Select the frequency sweeping range.
General Freq: frequencies based on the LoRaWAN
®
regional parameters document
Custom: custom the frequency range
General Feq
Sweep Time
Enable the noise analyzer continuously or within a
period of time.
If Custom is selected, the noise analyzer will stop
automatically after the pre-configured time.
Note: It’s suggested to custom the time since noise
analyzer feature will affect the normal data
transmission.
Custom/24h
Table 3-2-1-6 Noise Analyzer Setting Parameters
3.2.1.4 Advanced
This section is about settings in details of beacon transmitting and validating.

26
Figure 3-2-1-8
Advanced-Beacon Setting
Item
Description
Default
Beacon Period
Interval of gateway sending beacons for Class B
device time synchronization. 0 means the gateway
will not send beacons.
0
Beacon Freq
The frequency of beacons.
Based on the
supported
frequency
Beacon
Datarate
The datarate of beacons.
Based on the
supported
frequency
Beacon Channel
Number
When selecting Custom, it allows users to custom
range from 1 to 8.
1
Beacon Freq
Step
Frequency interval of beacons.
200000
Beacon
Bandwidth
The bandwidth of beacons. Unit: Hz
12500 Hz
Beacon TX
Power
The TX power of beacons.
Based on the
supported
frequency
Table 3-2-1-7 Advanced-Beacon Parameters

27
Figure 3-2-1-9
Item
Description
Default
Keep Alive
Interval
Enter the interval of keepalive packet which is sent
from gateway to network server to keep the connection
stable and alive.
Range: 1-3600.
10
Stat Interval
Enter the interval to update the network server with
gateway statistics. Range: 1-3600.
30
Push Timeout
Enter the timeout to wait for the response from server
after the gateway sends data of node. Rang: 1-1999.
100
Forward CRC
Disabled
Enable to send packets received with CRC disabled to
the network server.
Disabled
Forward CRC
Error
Enable to send packets received with CRC errors to the
network server.
Disabled
Forward CRC
Valid
Enable to send packets received with CRC valid to the
network server.
Enabled
Table 3-2-1-8 Advanced Parameters
3.2.1.5 Custom
When Custom Configuration mode is enabled, you can write your own packet forwarder
configuration file in the edit box to configure packet forwarder. Click “Save” to save your
custom configuration file content, and click “Apply” to take effect. You can click “Clear” to
erase all content in the edit box. If you don’t know how to write configuration file, please
click “Example” to go to reference page.

28
Figure 3-2-1-10
3.2.1.6 Traffic
When navigating to the traffic page, any recent traffic received by the gateway will display.
To watch live traffic, click Refresh.
Figure 3-2-1-11
Item
Description
Refresh
Click to obtain the latest data.
Clear
Click to clear all data.
Rfch
Show the channel of this packet.
Direction
Show the direction of this packet.
Time
Show the receiving time of this packet.
Ticks
Show the ticks of this packet.

29
Frequency
Show the frequency of the channel.
Datarate
Show the datarate of the channel.
Coderate
Show the coderate of this packet.
RSSI
Show the received signal strength.
SNR
Show the signal to noise ratio of this packet.
Table 3-2-1-9 Traffic Parameters
3.2.2 Network Server
3.2.2.1 General
Figure 3-2-2-1
Item
Description
Default
General Setting
Enable
Click to enable Network Server mode.
Enabled
Platform Mode
Enabled to connect gateway to Milesight IoT
Cloud or Yeastar Workplace platform .
Disabled
NetID
Enter the network identifier.
010203
Join Delay
Enter the interval time between when the
end-device sends a Join_request_message to
network server and when the end-device prepares
to open RX1 to receive the Join_accept_message
sent from network server.
5
RX1 Delay
Enter the interval time between when the
1

30
end-device sends uplink packets and when the
end-device prepares to open RX1 to receive the
downlink packet.
Lease Time
Enter the amount of time till a successful join
expires. The format is hours-minutes-seconds. If
the join-type is OTAA, then the end-devices need
to join the network server again when it exceeds
the lease time.
876000-00-00
Log level
Choose the log level.
Info
Channel Plan Setting
Channel Plan
Choose LoRaWAN
®
channel plan used for the
upstream and downlink frequencies and
datarates. Available channel plans depend on the
gateway’s model.
Depend on the
gateway’s
frequency
Channel
Enabled frequencies are controlled using channel
mask.
Leave it blank means using all the default
standard usable channels specified in the
LoRaWAN
®
regional parameters document.
It allows to enter the index of the cahnnels.
Examples:
1, 40: Enabling Channel 1 and Channel 40
1-40: Enabling Channel 1 to Channel 40
1-40, 60: Enabling Channel 1 to Channel 40 and
Channel 60
All: Enabling all channels
Null: Indicates that all channels are disabled
Depend on the
gateway’s
frequency
Table 3-2-2-1 General Parameters
Note: For some regional variants, if allowed by your LoRaWAN
®
region, you can use
Additional Plan to configure additional channels undefined by the LoRaWAN
®
Regional
Parameters, like EU868 and KR920, as the following picture shows:
Figure 3-2-2-2
Additional Channels
Item
Description
Frequency/MHz
Enter the frequency of the additional plan.
Max Datarate
Enter the max datarate for the end-device. The range is based on
what is specified in the LoRaWAN
®
regional parameters
document.

31
Min Datarate
Enter the min datarate for the end-device. The range is based on
what is specified in the LoRaWAN
®
regional parameters document.
Table 3-2-2-2 Additional Plan Parameters
3.2.2.2 Application
An application is a collection of devices with the same purpose/of the same type. Users
can add a series of devices to the same application which needs to send to the same
server.
You can edit the application by clicking or create a new application by clicking .
Figure 3-2-2-3
Application
Item
Description
Name
Enter the name of the application profile.
E.g: smoker-sensor-app.
Description
Enter the description of this application.
E.g: an application for smoker sensor.
Data
Transmission
Data will be sent to your custom server using the MQTT, HTTP,
HTTPS or BACnet/IP protocol. One application can add 3 data
transmissions at most and every protocol can be selected only once.
Table 3-2-2-3 Application Parameters

32
Figure 3-2-2-4
Figure 3-2-2-5
MQTT Settings
Item
Description
General
Broker
Address
MQTT broker address to receive data.
Broker Port
MQTT broker port to receive data.
33
Client ID
Client ID is the unique identity of the client to the server.
It must be unique when all clients are connected to the same server, and
it is the key to handle messages at QoS 1 and 2.
Connection
Timeout/s
If the client does not get a response after the connection timeout, the
connection will be considered as broken. The Range: 1-65535.
Keep Alive
Interval/s
After the client is connected to the server, the client will send heartbeat
packet to the server regularly to keep alive. Range: 1-65535.
User Credentials
Enable
Enable user credentials.
Username
The username used for connecting to the MQTT broker.
Password
The password used for connecting to the MQTT broker.
TLS
Enable
Enable the TLS encryption in MQTT communication.
Mode
Select from “Self signed certificates”, “CA signed server certificate”.
CA signed server certificate: verify with the certificate issued by
Certificate Authority (CA) that pre-loaded on the device.
Self signed certificates: upload the custom CA certificates, client
certificates and secret key for verification.
Topic
Data Type
Data type sent to MQTT broker.
Topic
Topic name of the data type used for publishing.
QoS
QoS 0 – Only Once
This is the fastest method and requires only 1 message. It is also the
most unreliable transfer mode.
QoS 1 – At Least Once
This level guarantees that the message will be delivered at least once,
but may be delivered more than once.
QoS 2 – Exactly Once
QoS 2 is the highest level of service in MQTT. This level guarantees that
each message is received only once by the intended recipients. QoS 2 is
the safest and slowest quality of service level.
Table 3-2-2-4 MQTT Settings Parameters

34
Figure 3-2-2-6
HTTP/HTTPS Settings
Item
Description
HTTP Header
Header Name
A core set of fields in the HTTP header.
Header Value
Value of the HTTP header.
URL
Data Type
Data type sent to HTTP/HTTPS server.
Topic
Topic name of the data type used for publishing.
URL
HTTP/HTTPS server URL to receive data.
Table 3-2-2-5 HTTP/HTTPS Settings Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Application configuration
3.2.2.3 Payload Codec
Payload Codec provides the inbuilt payload codec library of Milesight LoRaWAN devices to
decode and encode the data easily. Users can also customize the payload codec of other
brands of devices or adjust the uplink and downlink contents as requirements.

35
Figure 3-2-2-7
Inbuilt Payload Codec Library
Item
Description
Library
Version
Show the version of the Milesight LoRaWAN node payload codec
library.
Obtaining
Type
Select the type to update the Milesight devices payload codec library.
Online: update automatically if gateway detects there is version update
every time gateway powers on and accesses the Internet. Users can
also click Obtain button to check update status manually.
Local Upload: click Browse to upload the zip format payload codec
package and click Import to update the library.
Name
Show the corresponding Milesight product model of the payload codec.
Payload
decoder/enc
oder function
Show if decoder and encoder are existed.
Details
Show the details of decoder and encoder. If this does not meet your
requirement, please customize your payload codec.
Table 3-2-2-6 Inbuilt Payload Codec Library Parameters

36
Figure 3-2-2-8
Custom Payload Codec
Item
Description
Name
Enter the unique name of the custom payload codec.
Description
Enter the description of this payload codec.
Template
Select an existing inbuilt payload codec as a template.
Payload
Decoder/Encoder
Function
Customize the device payload decoder or encoder. Note that the
function header should be the same as the example on the blanks.
Payload Codec
test
Disable or enable payload codec test.
fPort
Application port of LoRaWAN devices. It’s 85 by default for
Milesight LoRaWAN devices.
Decode
Enter the hex format raw data and click Decode to check the result.
Encode
Enter the JSON format command and check Encode to check the
result.
Table 3-2-2-7 Custom Payload Codec Parameters

37
3.2.2.4 Profiles
A Profile defines the device capabilities and boot parameters that are needed by the Netwo
rk Server for setting the LoRaWAN
®
radio access service. These information elements shall
be provided by the end-device manufacturer.
You can edit the device profile by clicking or create a new device profile by clicking
.
Figure 3-2-2-9
Figure 3-2-2-10
Device Profiles Settings
Item
Description
Name
Enter the name of the device profile.
Max
TXPower
Enter the maximum transmit power.
The TXPower indicates power levels relative to the Max EIRP level of
the end-device. 0 means using the max EIRP. EIRP refers to the
Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power.
Join Type
Select from: “OTAA” and “ABP”.
Class Type
Device type is Class A by default. Users can check the box of Class
B or Class C to add the class type.
Note: Beacon period should be set to nonzero value in “Packet
Forwarder”> “Advanced” if you use Class B.
Table 3-2-2-8 Device Profiles Setting Parameters

38
Figure 3-2-2-11
Device Profile Advanced Settings
Item
Description
Default
MAC Version
Choose the version of the LoRaWAN
®
supported
by the end-device.
1.0.2
Regional
Parameter
Revision
Revision of the Regional Parameters document
supported by the end-device.
B
RX1 Datarate
Offset
The offset which used for calculating the RX1
data-rate, based on the uplink data-rate.
Based on what
is specified in
the LoRaWAN
®
regional
parameters
document
RX2 Datarate
Enter the RX2 datarate which used for the RX2
receive-window.
RX2 Channel
Frequency
RX2 channel frequency which used for the RX2
receive-window.
Frequency List
List of factory-preset frequencies. The range is
based on what is specified in the LoRaWAN
®
regional parameters document.
Null
Device Channel
Change this device frequency channel by typing
the channel indexs. When configured, it takes
precedence over the global channel. This setting
only works for CN470/US915/AU915 gateway.
Null
PingSlot Period
Period of opening the pingslot.
Every Second
PingSlot
DataRate
Datarate of the node receiving downlinks.
Based on the
supported
frequency
PingSlot Freq
Frequency of the node receiving downlinks.
Based on the
supported
frequency
ACK Timeout
The time for confirmed downlink transmissions.
This option is only applicable to class B and class
Class B: 10
Class C: 10

39
C.
Table 3-2-2-9 Device Profiles Advanced Setting Parameters
3.2.2.5 Device
A device is the end-device connecting to, and communicating over the LoRaWAN
®
network.
Figure 3-2-2-12
Item
Description
Add
Add a device.
Bulk Import
Download template and import multiple devices.
Delete All
Delete all devices in the list.
Device Name
Show the name of the device.
Device EUI
Show the EUI of the device.
Device-Profile
Show the name of the device’s device profile.
Application
Show the name of the device’s application.
Last Seen
Show the time of last packet received.
Activated
Show the status of the device . means that the device
has been activated.
Operation
Edit or delete the device.
Table 3-2-2-10 Device Parameters

40
Figure 3-2-2-13
Device Configuration
Item
Description
Device Name
Enter the name of this device.
Description
Enter the description of this device.
Device EUI
Enter the EUI of this device.
Device-Profile
Choose the device profile.
Application
Choose the application profile.
Payload Codec
Choose the payload codec existed on Payload Codec page.
fPort
Enter the downlink port of device, it’s 85 by default for Milesight
devices.
Modbus RTU
Data
Transmission
Choose from: "Disable", "Modbus RTU to TCP", "Modbus RTU over
TCP". This feature is only applicable to Milesight LoRaWAN
®
controllers.(UC501/UC300, etc.)
Modbus RTU to TCP: TCP client can send Modbus TCP commands
to ask for controller Modbus data.
Modbus RTU over TCP: TCP client can send Modbus RTU commands
to ask for controller Modbus data.
Modbus RTU
Fport
Enter the LoRaWAN
®
frame port for transparent transmission
between Milesight LoRaWAN
®
controllers and UG65.

41
Range: 2-84, 86-223.
Note: this value must be the same as the Milesight LoRaWAN
®
controller’s fPort.
TCP Port
Enter the TCP port for data transmission between the TCP Client and
UG65 (as TCP Server).Range: 1-65535.
Frame-Counter
Validation
If disable the frame-counter validation, it will compromise security as
it enables people to perform replay-attacks.
Application Key
Whenever an end-device joins a network via over-the-air activation,
the application key is used for derive the Application Session key.
Device Address
The device address identifies the end-device within
the current network.
Network
Session Key
The network session key specific for the end-device. It is used by the
end-device to calculate the MIC or part of the MIC (message integrity
code) of all uplink data messages to ensure data integrity.
Application
Session Key
The AppSKey is an application session key specific for the
end-device. It is used by both the application server and the
end-device to encrypt and decrypt the payload field of
application-specific data messages.
Uplink
Frame-counter
The number of data frames which sent uplink to the network server.
It will be incremented by the end-device and received by the
end-device.
Users can reset the a personalized end-device manually, then the
frame counters on the end-device and the frame counters on the
network server for that end-device will be reset to 0.
Downlink
Frame-counter
The number of data frames which received by the end-device
downlink from the network server. It will be incremented by the
network server.
Users can reset the a personalized end-device manually, then the
frame counters on the end-device and the frame counters on the
network server for that end-device will be reset to 0.
Table 3-2-2-11 Device Setting Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Device configuration
3.2.2.6 Multicast Groups
Milesight gateways support for creating Class B or Class C multicast groups to send
downlink messages to a group of end devices. A multicast group is a virtual ABP device (i.e.
shared session keys), does not support uplink, confirmed downlink nor MAC commands.

42
Figure 3-2-2-14
Item
Description
Add
Add a multicast group.
Group Name
Show the name of the group.
Number of Devices
Show the device number of the group.
Operation
Edit or delete the multicast group.
Table 3-2-2-12 Multicast Group Parameters
Figure 3-2-2-15
Multicast Group Configuration
Item
Description
Group Name
Enter the name of this multicast group.
Multicast Address
Device address (Dev Addr) of all devices in this group.
Multicast Network
Session Key
The network session key (Netwks Key) of all devices in this group.
Multicast
Application
Session Key
The application session key (AppSKey) of all devices in this
group.

43
Class Type
Class B and Class C are optional.
Datarate
Datarate of the node receiving downlinks.
Frequency
Downlink frequency of all devices in this group.
Frame-counter
The number of data frames which received by the end-device
downlink from the network server. It will be incremented by the
network server.
Ping Slot
Periodicity
Period of opening the pingslot. This is only applied to Class B end
devices.
Selected Devices
Show all device names in this group.
Add Device
Add devices in the pull-down list.
Table 3-2-2-13 Multicast Group Setting Parameters
3.2.2.7 Gateway Fleet
Milesight gateways can connect to UG65 network server. It is suggested to add not more
than 5 gateways.
Figure 3-2-2-16
Item
Description
Gateway ID
Show the gateway ID.
Name
Show the name of the gateway.
Status
Show the connection status of the gateway.
Last Seen
Show the time of last packet received.
Operation
Edit or delete the gateway.
Table 3-2-2-14 Gateway Fleet Parameters
Figure 3-2-2-17

44
Item
Description
Gateway ID
Enter the unique gateway ID to recognize the gateway.
Name
Enter the name of this gateway.
Location
GPS data of the gateway can be edited here. If gateway sends GPS
data it will replace your customized data.
Table 3-2-2-15 Gateway Setting Parameters
3.2.2.8 Packets
Figure 3-2-2-18
Send Data To Device/Multicast Group
Item
Description
Device EUI
Enter the EUI of the device to receive
the payload.
Multicast
Group
Select the multicast group to send downlinks. Multicast groups can be
added under Multicast Groups tab.
Type
Choose from: “ASCII”, “hex”, “base64”.
Choose the payload type to enter in the payload Input box.
Payload
Enter the message to be sent to this device.
Port
Enter the LoRaWAN
®
frame port for packet transmission between
device and Network Server.
Confirmed
After enabled, the end device will receive downlink packet and should
answer “confirmed” to the network server. Multicast feature does not
support confirmed downlink.
Table 3-2-2-16 Send Data to Device Parameters
Network Server
Item
Description
Device EUI/Group
Show the EUI of the device or multicast group.
Frequency
Show the used frequency to transmit packets.

45
Datarate
Show the used datarate to transmit packets.
SNR
Show the signal-noise ratio.
RSSI
Show the received signal strength indicator.
Size
Show the size of payload.
Fcnt
Show the frame counter.
Type
Show the type of the packet:
JnAcc - Join Accept Packet
JnReq - Join Request Packet
UpUnc - Uplink Unconfirmed Packet
UpCnf - Uplink Confirmed Packet - ACK response from
network requested
DnUnc - Downlink Unconfirmed Packet
DnCnf - Downlink Confirmed Packet- ACK response from
end-device requested
Time
Show the time of packet was sent or received.
Table 3-2-2-17 Packet Parameters
Click to get more details about the packet. As shown:
Figure 3-2-2-19
Item
Description
Dev
Addr/Multicast
Addr
Show the address of the device/multicast group.
GwEUI
Show the EUI of the gateway.
AppEUI
Show the EUI of the application.
DevEUI/Group
Name
Show the EUI of the device/multicast group name.
Class Type
Show the class type of the device or multicast group.

46
Immediately
True: Device may transmit an explicit (possibly empty)
acknowledgement data message immediately after the reception of a
data message requiring a confirmation.
Timestamp
Show the timestamp of this packet.
Type
Show the type of the packet:
JnAcc - Join Accept Packet
JnReq - Join Request Packet
UpUnc - Uplink Unconfirmed Packet
UpCnf - Uplink Confirmed Packet - ACK response from network
requested
DnUnc - Downlink Unconfirmed Packet
DnCnf - Downlink Confirmed Packet- ACK response from end-device
requested
Adr
True: The end-node has enabled ADR.
False: The end-node has not enabled ADR.
AdrAcKReq
In order to validate that the network is receiving the uplink messages,
nodes periodically transmit ADRACKReq message. This is 1 bit long.
True: Network should respond in ADR_ACK_DELAY time to confirm that
it is receiving the uplink messages.
False: ADR is disabled or Network does not respond in
ADR_ACK_DELAY.
Ack
True: This frame is ACK.
False: This frame is not ACK.
Fcnt
Show the frame-counter of this packet.The network server tracks the
uplink frame counter and generates the
downlink counter for each end-device.
FPort
FPort is a multiplexing port field. If the frame payload field is not
empty, the port field must be present. If present, a FPort
16 value of 0 indicates that the FRMPayload contains MAC commands
only.When this is the case, the FOptsLen field must be zero. FOptsLen
is the length of the FOpts field in bytes.
Modulation
LoRa means the physical layer uses the LoRa modulation.
Bandwidth
Show the bandwidth of this channel.
SpreadFactor
Show the spreadFactor of this channel.
Bitrate
Show the bitrate of this channel.
CodeRate
Show the coderate of this channel.
SNR
Show the SNR of this channel.
RSSI
Show the RSSI of this channel.
Power
Show the transmit power of the device.
Payload (b64)
Show the application payload of this packet.
Payload (hex)
Show the application payload of this packet.
Json
Show the data after decoded.
MIC
Show the MIC of this packet. MIC is a cryptographic message integrity
code, computed over the fields MHDR, FHDR, FPort and the encrypted

47
FRMPayload.
Table 3-2-2-18 Packets Details Parameters
Related Topic
Send Data to Device
3.3 Protocol Integration
3.3.1 BACnet Server
UG65 can work as LoRaWAN to BACnet gateway to integrate with BMS system easily.
3.3.1.1 Server
Figure 3-3-1-1
Server Settings
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable BACnet server function.
UDP Port
Set communication port of BACnet/IP. Range: 1-65535.
The default port is 47808.
Device ID
The unique BACnet device identifier which needs to avoid conflict
with other devices.
Device Name
The device name to represent the device.
BBMD
Enable BBMD(BACnet/IP Broadcast Management Device) if
BACnet devices of different network subnets should work together.
IP Address
Fill in the IP address of BBMD device or external device registrar.
IP Port
Fill in the UDP/IP port for external device registration.
Time TO Live
Number of seconds used on external device registration.
Table 3-3-1-1 Server Parameters

48
3.3.1.2 BACnet Object
Figure 3-3-1-2
Item
Description
Add
Add a BACnet object. The gateway supports adding 2000
objects at most.
Bulk Import
Download template and import multiple BACnet objects.
Bulk Export
Export all generated BACnet object settings.
Delete All
Delete all objects in the list.
Object Name
Show the name of the BACnet object.
Object Type
Show the type of this object.
Object Instance Nr
Show the instance number of this object.
Present Value
Show the latest value of object.
Units
Show the unit of this object value.
Updates
Show the update times of this object value.
Update time
Show the time for this object to get and update the data.
COV
Show if COV (Change of value) is enabled.
Operation
Edit or delete the object.
Table 3-3-1-2 BACnet Object List Parameters
Figure 3-3-1-3
BACnet Object Configuration
Item
Description
Device Name
Select the device added on Network Server > Device page.

49
LoRa Object
Select one of device variables as an object.
Object Name
Customize an unique name for this object.
Object Type
Select the object type as binary input/output/value or analog
input/output/value.
Unit
Select the unit of this object value.
Description
Enter the description of this object.
COV
When object value changes, the BACnet server (gateway) will send
notification of new value to BACnet client. This only applies to
analog type objects.
COV Increment
Only when the object value reaches or over this increment, the
BACnet server (gateway) will send the notification.
Polarity
Define the binary input/output status as Normal or Reverse.
Active Text
Characterize the intended effect of active state of binary type object
value. Example: when a button is pressed and binary input is 1,
active text can be defined as “Pressed”.
Inactive Text
Characterize the intended effect of inactive state of binary type
object value. Example: for a button, inactive text can be defined as
“Unpressed”.
Relinquish
Default
If there is no command, the analog output or binary output will be
set as this relinquish default value.
Table 3-3-1-3 BACnet Object Configuration Parameters
3.4 Network
3.4.1 Interface
3.4.1.1 Port
The Ethernet port can be connected with Ethernet cable to get Internet access. It supports
3 connection types.
- Static IP: configure IP address, netmask and gateway for Ethernet WAN interface.
- DHCP Client: configure Ethernet WAN interface as DHCP Client to obtain IP address
automatically.
- PPPoE: configure Ethernet WAN interface as PPPoE Client.

50
Figure 3-4-1-1
Port Setting
Item
Description
Default
Port
The port that is fixed as eth0 port and enabled.
eth 0
Connection
Type
Select from "Static IP", "DHCP Client" and "PPPoE".
Static IP
MTU
Set the maximum transmission unit.
1500
Primary DNS
Server
Set the primary DNS.
8.8.8.8
Secondary DNS
Server
Set the secondary DNS.
114.114.114.1
14
Enable NAT
Enable or disable NAT function. When enabled, a
private IP can be translated to a public IP.
Enable
Table 3-4-1-1 Port Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Ethernet Connection
1. Static IP Configuration
If the external network assigns a fixed IP for the Ethernet port, user can select “Static IP”
mode.

51
Figure 3-4-1-2
Static IP
Item
Description
Default
IP Address
Set the IP address which can access Internet.
192.168.23.150
Netmask
Set the Netmask for Ethernet port.
255.255.255.0
Gateway
Set the gateway's IP address for Ethernet port.
192.168.23.1
Multiple IP
Address
Set the multiple IP addresses for Ethernet port.
Null
Table 3-4-1-2 Static IP Parameters
2. DHCP Client
If the external network has DHCP server enabled and has assigned IP addresses to the
Ethernet WAN interface, user can select “DHCP client” mode to obtain IP address
automatically.

52
Figure 3-4-1-3
DHCP Client
Item
Description
Use Peer DNS
Obtain peer DNS automatically during PPP dialing. DNS is
necessary when user visits domain name.
Table 3-4-1-3 DHCP Client Parameters
3. PPPoE
PPPoE refers to a point to point protocol over Ethernet. User has to install a PPPoE client
on the basis of original connection way. With PPPoE, remote access devices can get
control of each user.
Figure 3-4-1-4
PPPoE
Item
Description
Username
Enter the username provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Password
Enter the password provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Link Detection
Interval (s)
Set the heartbeat interval for link detection. Range: 1-600.
Max Retries
Set the maximum retry times after it fails to dial up. Range: 0-9.
Use Peer DNS
Obtain peer DNS automatically during PPP dialing. DNS is necessary
when user visits domain name.
Table 3-4-1-4 PPOE Parameters
3.4.1.2 WLAN
This section explains how to set the related parameters for Wi-Fi network. UG65 supports
802.11 b/g/n, as AP or client mode.

53
Figure 3-4-1-5
Figure 3-4-1-6
WLAN Settings
Item
Description
Enable
Enable/disable WLAN.

54
Work Mode
Select gateway's work mode. The options are "Client" or "AP".
BSSID
Fill in the MAC address of the access point. Either SSID or BSSID
can be filled to joint the network.
SSID
Fill in the SSID of the access point.
Client Mode
Scan
Click "Scan" button to search the nearby access point.
Encryption Mode
Select encryption mode. The options are “No Encryption", “WEP
Open System" , “WEP Shared Key", “WPA-PSK", “WPA2-PSK" ,
“WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK", “WPA-Enterprise”, “WPA2-Enterprise”and
“WPA-Enterprise/WPA2-Enterprise”.
Cipher
Select cipher. The options are “Auto", “AES", “TKIP" and
“AES/TKIP".
Key
Fill the pre-shared key of WEP/WPA encryption.
XSupplicant Type
Select from “Peap”, “Leap”, “TLS” and “TTLS”.
User
Fill the user of WPA/WPA2-Enterprise.
Anonymous
Identity
Fill the anonymous identity of WPA/WPA2-Enterprise.
Phase2
Fill the phase2 of WPA/WPA2-Enterprise.
Public Server
Certificate
The public server certificate used for verifying with
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise access point.
AP Mode
SSID Broadcast
When SSID broadcast is disabled, other wireless devices can't not
find the SSID, and users have to enter the SSID manually to
access to the wireless network.
AP Isolation
When AP isolation is enabled, all users which access to the AP
are isolated without communication with each other.
Radio Type
Select Radio type. The options are “802.11b (2.4 GHz)", “802.11g
(2.4 GHz)", “802.11n (2.4 GHz)””.
Channel
Select wireless channel. The options are "Auto", "1", "2"......"11".
Encryption Mode
Select encryption mode. The options are “No Encryption", “WEP
Open System" , “WEP Shared Key", “WPA-PSK", “WPA2-PSK" and
“WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK".
Cipher
Select cipher. The options are “Auto", “AES", “TKIP" and
“AES/TKIP".
Key
Fill the pre-shared key of WPA encryption.
Bandwidth
Select bandwidth. The options are "20MHz" and "40MHz".
Max Client Number
Set the maximum number of client to access when the gateway
is configured as AP.
IP Setting
Protocol
Set the protocol in wireless network.
IP Address
Set the IP address in wireless network.
Netmask
Set the netmask in wireless network.
Gateway
Set the gateway in wireless network.

55
Table 3-4-1-5 WLAN Parameters
Figure 3-4-1-7
Client Mode-Scan
SSID
Show SSID.
Channel
Show wireless channel.
Signal
Show wireless signal.
BSSID
Show the MAC address of the access point.
Security
Show the encryption mode.
Frequency
Show the frequency of radio.
Join Network
Click the button to join the wireless network.
Table 3-4-1-6 WLAN Scan Parameters
Related Topic
Wi-Fi Application Example
3.4.1.3 Cellular
This section explains how to set the related parameters for cellular network.

56
Figure 3-4-1-8
Figure 3-4-1-9
General Settings
Item
Description
Default
Enable
Check the option to enable the corresponding SIM
card.
Enable
Network Type
Select from "Auto”, "Auto 3G/4G”, "4G Only" and "3G
Only".
Auto: connect to the network with the strongest signal
automatically.
4G Only: connect to 4G network only.
And so on.
Auto
APN
Enter the Access Point Name for cellular dial-up
connection provided by local ISP.
Null
Username
Enter the username for cellular dial-up connection
provided by local ISP.
Null
Password
Enter the password for cellular dial-up connection
provided by local ISP.
Null
Access Number
Enter the dial-up center NO. For cellular dial-up
connection provided by local ISP.
Null
PIN Code
Enter a 4-8 characters PIN code to unlock the SIM.
Null
Authentication
Type
Select from "Auto", "PAP", "CHAP", "MS-CHAP", and
"MS-CHAPv2".
Auto
Roaming
Enable or disable roaming.
Enable
SMS Center
Enter the local SMS center number for storing,
forwarding, converting and delivering SMS message.
Null
Enable NAT
Enable or disable NAT function.
Enabled
Restart When
When this function is enabled, the gateway will restart
Disabled

57
Dial-up failed
automatically if the dial-up fails several times.
ICMP Server
Set the ICMP detection server's IP address.
8.8.8.8
Secondary ICMP
Server
Set the secondary ICMP detection server's IP address.
114.114.11
4.114
ICMP Detection
Max Retries
Set max number of retries when ICMP detection fails.
3
ICMP Detection
Timeout
Set timeout of ICMP detection.
5
ICMP Detection
Interval
Set interval of ICMP detection.
15
SMS Mode
Select SMS mode from “TEXT” and “PDU”.
PDU
Table 3-4-1-7 Cellular Parameters
Figure 3-4-1-10
Item
Description
Connection Mode
Connection Mode
Select from "Always Online" and "Connect on Demand".
Redial Interval(s)
Set the time interval between redials. Range: 0-3600.
Max Idle Time(s)
Set the maximum duration of the gateway when current link is
under idle status. Range: 10-3600.
Triggered by Call
The gateway will switch from offline mode to cellular network
mode automatically when it receives a call from the specific
phone number.
Call Group
Select a call group for call trigger. Go to "System > General
Settings > Phone" to set up phone group.
Triggered by SMS
The gateway will switch from offline mode to cellular network
mode automatically when it receives a specific SMS from the
specific mobile phone.
SMS Group
Select a SMS group for trigger. Go to "System > General
Settings > Phone" to set up SMS group.
SMS Text
Fill in the SMS content for triggering.
Table 3-4-1-8 Cellular Parameters
Related Topics
Cellular Connection Application Example

58
Phone Group
3.4.1.4 Loopback
Loopback interface is used for replacing gateway's ID as long as it is activated. When the
interface is DOWN, the ID of the gateway has to be selected again which leads to long
convergence time of OSPF. Therefore, Loopback interface is generally recommended as
the ID of the gateway.
Loopback interface is a logic and virtual interface on gateway. Under default conditions,
there's no loopback interface on gateway, but it can be created as required.
Figure 3-4-1-11
Loopback
Item
Description
Default
IP Address
Unalterable
127.0.0.1
Netmask
Unalterable
255.0.0.0
Multiple IP
Addresses
Apart from the IP above, user can configure other IP
addresses.
Null
Table 3-4-1-9 Loopback Parameters
3.4.1.5 VLAN Trunk
UG65 gateway supports the Ethernet port working as VLAN Trunk client and be assigned a
VLAN ID, which easy to traffic classification. When VLAN ID is set, port on “Network” >
“Interface” > “Port” can be chosen as eth0.x with x being VLAN ID. VLAN Setting is blank by
default, you can add a new VLAN label to certain interface by clicking .
Figure 3-4-1-12

59
VLAN Trunk
Item
Description
Interface
Select the VLAN interface, it’s fixed as eth0.
VID
Set the label ID of the VLAN. Range: 1-4094.
Table 3-4-1-10 VLAN Trunk Parameters
3.4.2 Firewall
This section describes how to set the firewall parameters, including website block, ACL,
DMZ, Port Mapping and MAC Binding.
The firewall implements corresponding control of data flow at entry direction (from
Internet to local area network) and exit direction (from local area network to Internet)
according to the content features of packets, such as protocol style, source/destination IP
address, etc. It ensures that the gateway operate in a safe environment and host in local
area network.
3.4.2.1 Security
Figure 3-4-2-1
Website Blocking
URL Address
Enter the HTTP address which you want to block.
Keyword
You can block specific website by entering keyword. The
maximum number of character allowed is 64.
Table 3-2-2-1 Security Parameters
3.4.2.2 ACL
Access control list, also called ACL, implements permission or prohibition of access for
specified network traffic (such as the source IP address) by configuring a series of
matching rules so as to filter the network interface traffic. When gateway receives packet,
the field will be analyzed according to the ACL rule applied to the current interface. After

60
the special packet is identified, the permission or prohibition of corresponding packet will
be implemented according to preset strategy.
The data package matching rules defined by ACL can also be used by other functions
requiring flow distinction.
Figure 3-4-2-2
Item
Description
ACL Setting
Default Filter Policy
Select from "Accept" and "Deny".
The packets which are not included in the access control list will
be processed by the default filter policy.
Access Control List
Type
Select type from "Extended" and "Standard".
ID
User-defined ACL number. Range: 1-199.
Action
Select from "Permit" and "Deny".
Protocol
Select protocol from "ip", "icmp", "tcp", "udp", and "1-255".
Source IP
Source network address (leaving it blank means all).
Source Wildcard
Mask
Wildcard mask of the source network address.
Destination IP
Destination network address (0.0.0.0 means all).
Destination Wildcard
Mask
Wildcard mask of destination address.
Description
Fill in a description for the groups with the same ID.
ICMP Type
Enter the type of ICMP packet. Range: 0-255.
ICMP Code
Enter the code of ICMP packet. Range: 0-255.

61
Source Port Type
Select source port type, such as specified port, port range, etc.
Source Port
Set source port number. Range: 1-65535.
Start Source Port
Set start source port number. Range: 1-65535.
End Source Port
Set end source port number. Range: 1-65535.
Destination Port
Type
Select destination port type, such as specified port, port range,
etc.
Destination Port
Set destination port number. Range: 1-65535.
Start Destination
Port
Set start destination port number. Range: 1-65535.
End Destination Port
Set end destination port number. Range: 1-65535.
More Details
Show information of the port.
Interface List
Interface
Select network interface for access control.
In ACL
Select a rule for incoming traffic from ACL ID.
Out ACL
Select a rule for outgoing traffic from ACL ID.
Table 3-4-2-2 ACL Parameters
3.4.2.3 DMZ
DMZ is a host within the internal network that has all ports exposed, except those
forwarded ports in port mapping.
Figure 3-4-2-3
DMZ
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable DMZ.
DMZ Host
Enter the IP address of the DMZ host on the internal network.
Source Address
Set the source IP address which can access to DMZ host.
"0.0.0.0/0" means any address.
Table 3-4-2-3 DMZ Parameters
3.4.2.4 Port Mapping
Port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a
communication request from the combination of an address and port number to another
while the packets are traversing a network gateway such as a gateway or firewall.

62
Click to add a new port mapping rules.
Figure 3-4-2-4
Port Mapping
Item
Description
Source IP
Specify the host or network which can access local IP address.
0.0.0.0/0 means all.
Source Port
Enter the TCP or UDP port from which incoming packets are
forwarded. Range: 1-65535.
Destination IP
Enter the IP address that packets are forwarded to after being
received on the incoming interface.
Destination Port
Enter the TCP or UDP port that packets are forwarded to after
being received on the incoming port(s). Range: 1-65535.
Protocol
Select from "TCP" and "UDP" as your application required.
Description
The description of this rule.
Table 3-4-2-4 Port Mapping Parameters
Related Configuration Example
NAT Application Example
3.4.2.5 MAC Binding
MAC Binding is used for specifying hosts by matching MAC addresses and IP addresses
that are in the list of allowed outer network access.
Figure 3-4-2-5

63
MAC Binding List
Item
Description
MAC Address
Set the binding MAC address.
IP Address
Set the binding IP address.
Description
Fill in a description for convenience of recording the meaning of the
binding rule for each piece of MAC-IP.
Table 3-4-2-5 MAC Binding Parameters
3.4.3 DHCP
UG65 can be set as a DHCP server to distribute IP address when Wi-Fi work as AP mode.
Figure 3-4-3-1
DHCP Server
Item
Description
Default
Enable
Enable or disable DHCP server.
Enable
Interface
Only wlan interface is allowed to distribute IP
addresses.
wlan0
Start
Address
Define the beginning of the pool of IP addresses
which will be leased to DHCP clients.
192.168.1.100
End Address
Define the end of the pool of IP addresses which will
be leased to DHCP clients.
192.168.1.199
Netmask
Define the subnet mask of IP address obtained by
DHCP clients from DHCP server.
255.255.255.0

64
Lease Time
(Min)
Set the lease time on which the client can use the IP
address obtained from DHCP server. Range: 1-10080.
1440
Primary
DNS Server
Set the primary DNS server.
114.114.114.114
Secondary
DNS Server
Set the secondary DNS server.
Null
Windows
Name
Server
Define the Windows Internet Naming Service obtained
by DHCP clients from DHCP sever. Generally you can
leave it blank.
Null
Static IP
MAC
Address
Set a static and specific MAC address for the DHCP
client (it should be different from other MACs so as to
avoid conflict).
Null
IP Address
Set a static and specific IP address for the DHCP
client (it should be outside of the DHCP range).
Null
Table 3-4-3-1 DHCP Server Parameters
3.4.4 DDNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a method that automatically updates a name server in the Domain
Name System, which allows user to alias a dynamic IP address to a static domain name.
DDNS serves as a client tool and needs to coordinate with DDNS server. Before starting
configuration, user shall register on a website of proper domain name provider and apply
for a domain name.
Figure 3-4-4-1
DDNS
Item
Description
Name
Give the DDNS a descriptive name.
Interface
Set interface bundled with the DDNS.
Service Type
Select the DDNS service provider.
Username
Enter the username for DDNS register.
User ID
Enter User ID of the custom DDNS server.
Password
Enter the password for DDNS register.
Server
Enter the name of DDNS server.
Hostname
Enter the hostname for DDNS.

65
Append IP
Append your current IP to the DDNS server update path.
Table 3-4-4-1 DDNS Parameters
3.4.5 Link Failover
This section describes how to configure link failover strategies, such as VRRP strategies.
Configuration Steps
1. Define one or more SLA operations (ICMP probe).
2. Define one or more track objects to track the status of SLA operation.
3. Define applications associated with track objects, such as VRRP or static routing.
3.4.5.1 SLA
SLA setting is used for configuring link probe method. The default probe type is ICMP.
Figure 3-4-5-1
SLA
Item
Description
Default
ID
SLA index. Up to 10 SLA settings can be added.
Range: 1-10.
1
Type
ICMP-ECHO is the default type to detect if the
link is alive.
icmp-echo
Destination Address
The detected IP address.
114.114.114.11
4
Secondary
Destination Address
The secondary detected IP address.
8.8.8.8
Data Size
User-defined data size. Range: 0-1000.
56
Interval (s)
User-defined detection interval. Range: 1-608400.
30
Timeout (ms)
User-defined timeout for response to determine
ICMP detection failure. Range: 1-300000.
5000
Packet Loss Count
Define packet loss count in each SLA probe. SLA
probe fails when the preset packet loss count is
exceeded.
5

66
Start Time
Detection start time; select from "Now" and blank
character. Blank character means this SLA
detection doesn't start.
now
Table 3-4-5-1 SLA Parameters
3.4.5.2 Track
Track setting is designed for achieving linkage among SLA module, Track module and
Application module. Track setting is located between application module and SLA module
with main function of shielding the differences of various SLA modules and providing
unified interfaces for application module.
Linkage between Track Module and SLA module
Once you complete the configuration, the linkage relationship between Track module and
SLA module will be established. SLA module is used for detection of link status, network
performance and notification of Track module. The detection results help track status
change timely.
- For successful detection, the corresponding track item is Positive.
- For failed detection, the corresponding track item is Negative.
Linkage between Track Module and Application Module
After configuration, the linkage relationship between Track module and Application module
will be established. When any change occurs in track item, a notification that requires
corresponding treatment will be sent to Application module.
Currently, the application modules like VRRP and static routing can get linkage with track
module.
If it sends an instant notification to Application module, the communication may be
interrupted in some circumstances due to routing's failure like timely restoration or other
reasons. Therefore, user can set up a period of time to delay notifying application module
when the track item status changes.
Figure 3-4-5-2
Item
Description
Default
Index
Track index. Up to 10 track settings can be
configured. Range: 1-10.
1
Type
The options are "sla" and "interface".
SLA
SLA ID
Defined SLA ID.
1

67
Interface
Select the interface whose status will be detected.
cellular0
Negative Delay (s)
When interface is down or SLA probing fails, it will
wait according to the time set here before actually
changing its status to Down. Range: 0-180 (0 refers
to immediate switching).
0
Positive Delay (s)
When failure recovery occurs, it will wait according
to the time set here before actually changing its
status to Up. Range: 0-180 (0 refers to immediate
switching).
1
Table 3-4-5-2 Track Parameters
3.4.5.3 WAN Failover
WAN failover refers to failover between Ethernet WAN interface and cellular interface.
When service transmission can’t be carried out normally due to malfunction of a certain
interface or lack of bandwidth, the rate of flow can be switched to backup interface quickly.
Then the backup interface will carry out service transmission and share network flow so as
to improve reliability of communication of data equipment.
When link state of main interface is switched from up to down, system will have the pre-set
delay works instead of switching to link of backup interface immediately. Only if the state
of main interface is still down after delay, will the system switch to link of backup interface.
Otherwise, system will remain unchanged.
Figure 3-4-5-3
WAN Failover
Parameters
Description
Default
Main Interface
Select a link interface as the main link.
--
Backup Interface
Select a link interface as the backup link.
--
Startup Delay (s)
Set how long to wait for the startup tracking detection policy
to take effect. Range: 0-300.
30
Up Delay (s)
When the primary interface switches from failed detection
to successful detection, switching can be delayed based on
the set time. Range: 0-180 (0 refers to immediate switching)
0
Down Delay (s)
When the primary interface switches from successful
0

68
detection to failed detection, switching can be delayed
based on the set time. Range: 0-180 (0 refers to immediate
switching).
Track ID
Track detection, select the defined track ID.
--
Table 3-4-5-3 WAN Failover Parameters
3.4.6 VPN
Virtual Private Networks, also called VPNs, are used to securely connect two private
networks together so that devices can connect from one network to the other network via
secure channels.
UG65 supports DMVPN, IPsec, GRE, L2TP, PPTP, OpenVPN, as well as GRE over IPsec and
L2TP over IPsec.
3.4.6.1 DMVPN
A dynamic multi-point virtual private network (DMVPN), combining mGRE and IPsec, is a
secure network that exchanges data between sites without passing traffic through an
organization's headquarter VPN server or gateway.
Figure 3-4-6-1

69
Figure 3-4-6-2
DMVPN
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable DMVPN.
Hub Address
The IP address or domain name of DMVPN Hub.
Local IP address
DMVPN local tunnel IP address.
GRE Hub IP Address
GRE Hub tunnel IP address.
GRE Local IP Address
GRE local tunnel IP address.
GRE Netmask
GRE local tunnel netmask.
GRE Key
GRE tunnel key.
Negotiation Mode
Select from "Main" and "Aggressive".
Authentication
Algorithm
Select from "DES", "3DES", "AES128", "AES192" and
"AES256".
Encryption Algorithm
Select from "MD5" and "SHA1".
DH Group
Select from "MODP768_1", "MODP1024_2" and
"MODP1536_5".
Key
Enter the preshared key.
Local ID Type
Select from "Default", "ID", "FQDN", and "User FQDN"
IKE Life Time (s)
Set the lifetime in IKE negotiation. Range: 60-86400.
SA Algorithm
Select from "DES_MD5", "DES_SHA1", "3DES_MD5",
"3DES_SHA1", "AES128_MD5", "AES128_SHA1",
"AES192_MD5", "AES192_SHA1", "AES256_MD5" and
"AES256_SHA1".
PFS Group
Select from "NULL", "MODP768_1", "MODP1024_2" and
"MODP1536-5".
Life Time (s)
Set the lifetime of IPsec SA. Range: 60-86400.
DPD Interval Time (s)
Set DPD interval time
DPD Timeout (s)
Set DPD timeout.
Cisco Secret
Cisco Nhrp key.
NHRP Holdtime (s)
The holdtime of Nhrp protocol.
Table 3-4-6-1 DMVPN Parameters
3.4.6.2 IPSec
IPsec is especially useful for implementing virtual private networks and for remote user
access through dial-up connection to private networks. A big advantage of IPsec is that
security arrangements can be handled without requiring changes to individual user
computers.
IPsec provides three choices of security service: Authentication Header (AH),
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP), and Internet Key Exchange (IKE). AH essentially
allows authentication of the senders’ data. ESP supports both authentication of the sender
and data encryption. IKE is used for cipher code exchange. All of them can protect one and
more data flows between hosts, between host and gateway, and between gateways.

70
Figure 3-4-6-3
IPsec
Item
Description
Enable
Enable IPsec tunnel. A maximum of 3 tunnels is allowed.
IPsec Gateway Address
Enter the IP address or domain name of remote IPsec
server.
IPsec Mode
Select from "Tunnel" and "Transport".
IPsec Protocol
Select from "ESP" and "AH".
Local Subnet
Enter the local subnet IP address that IPsec protects.
Local Subnet Netmask
Enter the local netmask that IPsec protects.
Local ID Type
Select from "Default", "ID", "FQDN", and "User FQDN".
Remote Subnet
Enter the remote subnet IP address that IPsec protects.
Remote Subnet Mask
Enter the remote netmask that IPsec protects.
Remote ID type
Select from "Default", "ID", "FQDN", and "User FQDN".
Table 3-4-6-2 IPsec Parameters

71
Figure 3-4-6-4
IKE Parameter
Item
Description
IKE Version
Select from "IKEv1" and "IKEv2".
Negotiation Mode
Select from "Main" and "Aggressive".
Encryption Algorithm
Select from "DES", "3DES", "AES128", "AES192" and "AES256".
Authentication
Algorithm
Select from "MD5" and " SHA1"
DH Group
Select from "MODP768_1", "MODP1024_2" and "MODP1536_5".
Local Authentication
Select from "PSK" and "CA".
Local Secrets
Enter the preshared key.
XAUTH
Enter XAUTH username and password after XAUTH is enabled.
Lifetime (s)
Set the lifetime in IKE negotiation. Range: 60-86400.
SA Parameter
SA Algorithm
Select from "DES_MD5", "DES_SHA1", "3DES_MD5",
"3DES_SHA1", "AES128_MD5", "AES128_SHA1", "AES192_MD5",
"AES192_SHA1", "AES256_MD5" and "AES256_SHA1".
PFS Group
Select from "NULL", "MODP768_1" , "MODP1024_2" and
"MODP1536_5".
Lifetime (s)
Set the lifetime of IPsec SA. Range: 60-86400.

72
DPD Interval Time(s)
Set DPD interval time to detect if the remote side fails.
DPD Timeout(s)
Set DPD timeout. Range: 10-3600.
IPsec Advanced
Enable Compression
The head of IP packet will be compressed after it's enabled.
VPN Over IPsec Type
Select from "NONE", "GRE" and "L2TP" to enable VPN over
IPsec function.
Table 3-4-6-3 IPsec Parameters
3.4.6.3 GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a protocol that encapsulates packets in order to
route other protocols over IP networks. It’s a tunneling technology that provides a channel
through which encapsulated data message can be transmitted and encapsulation and
decapsulation can be realized at both ends.
In the following circumstances the GRE tunnel transmission can be applied:
- GRE tunnel can transmit multicast data packets as if it were a true network interface.
Single use of IPSec cannot achieve the encryption of multicast.
- A certain protocol adopted cannot be routed.
- A network of different IP addresses shall be required to connect other two similar
networks.
Figure 3-4-6-5
GRE
Item
Description
Enable
Check to enable GRE function.

73
Remote IP Address
Enter the real remote IP address of GRE tunnel.
Local IP Address
Set the local IP address.
Local Virtual IP
Address
Set the local tunnel IP address of GRE tunnel.
Netmask
Set the local netmask.
Peer Virtual IP Address
Enter remote tunnel IP address of GRE tunnel.
Global Traffic
Forwarding
All the data traffic will be sent out via GRE tunnel when this
function is enabled.
Remote Subnet
Enter the remote subnet IP address of GRE tunnel.
Remote Netmask
Enter the remote netmask of GRE tunnel.
MTU
Enter the maximum transmission unit. Range: 64-1500.
Key
Set GRE tunnel key.
Enable NAT
Enable NAT traversal function.
Table 3-4-6-4 GRE Parameters
3.4.6.4 L2TP
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is an extension of the Point-to-Point Tunneling
Protocol (PPTP) used by an Internet service provider (ISP) to enable the operation of a
virtual private network (VPN) over the Internet.
Figure 3-4-6-6
L2TP
Item
Description
Enable
Check to enable L2TP function.
Remote IP Address
Enter the public IP address or domain name of L2TP server.

74
Username
Enter the username that L2TP server provides.
Password
Enter the password that L2TP server provides.
Authentication
Select from "Auto", "PAP", "CHAP", "MS-CHAPv1" and
"MS-CHAPv2".
Global Traffic
Forwarding
All of the data traffic will be sent out via L2TP tunnel after
this function is enabled.
Remote Subnet
Enter the remote IP address that L2TP protects.
Remote Subnet Mask
Enter the remote netmask that L2TP protects.
Key
Enter the password of L2TP tunnel.
Use L2TP Peer DNS
Enable to use the DNS address of peer L2TP server .
Table 3-4-6-5 L2TP Parameters
Figure 3-4-6-7
Advanced Settings
Item
Description
Local IP Address
Set tunnel IP address of L2TP client. Client will obtain
tunnel IP address automatically from the server when it's
null.
Peer IP Address
Enter tunnel IP address of L2TP server.
Enable NAT
Enable NAT traversal function.
Enable MPPE
Enable MPPE encryption.
Address/Control
Compression
For PPP initialization. User can keep the default option.
Protocol Field
Compression
For PPP initialization. User can keep the default option.
Asyncmap Value
One of the PPP protocol initialization strings. User can keep
the default value. Range: 0-ffffffff.

75
MRU
Set the maximum receive unit. Range: 64-1500.
MTU
Set the maximum transmission unit. Range: 64-1500
Link Detection Interval
(s)
Set the link detection interval time to ensure tunnel
connection. Range: 0-600.
Max Retries
Set the maximum times of retry to detect the L2TP
connection failure. Range: 0-10.
Expert Options
User can enter some other PPP initialization strings in this
field and separate the strings with blank space.
Table 3-4-6-6 L2TP Parameters
3.4.6.5 PPTP
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a protocol that allows corporations to extend
their own corporate network through private "tunnels" over the public Internet. Effectively, a
corporation uses a wide-area network as a single large local area network.
Figure 3-4-6-8
PPTP
Item
Description
Enable
Enable PPTP client. A maximum of 3 tunnels is allowed.
Remote IP Address
Enter the public IP address or domain name of PPTP
server.
Username
Enter the username that PPTP server provides.
Password
Enter the password that PPTP server provides.
Authentication
Select from "Auto", "PAP", "CHAP", "MS-CHAPv1", and
"MS-CHAPv2".
Global Traffic
Forwarding
All of the data traffic will be sent out via PPTP tunnel once
enable this function.
Remote Subnet
Set the peer subnet of PPTP.

76
Remote Subnet
Mask
Set the netmask of peer PPTP server.
Table 3-4-6-7 PPTP Parameters
Figure 3-4-6-9
PPTP Advanced Settings
Item
Description
Local IP Address
Set IP address of PPTP client.
Peer IP Address
Enter tunnel IP address of PPTP server.
Enable NAT
Enable the NAT faction of PPTP.
Enable MPPE
Enable MPPE encryption.
Address/Control
Compression
For PPP initialization. User can keep the default option.
Protocol Field
Compression
For PPP initialization. User can keep the default option.
Asyncmap Value
One of the PPP protocol initialization strings. User can keep
the default value. Range: 0-ffffffff.
MRU
Enter the maximum receive unit. Range: 0-1500.
MTU
Enter the maximum transmission unit. Range: 0-1500.
Link Detection Interval
(s)
Set the link detection interval time to ensure tunnel
connection. Range: 0-600.
Max Retries
Set the maximum times of retrying to detect the PPTP
connection failure. Range: 0-10.
Expert Options
User can enter some other PPP initialization strings in this
field and separate the strings with blank space.
Table 3-4-6-8 PPTP Parameters

77
3.4.6.6 OpenVPN Client
OpenVPN is an open source virtual private network (VPN) product that offers a simplified
security framework, modular network design, and cross-platform portability.
Advantages of OpenVPN include:
- Security provisions that function against both active and passive attacks.
- Compatibility with all major operating systems.
- High speed (1.4 megabytes per second typically).
- Ability to configure multiple servers to handle numerous connections simultaneously.
- All encryption and authentication features of the OpenSSL library.
- Advanced bandwidth management.
- A variety of tunneling options.
- Compatibility with smart cards that support the Windows Crypt application program
interface (API).
Figure 3-4-6-10
OpenVPN Client
Item
Description
Enable
Enable OpenVPN client. A maximum of 3 tunnels is allowed.

78
Protocol
Select from "UDP" and "TCP".
Remote IP Address
Enter remote OpenVPN server's IP address or domain name.
Port
Enter the listening port number of remote OpenVPN server.
Range: 1-65535.
Interface
Select from "tun" and "tap".
Authentication
Select from "None", "Pre-shared", "Username/Password",
"X.509 cert", and "X.509 cert+user".
Local Tunnel IP
Set local tunnel address.
Remote Tunnel IP
Enter remote tunnel address.
Global Traffic
Forwarding
All the data traffic will be sent out via OpenVPN tunnel when
this function is enabled.
Enable TLS
Authentication
Check to enable TLS authentication.
Username
Enter username provided by OpenVPN server.
Password
Enter password provided by OpenVPN server.
Enable NAT
Enable NAT traversal function.
Compression
Select LZO to compress data.
Link Detection Interval
(s)
Set link detection interval time to ensure tunnel connection.
Range: 10-1800.
Link Detection Timeout
(s)
Set link detection timeout. OpenVPN will be reestablished
after timeout. Range: 60-3600.
Cipher
Select from "NONE", "BF-CBC", "DE-CBC", "DES-EDE3-CBC",
"AES-128-CBC", "AES-192-CBC" and "AES-256-CBC".
MTU
Enter the maximum transmission unit. Range: 128-1500.
Max Frame Size
Set the maximum frame size. Range: 128-1500.
Verbose Level
Select from "ERROR", "WARING", "NOTICE" and "DEBUG".
Expert Options
User can enter some other initialization strings in this field
and separate the strings with semicolon.
Local Route
Subnet
Set the local route's IP address.
Subnet Mask
Set the local route's netmask.
Table 3-4-6-9 OpenVPN Client Parameters
3.4.6.7 OpenVPN Server
UG65 supports OpenVPN server to create secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections
in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities.

79
Figure 3-4-6-11
Figure 3-4-6-12
OpenVPN Server
Item
Description
Enable
Enable/disable OpenVPN server.
Protocol
Select from TCP and UDP.
Port
Fill in listening port number. Range: 1-65535.
Listening IP
Enter WAN IP address or LAN IP address. Leaving it blank
refers to all active WAN IP and LAN IP address.
Interface
Select from " tun" and "tap".
Authentication
Select from "None", "Pre-shared", "Username/Password",
"X.509 cert" and "X. 509 cert +user".
Local Virtual IP
The local tunnel address of OpenVPN's tunnel.

80
Remote Virtual IP
The remote tunnel address of OpenVPN's tunnel.
Client Subnet
Local subnet IP address of OpenVPN client.
Client Netmask
Local netmask of OpenVPN client.
Renegotiation Interval(s)
Set interval for renegotiation. Range: 0-86400.
Max Clients
Maximum OpenVPN client number. Range: 1-128.
Enable CRL
Enable CRL
Enable Client to Client
Allow access between different OpenVPN clients.
Enable Dup Client
Allow multiple users to use the same certification.
Enable NAT
Check to enable the NAT traversal function.
Compression
Select "LZO" to compress data.
Link Detection Interval
Set link detection interval time to ensure tunnel connection.
Range: 10-1800.
Cipher
Select from "NONE", "BF-CBC", "DES-CBC", "DES-EDE3-CBC",
"AES-128-CBC", "AES-192-CBC" and "AES-256-CBC".
MTU
Enter the maximum transmission unit. Range: 64-1500.
Max Frame Size
Set the maximum frame size. Range: 64-1500.
Verbose Level
Select from "ERROR", "WARING", "NOTICE" and "DEBUG".
Expert Options
User can enter some other initialization strings in this field
and separate the strings with semicolon.
Local Route
Subnet
The real local IP address of OpenVPN client.
Netmask
The real local netmask of OpenVPN client.
Account
Username & Password
Set username and password for OpenVPN client.
Table 3-4-6-10 OpenVPN Server Parameters
3.4.6.8 Certifications
User can import/export certificate and key files for OpenVPN and IPsec on this page.
Figure 3-4-6-13
OpenVPN Client
Item
Description
CA
Import/Export CA certificate file.

81
Public Key
Import/Export public key file.
Private Key
Import/Export private key file.
TA
Import/Export TA key file.
Preshared Key
Import/Export static key file.
PKCS12
Import/Export PKCS12 certificate file.
Table 3-4-6-11 OpenVPN Client Certification Parameters
Figure 3-4-6-14
OpenVPN Server
Item
Description
CA
Import/Export CA certificate file.
Public Key
Import/Export public key file.
Private Key
Import/Export private key file.
DH
Import/Export DH key file.
TA
Import/Export TA key file.
CRL
Import/Export CRL.
Preshared Key
Import/Export static key file.
Table 3-4-6-12 OpenVPN Server Parameters
Figure 3-4-6-15

82
IPsec
Item
Description
CA
Import/Export CA certificate.
Client Key
Import/Export client key.
Server Key
Import/Export server key.
Private Key
Import/Export private key.
CRL
Import/Export certificate recovery list.
Table 3-4-6-13 IPsec Parameters
3.5 System
This section describes how to configure general settings, such as administration account,
access service, system time, common user management, SNMP, event alarms, etc.
3.5.1 General Settings
3.5.1.1 General
General settings include system info, access service and HTTPS certificates.
Figure 3-5-1-1
General
Item
Description
Default
System
Hostname
User-defined gateway name, needs to start with a letter.
GATEWAY

83
Web Login
Timeout (s)
You need to log in again if it times out. Range: 100-3600.
1800
Access Service
Port
Set port number of the services. Range: 1-65535.
--
HTTP
Users can log in the device locally via HTTP to access
and control it through Web after the option is checked.
80
HTTPS
Users can log in the device locally and remotely via
HTTPS to access and control it through Web after
option is checked.
443
TELNET
Users can log in the device locally and remotely via
TELNET to access and control it through Web after
option is checked.
23
SSH
Users can log in the device locally and remotely via SSH
after the option is checked.
22
HTTPS Certificates
Certificate
Click "Browse" button, choose certificate file on the PC,
and then click "Import" button to upload the file into
gateway. Click "Export" button will export the file to the
PC. Click "Delete" button will delete the file.
--
Key
Click "Browse" button, choose key file on the PC, and
then click "Import" button to upload the file into gateway.
Click "Export" button will export file to the PC.
Click "Delete" button will delete the file.
--
Table 3-5-1-1 General Setting Parameters
3.5.1.2 System Time
This section explains how to set the system time including time zone and time
synchronization type.
Note: to ensure that the gateway runs with the correct time, it’s recommended that you set
the system time when configuring the gateway.
Figure 3-5-1-2

84
Figure 3-5-1-3
Figure 3-5-1-4
System Time
Item
Description
Current Time
Show the current system time.
Time Zone
Click the drop down list to select the time zone you are in.
Sync Type
Click the drop down list to select the time synchronization
type.
Sync with Browser
Synchronize time with browser.
Browser Time
Show the current time of browser.
Set up Manually
Manually configure the system time.
Sync with NTP Server
Synchronize time with NTP server so as to achieve time
synchronization of all devices equipped with a clock on
network.
Sync with NTP Server
NTP Server Address
Set NTP server address (domain name/IP).
Enable NTP Server
NTP client on the network can achieve time synchronization
with gateway after "Enable NTP Server" option is checked.
Table 3-5-1-2 System Time Parameters

85
3.5.1.3 SMTP
SMTP, short for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is a TCP/IP protocol used in sending and
receiving e-mail. This section describes how to configure email settings.
Figure 3-5-1-5
SMTP
Item
Description
SMTP Client Settings
Enable
Enable or disable SMTP client function.
Email Address
Enter the sender's email account.
Password
Enter the sender's email password.
SMTP Server Address
Enter SMTP server's domain name.
Port
Enter SMTP server port. Range: 1-65535.
Enable TLS
Enable or disable TLS encryption.
Table 3-5-1-3 SMTP Setting
Related Topics
Events Setting
3.5.1.4 Phone
Phone settings involve in call/SMS trigger and SMS alarm for events. This is only applied to
gateway with cellular feature.

86
Figure 3-5-1-6
Phone
Item
Description
Phone Number List
Name
Set phone group name.
Number
Enter the telephone number. Digits, "+" and "-" are allowed.
You can divide multiple numbers by “;”.
Table 3-5-1-4 Phone Settings
Related Topic
Connect on Demand
3.5.1.5 Email
Email settings involve email alarm for events.
Figure 3-5-1-7
Email
Item
Description
Email List
Name
Set Email group name.
Email Address
Enter the Email address. You can divide multiple Email
addresses by “;”.
Table 3-5-1-5 Email Settings

87
3.5.2 User Management
3.5.2.1 Account
Here you can change the login username and password of the administrator.
Note: it is strongly recommended that you modify them for the sake of security.
Figure 3-5-2-1
Account
Item
Description
Username
Enter a new username. You can use characters such as a-z,
0-9, "_", "-", "$". The first character can't be a digit.
Old Password
Enter the old password.
New Password
Enter a new password.
Confirm New Password
Enter the new password again.
Table 3-5-2-1 Account Information
3.5.2.2 User Management
This section describes how to create common user accounts.
The common user permission includes Read-Only and Read-Write.
Figure 3-5-2-2
User Management
Item
Description
Username
Enter a new username. You can use characters such as a-z,
0-9, "_", "-", "$". The first character can't be a digit.
Password
Set password.

88
Permission
Select user permission from “Read-Only” and “Read-Write”.
-
Read-Only: users can only view the configuration of
gateway in this level.
-
Read-Write: users can view and set the configuration of
gateway in this level.
Table 3-5-2-2 User Management
3.5.3 SNMP
SNMP is widely used in network management for network monitoring. SNMP exposes
management data with variables form in managed system. The system is organized in a
management information base (MIB) which describes the system status and configuration.
These variables can be remotely queried by managing applications.
Configuring SNMP in networking, NMS, and a management program of SNMP should be
set up at the Manager.
Configuration steps are listed as below for achieving query from NMS:
1. Enable SNMP setting.
2. Download MIB file and load it into NMS.
3. Configure MIB View.
4. Configure VCAM.
3.5.3.1 SNMP
UG65 supports SNMPv1, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 version. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c employ
community name authentication. SNMPv3 employs authentication encryption by username
and password.
Figure 3-5-3-1
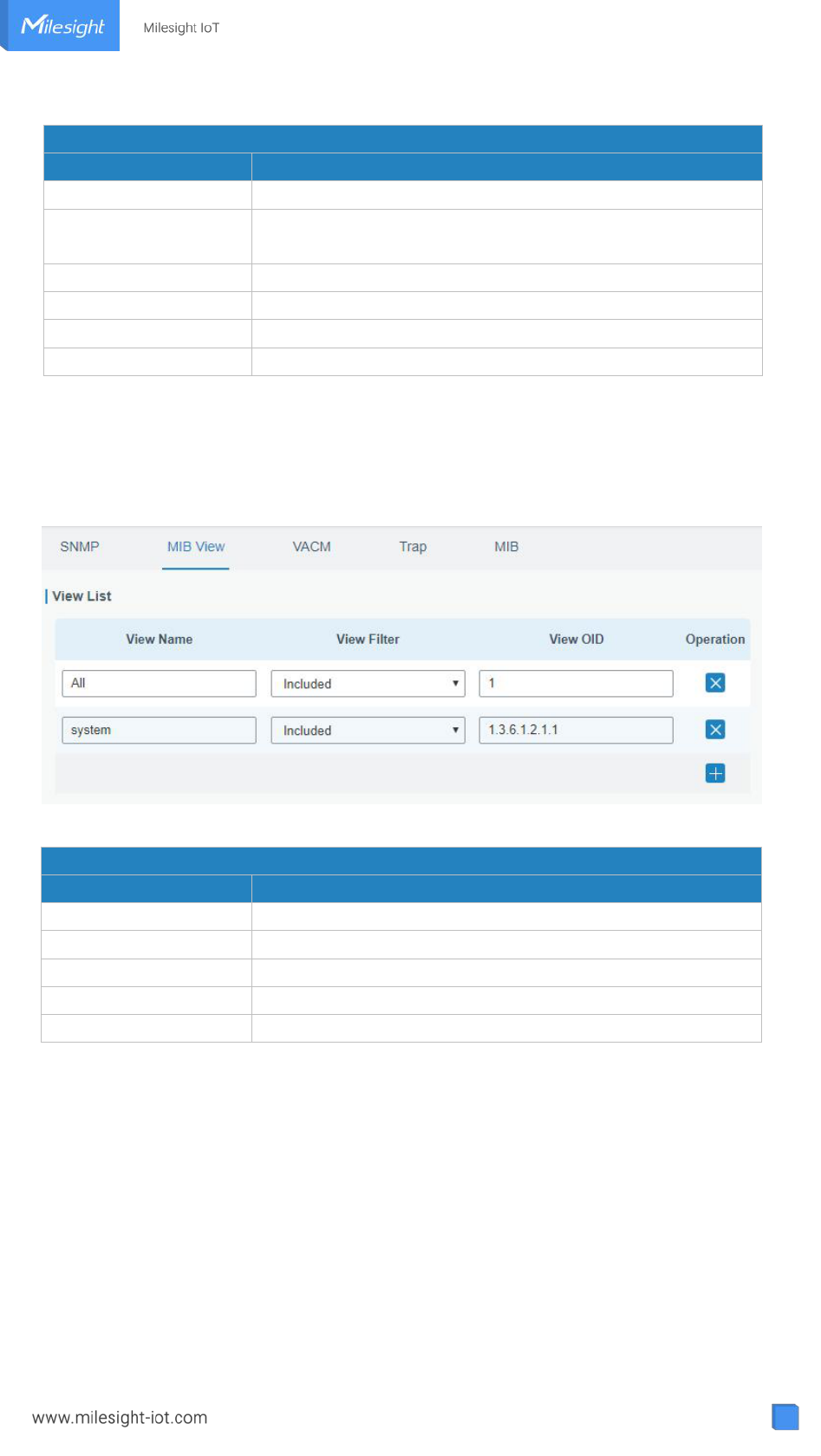
89
SNMP Settings
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable SNMP function.
Port
Set SNMP listened port. Range: 1-65535.
The default port is 161.
System Name
Fill in the system name to represent the gateway.
SNMP Version
Select SNMP version; support SNMP v1/v2c/v3.
Location Information
Fill in the location information.
Contact Information
Fill in the contact information.
Table 3-5-3-1 SNMP Parameters
3.5.3.2 MIB View
This section explains how to configure MIB view for the objects.
Figure 3-5-3-2
MIB View
Item
Description
View Name
Set MIB view's name.
View Filter
Select from "Included" and "Excluded".
View OID
Enter the OID number.
Included
You can query all nodes within the specified MIB node.
Excluded
You can query all nodes except for the specified MIB node.
Table 3-5-3-2 MIB View Parameters
3.5.3.3 VACM
This section describes how to configure VCAM parameters.

90
Figure 3-5-3-3
VACM
Item
Description
SNMP v1 & v2 User List
Community
Set the community name.
Permission
Select from "Read-Only" and "Read-Write".
MIB View
Select an MIB view to set permissions from the MIB view list.
Network
The IP address and bits of the external network accessing the MIB view.
Read-Write
The permission of the specified MIB node is read and write.
Read-Only
The permission of the specified MIB node is read only.
SNMP v3 User List
Group Name
Set the name of SNMPv3 group.
Security Level
Select from "NoAuth/NoPriv", "Auth/NoPriv", and " Auth/Priv".
Read-Only View
Select an MIB view to set permission as "Read-only" from the MIB view
list.
Read-Write View
Select an MIB view to set permission as "Read-write" from the MIB view
list.
Inform View
Select an MIB view to set permission as "Inform" from the MIB view list.
Table 3-5-3-3 VACM Parameters
3.5.3.4 Trap
This section explains how to enable network monitoring by SNMP trap.
Figure 3-5-3-4

91
SNMP Trap
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable SNMP Trap function.
SNMP Version
Select SNMP version; support SNMP v1/v2c/v3.
Server Address
Fill in NMS's IP address or domain name.
Port
Fill in UDP port. Port range is 1-65535. The default port is
162.
Name
Fill in the group name when using SNMP v1/v2c; fill in
the username when using SNMP v3.
Auth/Priv Mode
Select from "NoAuth & No Priv", "Auth & NoPriv", and
"Auth & Priv".
Table 3-5-3-4 Trap Parameters
3.5.3.5 MIB
This section describes how to download MIB files.
Figure 3-5-3-5
MIB
Item
Description
MIB File
Select the MIB file you need.
Download
Click "Download" button to download the MIB file to PC.
Table 3-5-3-5 MIB Download
3.5.4 Device Management
You can connect the device to the DeviceHub on this page so as to manage the gateway
centrally and remotely. For details refer to DeviceHub User Guide.

92
Figure 3-5-4-1
DeviceHub
Item
Description
Status
Show the connection status between the gateway and the
DeviceHub.
Disconnected
Click this button to disconnect the gateway from the DeviceHub.
Activation Server
Address
IP address or domain of the DeviceHub.
DeviceHub Server
Address
The URL address for the device to connect to the DeviceHub,
e.g. http://220.82.63.79:8080/acs.
Activation Method
Select activation method to connect the gateway to the
DeviceHub server, options are "By Authentication ID" and "By ID".
Authentication Code
Fill in the authentication code generated from the DeviceHub.
ID
Fill in the registered DeviceHub account (email) and password.
Password
Table 3-5-4-1
3.5.5 Events
Event feature is capable of sending alerts by Email when certain system events occur.
3.5.5.1 Events
You can view alarm messages on this page.

93
Figure 3-5-5-1
Events
Item
Description
Mark as Read
Mark the selected event alarm as read.
Delete
Delete the selected event alarm.
Mark All as Read
Mark all event alarms as read.
Delete All Alarms
Delete all event alarms.
Status
Show the reading status of the event alarms, such as “Read” and
“Unread”.
Type
Show the event type that should be alarmed.
Time
Show the alarm time.
Message
Show the alarm content.
Table 3-5-5-1 Events Parameters
3.5.5.2 Events Settings
In this section, you can decide what events to record and whether you want to receive
email and SMS notifications when any change occurs.

94
Figure 3-5-5-2
Event Settings
Item
Description
Enable
Check to enable "Events Settings".
Cellular Up
Cellular network is connected.
Cellular Down
Cellular network is disconnected.
WAN Up
Ethernet cable is connected to WAN port.
WAN Down
Ethernet cable is disconnected to WAN port.
VPN Up
VPN is connected.
VPN Down
VPN is disconnected.
Power On
The gateway has powered on.
Record
The relevant content of event alarm will be recorded on "Event"
page if this option is checked.
Email
The relevant content of event alarm will be sent out via email if
this option is checked.
Email Setting
Click and you will be redirected to the page "Email" to configure
the Email group.
SMS
The relevant content of event alarm will be sent out via SMS if
this option is checked.
SMS Setting
Click and you will be redirected to the page of "Phone" to
configure phone group list.
Phone Group List
Select phone group to receive SMS alarm.
Email Group List
Select Email group to receive Email alarm.
Table 3-5-5-2 Events Parameters

95
Related Topics
Email Setting
Phone Setting
3.6 Maintenance
This section describes system maintenance tools and management.
3.6.1 Tools
Troubleshooting tools includes ping and traceroute.
3.6.1.1 Ping
Ping tool is engineered to ping outer network.
Figure 3-6-1-1
PING
Item
Description
Host
Ping outer network from the gateway.
Table 3-6-1-1 IP Ping Parameters
3.6.1.2 Traceroute
Traceroute tool is used for troubleshooting network routing failures.
Figure 3-6-1-2
Traceroute
Item
Description
Host
Address of the destination host to be detected.
Table 3-6-1-2 Traceroute Parameters

96
3.6.1.3 Qxdmlog
This section allow collecting diagnostic logs via QXDM tool.
Figure 3-6-1-3
3.6.2 Schedule
This section explains how to configure scheduled reboot on the gateway.
Figure 3-6-2-1
Schedule
Item
Description
Schedule
Select schedule type.
Reboot
Reboot the gateway regularly.
Frequency
Select the frequency to execute the schedule.
Hour & Minute
Select the time to execute the schedule.
Table 3-6-2-1 Schedule Parameters
3.6.3 Log
The system log contains a record of informational, error and warning events that indicates
how the system processes. By reviewing the data contained in the log, an administrator or
user troubleshooting the system can identify the cause of a problem or whether the system
processes are loading successfully. Remote log server is feasible, and gateway will upload
all system logs to remote log server such as Syslog Watcher.
3.6.3.1 System Log
This section describes how to download log file and view the recent log on web.

97
Figure 3-6-3-1
System Log
Item
Description
Download
Download log file.
View recent (lines)
View the specified lines of system log.
Clear Log
Clear the current system log.
Table 3-6-3-1 System Log Parameters
3.6.3.2 Log Settings
This section explains how to enable remote log server and local log setting.
Figure 3-6-3-2
Log Settings
Item
Description
Remote Log Server

98
Enable
With “Remote Log Server” enabled, gateway will send all
system logs to the remote server.
Syslog Server Address
Fill in the remote system log server address (IP/domain
name).
Port
Fill in the remote system log server port.
Local Log File
Storage
User can store the log file in memory.
Size
Set the size of the log file to be stored.
Log Severity
The list of severities follows the syslog protocol.
Table 3-6-3-2 System Log Parameters
3.6.4 Upgrade
This section describes how to upgrade the gateway firmware via web. Generally you don’t
need to do the firmware upgrade.
Note: any operation on web page is not allowed during firmware upgrade, otherwise the
upgrade will be interrupted, or even the device will break down.
Figure 3-6-4-1
Upgrade
Item
Description
Firmware Version
Show the current firmware version.
Reset Configuration to
Factory Default
When this option is checked, the gateway will be reset to
factory defaults after upgrade.
Upgrade Firmware
Click "Browse" button to select the new firmware file, and
click "Upgrade" to upgrade firmware.
Table 3-6-4-1 Upgrade Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Firmware Upgrade

99
3.6.5 Backup and Restore
This section explains how to create a backup of the whole system configurations to a file,
replicate parts of important configuration only for batch backup, restore the config file to
the gateway and reset to factory defaults.
Figure 3-6-5-1
Backup and Restore
Item
Description
Config File
Click "Browse" button to select configuration file, and then click "Import"
button to upload the configuration file to the gateway.
Full Backup
Click "Full Backup" to export the current configuration file to the PC.
Batch
Backup
Click “Batch Backup” to export current configuration except gateway ID
of packet forwarder, all embedded NS settings, static IP address of
WAN, WLAN settings, user management settings, DeviceHub
authentication code, all APP settings.
Reset
Click "Reset" button to reset factory default settings. gateway will
restart after reset process is done.
Table 3-6-5-1 Backup and Restore Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Restore Factory Defaults
3.6.6 Reboot
On this page you can reboot the gateway and return to the login page. We strongly
recommend clicking “Save” button before rebooting the gateway so as to avoid losing the
new configuration.

100
Figure 3-6-6-1
3.7 APP
3.7.1 Python
Python is an object-oriented programming language that has gained popularity because of
its clear syntax and readability.
As an interpreted language, Python has a design philosophy that emphasizes code
readability, notably using whitespace indentation to delimit code blocks rather than curly
brackets or keywords, and a syntax that allows programmers to express concepts in fewer
lines of code than it’s used in other languages such as C++ or Java. The language provides
constructs and intends to enable writing clear programs on both small and large scale.
Users can use Python to quickly generate the prototype of the program, which can be the
final interface of the program, rewrite it with a more appropriate language, and then
encapsulate the extended class library that Python can call.
This section describes how to view the relevant running status such as App-manager, SDK
version, extended storage, etc. Also you can change the App-manager configuration, and
import the Python App package from here.
3.7.1.1 Python

101
Figure 3-7-1-1
Python
Item
Description
AppManager Status
Show AppManager's running status, like "Uninstalled",
"Running" or "Stopped".
SDK Version
Show the version of the installed SDK.
SDK Path
Show the SDK installation path.
Available Storage
Select available storage to install SDK.
SDK Upload
Upload and install SDK for Python.
Uninstall
Uninstall SDK.
View
View application status managed by AppManager.
Table 3-7-1-1 Python Parameters
3.7.1.2 App Manager Configuration
Figure 3-7-1-2

102
AppManager Configuration
Item
Description
Enable
After enabling Python AppManager, user can click "View" button on
the "Python" webpage to view the application status managed by
AppManager.
App Management
ID
Show the ID of the imported App.
App Command
Show the name of the imported App.
Logfile Size(MB)
User-defined Logfile size. Range: 1-50.
Uninstall
Uninstall APP.
App Status
App Name
Show the name of the imported App.
App Version
Show the version of the imported App.
SDK Version
Show the SDK version which the imported App is based on.
Table 3-7-1-2 APP Manager Parameters
3.7.1.3 Python App
Figure 3-7-1-3
Python APP
Item
Description
App Package
Select App package and import.
App Name
Select App to import configuration.
App Configuration
Select configuration file and import.

103
Debug File
Export script file.
Debug Script
Select Python script to be debugged and import.
Table 3-7-1-3 APP Parameters
3.7.2 Node-RED
Node-RED is a flow-based development tool for visual programming and wiring together
hardware devices, APIs and online services as part of the Internet of Things. Node-RED
provides a web-browser-based flow editor, which can easily wire together flows using the
wide range of nodes in the palette. Besides basic nodes, Milesight gateways provide
following customized nodes:
LoRa Input: receive the LoRa data, please ensure the network server mode is enabled
before using this node
LoRa Output: send downlinks to LoRaWAN
®
nodes
Device Filter: filter out the data of one or more specific LoRaWAN
®
nodes
Decoder: decode the Milesight LoRaWAN
®
end nodes data
GW Info: monitor alarm messages of gateway, please ensure the event detection is
enabled in “General -> Events -> Events Settings”
Email Output: send LoRa data or gateway alarms via email
SMS Input: receive SMS message. This only works when cellular is connected
SMS Output: send SMS message. This only works when cellular is connected
3.7.2.1 Node-RED
Figure 3-7-2-1

104
Node-RED
Item
Description
Enable
Enable the Node-RED.
Launch
Click to launch the web GUI of Node-RED.
Node-RED Version
Show the version of the Node-RED. The Node-RED version
can be upgraded only when you upgrade the gateway.
Node Library Version
Show the version of the node library.
Upgrade Node Library
Upgrade the node library by importing the library package.
All Flows Export
Export all flows as a JSON format file.
Restore Factory Default
Erase all flows data of Node-RED.
Table 3-7-2-1 Node-RED Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Node-RED

105
Chapter 4 Application Examples
4.1 Restore Factory Defaults
4.1.1 Via Web Interface
1. Log in web interface, and go to “Maintenance > Backup and Restore”.
2. Click “Reset” button under the “Restore Factory Defaults”.
You will be asked to confirm if you’d like to reset it to factory defaults. Then click “Reset”
button.
Then the gateway will reboot and restore to factory settings immediately.

106
Please wait till SYS light staticly and the login page pops up again, which means the
gateway has already been reset to factory defaults successfully.
Related Topic
Restore Factory Defaults
4.1.2 Via Hardware
Locate the reset button on the gateway, and take corresponding actions based on the
status of STATUS LED.
STATUS LED
Action
Static Blue
Press and hold the reset button for more than 5 seconds.
Static Blue →
Rapidly Blinking
Release the button and wait.
Off → Static Blue
The gateway is now reset to factory defaults.
4.2 Firmware Upgrade
It is suggested that you contact Milesight technical support first before you upgrade
gateway firmware. Gateway firmware file suffix is “.bin”.
After getting firmware file please refer to the following steps to complete the upgrade.
1. Go to “Maintenance > Upgrade”.
2. Click “Browse” and select the correct firmware file from the PC.
3. Click “Upgrade” and the gateway will check if the firmware file is correct. If it’s correct,
the firmware will be imported to the gateway, and then the gateway will start to
upgrade.

108
4. Log in the web GUI via the newly assigned IP address and go to “Status -> Network” to
check Ethernet port status.
Related Topic
Port Setting
4.4 Cellular Connection
1. Go to “Network > Interface > Cellular > Cellular Setting” and configure the cellular info.
2. Choose relevant network type.
Click “Save” and “Apply” for configuration to take effect.
3. Check the cellular connection status by WEB GUI of gateway.
Click “Status > Cellular” to view the status of the cellular connection. If it shows
'Connected', SIM has dialed up successfully.

109
4. Check out if network works properly by browser on PC.
Open your preferred browser on PC, type any available web address into address bar and
see if it is able to visit Internet via the UG65.
Related Topic
Cellular Setting
Cellular Status
4.5 Wi-Fi Application Example
4.5.1 AP Mode
Application Example
Configure UG65 as AP to allow connection from users or devices.
Configuration Steps
1. Go to “Network > Interface > WLAN” to configure wireless parameters as below.

110
Click “Save” and “Apply” buttons after all configurations are done.
2. Use a smart phone to connect the access point of gateway. Go to “Status > WLAN”, and
you can check the AP settings and information of the connected client/user.

111
4.5.2 Client Mode
Application Example
Configure UG65 as Wi-Fi client to connect to an access point to have Internet access.
Configuration Steps
1. Go to “Network > Interface > WLAN” and click “Scan” to search for WiFi access point.
2. Select one access point and click “Join Network”, then type the password of the access
point.
Click “Save” and “Apply” buttons after all configurations are done.
3. Go to “Status > WLAN”, and you can check the connection status of the client.

112
Related Topic
WLAN Setting
WLAN Status
4.6 Packet Forwarder Configuration
UG65 gateway has installed multiple packet forwarders including Semtech, Basic station,
Chirpstack-Generic MQTT broker, etc. Before connecting make sure the gateway has
connected to network.
1. Go to “Packet Forwarder” > “General”.
2. Click to add a new network server. Fill in the network server information and

113
enable this server.
3. Go to “Packet Forwarder -> Radio” page to configure antenna type, center frequency
and channels. The channels of the gateway and network server need to be the same.
4. Add the gateway on network server page. For more details about the network server
connection please refer to Milesight IoT Support portal.
5. Go to “Traffic” page to view the data communication of UG65.

114
4.7 Connect to Milesight IoT Cloud
1. Go to “Packet Forwarder->General” page to enable the embedded network server.
2. Go to “Packet Forwarder-> Radio” page to select the antenna type, center frequency and
channels. The channels of the gateway and nodes need to be the same.
3. Go to “Network Server” → “General” page to enable the network server and “Cloud
mode”, then select “Milesight IoT Cloud”.

115
4. Log in the Milesight IoT Cloud. Then go to “My Devices” page and click “+New Devices”
to add gateway to Milesight IoT Cloud via SN. Gateway will be added under “Gateways”
menu.
5. The gateway is online on Milesight IoT Cloud.
4.8 Application Configuration
You can create a new application on this page, which is mainly used to define the method
of decoding the data sent from end-device and choosing the data transport protocol to
send data to another server address. The data will be sent to your custom server address
using MQTT, HTTP or HTTPS protocol.

116
1. Go to “Network Server” > “Application”.
2. Click to enter the configuration page, displayed as the following picture:
3. Click “Save” to create this application.
4. Click to add a data transmission type.
HTTP or HTTPS:
Step 1: select HTTP or HTTPS as transmission protocol.
Step 2: Enter the destination URL. Different types of data can be sent to different URLs.
Enter the header name and header value if there is user credentials when accessing the
HTTP(s) server.
MQTT:
Step 1: select the transmission protocol as MQTT.

117
Step 2: Fill in MQTT broker general settings.
Step 3: Select the authentication method required by the server.
If you select user credentials for authentication, you need to enter the username and
password for authentication.
If certificate is necessary for verification, please select mode and import CA certificate,
client certificate and client key file for authentication.
Step 4: Enter the topic to receive data and choose the QoS.

118
4.9 Device Configuration
Go to “Device” page and click “Add” to add LoRaWAN
®
node devices. Please select correct
device profile according to device type.
You can also click “Bulk Import” if you want to add many nodes all at once.
Click “Template Download” to download template file and add device information to this
file. Application and device profile should be the same as you created on web page.

119
Import this file to add bulks of devices.
4.10 Send Data to Device
1. Go to “Network Server” > “Packets”, check the packet in the network server list to make
sure that the device has joined the network successful.
2. Fill in the device EUI or select the multicast group which you need to send downlinks.
Then fill in the downlink commands, ports.
3. Click “Send”.
4. Check the packet in the network server list to make sure that the device has received this
message successful. It’s suggested to enable “Confirmed”. Multicast feature does not
support confirmed downlinks.
You can click “Refresh” to refresh the list or set automatic refreshing frequency for the list.
If the device’s class type is Class C, then the device will constantly receive packets.
This packet’s type is DnCnf (Downlink Confirmed Packet) and if the packet’s color is gray,
then it means the packet cannot be transmitted now because at least one message has
been in the queue. If the packet record is white, it means the packet has been delivered
successfully.
If the device receives this downlink confirmed packet, then the device will reply “ACK” when
delivering next.

120
Ack is “true” means that the device has received this packet.
If the device’s class type is Class A, only after the device sends out an uplink packet will the
network server sends out data to the device.

122
4.11.2 Send Data by Email
Application Example
Send AM104 device data by Email.
Configuration Steps
1. Add a “LoRa Input” node. Before adding please ensure network server mode is enabled
and LoRaWAN devices have joined the network.
2. If you add many devices and only need one device data, add “Device Filter” node behind
the “LoRa Input” and type the device EUI.
3. Add a “Decoder” node to decode the Milesight sensor data.

123
4. Add an “Email Output” and type the SMTP client settings, destination email address and
contents. Example content:
The time is {{time}}
Deveui is {{deveui}}
Humidity is {{payload.humidity}}
Note:
1) When you select SMTP Option as “Same as Gateway”, go to “System -> General Settings
-> SMTP” to configure the SMTP clients.
2) Basic format to call LoRaWAN node data is
{{property name}}
, you can click “Help” page
for more info about the Email or SMS payload format.
3) If you need to check the output content in every node, please add debug node.
5. After completing the configuration, click “Deploy” to save all your configuration.
6. When AM104 sends data to gateway, gateway will transfer the data to email.



